Mental health insurance provides coverage for therapy sessions, psychiatric treatments, and prescription medications aimed at improving emotional and psychological well-being. Life insurance offers financial protection to beneficiaries by providing a lump sum payment upon the policyholder's death, ensuring economic stability for their family. Discover the key differences and benefits of each insurance type to make an informed decision.
Why it is important
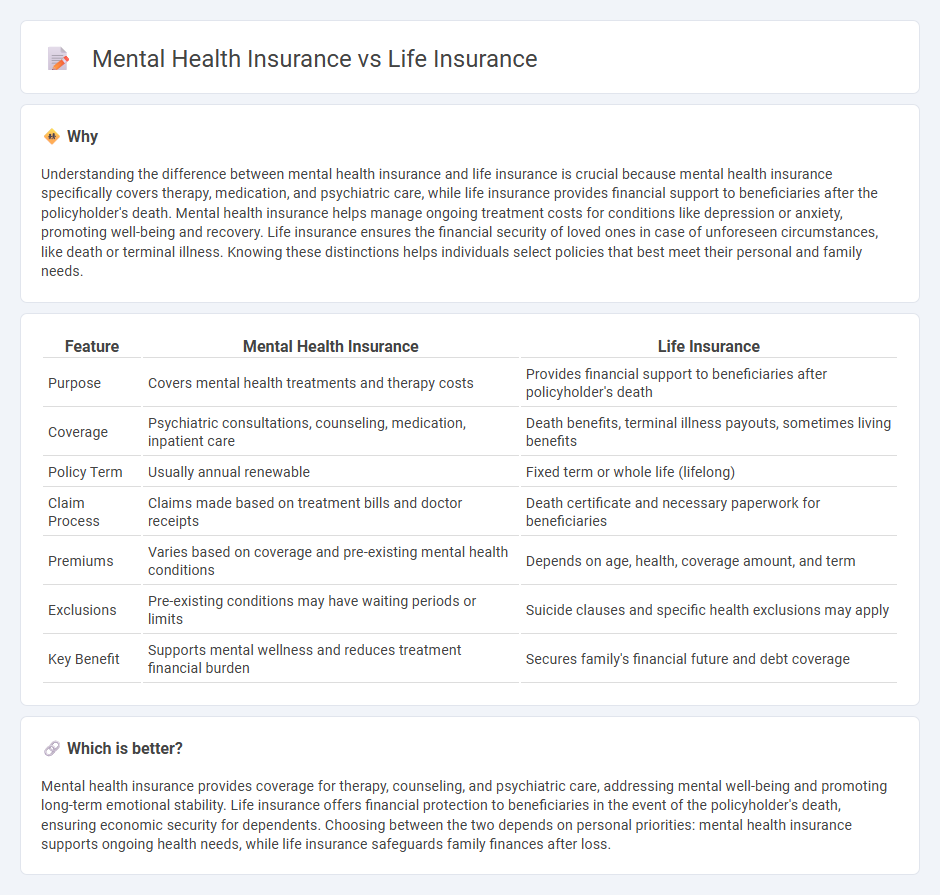
Understanding the difference between mental health insurance and life insurance is crucial because mental health insurance specifically covers therapy, medication, and psychiatric care, while life insurance provides financial support to beneficiaries after the policyholder's death. Mental health insurance helps manage ongoing treatment costs for conditions like depression or anxiety, promoting well-being and recovery. Life insurance ensures the financial security of loved ones in case of unforeseen circumstances, like death or terminal illness. Knowing these distinctions helps individuals select policies that best meet their personal and family needs.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Mental Health Insurance | Life Insurance |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Covers mental health treatments and therapy costs | Provides financial support to beneficiaries after policyholder's death |
| Coverage | Psychiatric consultations, counseling, medication, inpatient care | Death benefits, terminal illness payouts, sometimes living benefits |
| Policy Term | Usually annual renewable | Fixed term or whole life (lifelong) |
| Claim Process | Claims made based on treatment bills and doctor receipts | Death certificate and necessary paperwork for beneficiaries |
| Premiums | Varies based on coverage and pre-existing mental health conditions | Depends on age, health, coverage amount, and term |
| Exclusions | Pre-existing conditions may have waiting periods or limits | Suicide clauses and specific health exclusions may apply |
| Key Benefit | Supports mental wellness and reduces treatment financial burden | Secures family's financial future and debt coverage |
Which is better?
Mental health insurance provides coverage for therapy, counseling, and psychiatric care, addressing mental well-being and promoting long-term emotional stability. Life insurance offers financial protection to beneficiaries in the event of the policyholder's death, ensuring economic security for dependents. Choosing between the two depends on personal priorities: mental health insurance supports ongoing health needs, while life insurance safeguards family finances after loss.
Connection
Mental health insurance and life insurance are interconnected through risk assessment and premium calculations, as insurers evaluate mental health conditions to determine coverage eligibility and policy costs. Effective mental health coverage can reduce mortality risks and improve overall life expectancy, directly influencing life insurance underwriting and benefits. Integrating mental health support within life insurance policies promotes holistic wellness and financial security for policyholders.
Key Terms
Beneficiary
Life insurance policies designate beneficiaries who receive financial support upon the insured's death, ensuring the protection of loved ones. Mental health insurance, on the other hand, provides coverage for therapy, counseling, and psychiatric services, directly benefiting the insured rather than a third party. Explore the differences to choose the coverage that best supports you and your family's needs.
Premium
Life insurance premiums are primarily based on age, health status, lifestyle, and coverage amount, often requiring medical exams for accurate risk assessment. Mental health insurance premiums vary depending on coverage scope, individual risk factors, and whether the plan is standalone or part of a comprehensive health policy. Explore detailed comparisons to understand pricing strategies and select the best option for your needs.
Exclusions
Life insurance policies typically exclude coverage for deaths resulting from suicide within the first two years and may not cover illnesses related to certain mental health conditions unless explicitly stated. Mental health insurance, on the other hand, often excludes treatments not approved by regulatory bodies or experimental therapies, limiting coverage for certain psychiatric conditions. Explore the specific exclusions of both insurance types to make an informed decision tailored to your needs.
Source and External Links
Life Insurance - Provides options for term, whole, universal, and variable life insurance, ensuring comprehensive protection for various needs.
Life Insurance Policy - Offers term, whole, and final expense life insurance policies with options like guaranteed-issue coverage.
Life Insurance - Offers affordable term, whole, and universal life insurance options with the ability to get quotes online.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com