Mental health insurance specifically covers therapy sessions, psychiatric treatments, and medication for mental health conditions, while long-term care insurance focuses on assistance with daily living activities such as bathing, dressing, and eating in cases of chronic illness or disability. Mental health policies often include coverage for counseling and inpatient care, whereas long-term care insurance provides support for nursing home care, home health aides, and assisted living facilities. Learn more to understand how each policy can protect your well-being and financial future.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between mental health insurance and long-term care insurance is crucial for ensuring proper coverage and financial protection. Mental health insurance specifically covers therapy, counseling, and psychiatric treatment, while long-term care insurance focuses on assistance with daily living activities for chronic illnesses or disabilities. Choosing the appropriate insurance type prevents gaps in care and unexpected out-of-pocket expenses. Awareness of these distinctions helps individuals tailor their policies to meet specific healthcare needs effectively.
Comparison Table
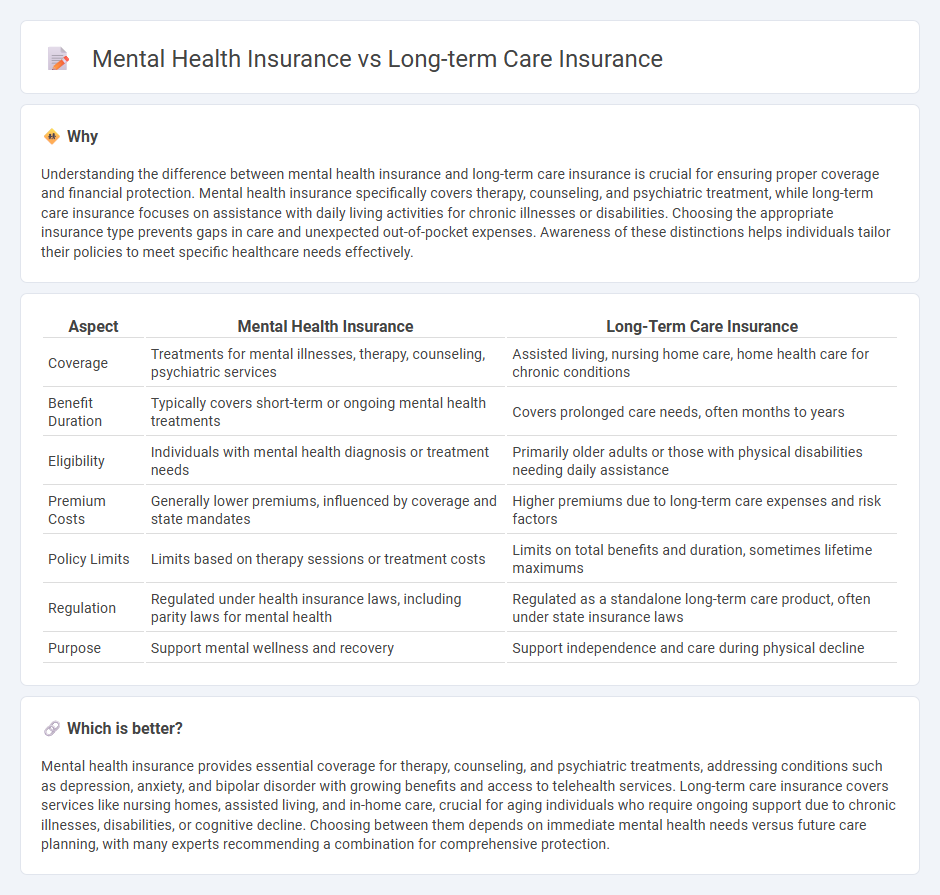
| Aspect | Mental Health Insurance | Long-Term Care Insurance |
|---|---|---|
| Coverage | Treatments for mental illnesses, therapy, counseling, psychiatric services | Assisted living, nursing home care, home health care for chronic conditions |
| Benefit Duration | Typically covers short-term or ongoing mental health treatments | Covers prolonged care needs, often months to years |
| Eligibility | Individuals with mental health diagnosis or treatment needs | Primarily older adults or those with physical disabilities needing daily assistance |
| Premium Costs | Generally lower premiums, influenced by coverage and state mandates | Higher premiums due to long-term care expenses and risk factors |
| Policy Limits | Limits based on therapy sessions or treatment costs | Limits on total benefits and duration, sometimes lifetime maximums |
| Regulation | Regulated under health insurance laws, including parity laws for mental health | Regulated as a standalone long-term care product, often under state insurance laws |
| Purpose | Support mental wellness and recovery | Support independence and care during physical decline |
Which is better?
Mental health insurance provides essential coverage for therapy, counseling, and psychiatric treatments, addressing conditions such as depression, anxiety, and bipolar disorder with growing benefits and access to telehealth services. Long-term care insurance covers services like nursing homes, assisted living, and in-home care, crucial for aging individuals who require ongoing support due to chronic illnesses, disabilities, or cognitive decline. Choosing between them depends on immediate mental health needs versus future care planning, with many experts recommending a combination for comprehensive protection.
Connection
Mental health insurance and long-term care insurance intersect by addressing ongoing care needs for chronic mental illnesses and cognitive impairments. Mental health coverage often includes therapy and psychiatric services, which can reduce the severity or progression of conditions that may eventually require long-term care support. Long-term care insurance provides financial protection for extended assistance with daily activities, crucial for individuals with severe mental health disorders who experience functional decline over time.
Key Terms
Coverage Scope
Long-term care insurance primarily covers services like nursing home care, assisted living, and home health care for chronic illnesses or disabilities, whereas mental health insurance focuses on therapy sessions, psychiatric treatment, and medication for mental disorders. Coverage scope in long-term care insurance tends to include physical and cognitive impairments, while mental health insurance centers on emotional and psychological well-being. Explore detailed comparisons to understand which insurance best fits your healthcare needs.
Benefit Triggers
Long-term care insurance primarily activates benefits when policyholders require assistance with daily living activities such as bathing, dressing, or eating due to chronic illness or disability. Mental health insurance triggers coverage based on the diagnosis of psychiatric conditions and the need for therapy, medication, or hospitalization. Explore our comprehensive comparison to understand which coverage best suits your needs and triggers optimal benefits.
Eligible Services
Long-term care insurance primarily covers services such as nursing home care, assisted living, and home health care for chronic illnesses or disabilities requiring extended support. Mental health insurance specifically covers therapy sessions, psychiatric evaluations, inpatient treatment, and prescription medications related to mental health conditions. Explore the differences in eligible services to choose the best coverage for your needs.
Source and External Links
Long-Term Care Insurance Explained - NerdWallet - Long-term care insurance helps cover costs for chronic illness, disability, or cognitive impairment, paying benefits after an elimination period when policyholders can't perform two of six daily living activities like bathing or dressing.
Long-term care costs & options - Fidelity Investments - Long-term care can be paid through government programs, traditional or hybrid insurance, or personal savings, with Medicaid available for low-income individuals and Medicare generally not covering long-term care.
What is Long-term Care Insurance? - Long-term care insurance covers personal and custodial care in various settings, reimbursing daily amounts for services with coverage limits based on policy terms and medical underwriting is often required to qualify.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com