Peer-to-peer insurance leverages group dynamics by pooling risks among members who share similar profiles, often resulting in lower premiums and greater transparency. Cooperative insurance is member-owned, emphasizing collective control and profits reinvested for members' benefits, fostering trust and community involvement. Explore how these innovative models reshape traditional insurance landscapes and empower policyholders.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between peer-to-peer insurance and cooperative insurance is important because peer-to-peer insurance leverages social networks to pool risk among members, potentially lowering costs and increasing transparency, whereas cooperative insurance operates as a member-owned organization prioritizing mutual benefit and democratic control. Knowing these distinctions helps consumers choose the most suitable insurance model based on their needs for risk-sharing, governance, and claims processing. Peer-to-peer insurance often offers faster claim settlements and reduced fraud due to its social structure. Cooperative insurance emphasizes long-term stability and community-focused services, making it essential for buyers to evaluate their priorities for coverage and participation.
Comparison Table
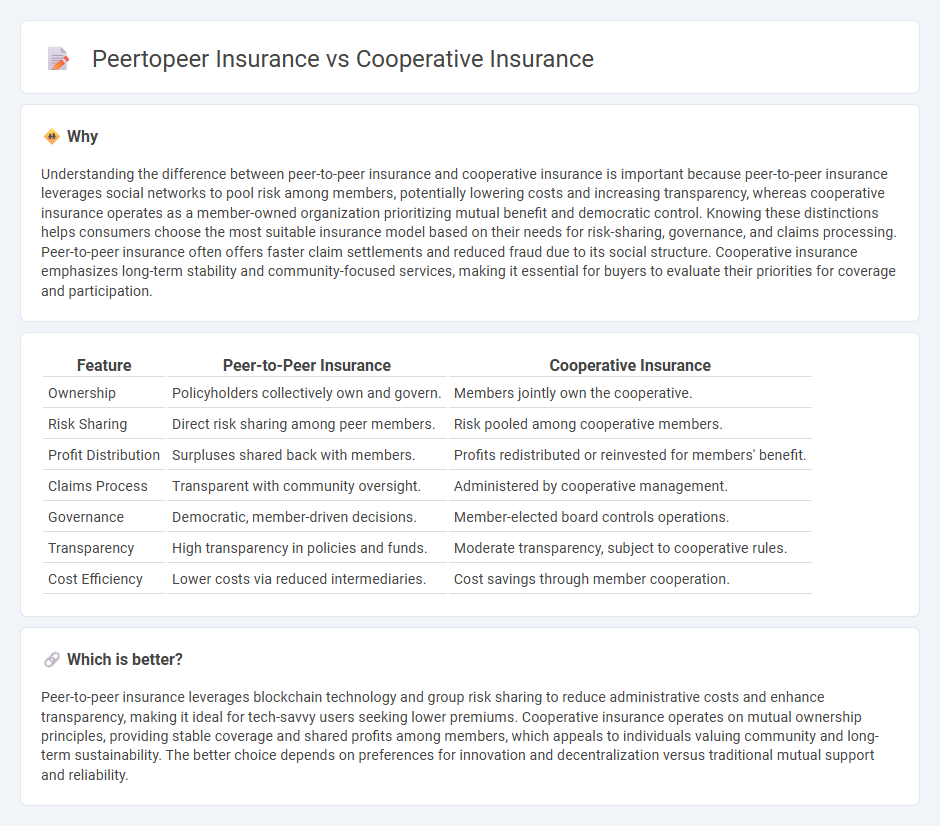
| Feature | Peer-to-Peer Insurance | Cooperative Insurance |
|---|---|---|
| Ownership | Policyholders collectively own and govern. | Members jointly own the cooperative. |
| Risk Sharing | Direct risk sharing among peer members. | Risk pooled among cooperative members. |
| Profit Distribution | Surpluses shared back with members. | Profits redistributed or reinvested for members' benefit. |
| Claims Process | Transparent with community oversight. | Administered by cooperative management. |
| Governance | Democratic, member-driven decisions. | Member-elected board controls operations. |
| Transparency | High transparency in policies and funds. | Moderate transparency, subject to cooperative rules. |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower costs via reduced intermediaries. | Cost savings through member cooperation. |
Which is better?
Peer-to-peer insurance leverages blockchain technology and group risk sharing to reduce administrative costs and enhance transparency, making it ideal for tech-savvy users seeking lower premiums. Cooperative insurance operates on mutual ownership principles, providing stable coverage and shared profits among members, which appeals to individuals valuing community and long-term sustainability. The better choice depends on preferences for innovation and decentralization versus traditional mutual support and reliability.
Connection
Peer-to-peer (P2P) insurance and cooperative insurance both emphasize collective risk-sharing among members, reducing reliance on traditional insurers. In P2P insurance, groups of individuals pool premiums to cover claims, promoting transparency and lower costs, similar to cooperative insurance where members jointly own and manage the policy funds. Both models leverage community trust and mutual benefit to provide more equitable and cost-effective coverage solutions.
Key Terms
Risk Pooling
Cooperative insurance and peer-to-peer insurance both rely on risk pooling to distribute potential losses among members, but cooperative insurance typically involves larger, structured groups with formal governance, while peer-to-peer insurance leverages smaller, more flexible groups often connected through digital platforms. The effectiveness of risk pooling in cooperative insurance stems from its scale and regulatory oversight, offering greater financial stability, whereas peer-to-peer models emphasize transparency and reduced costs by eliminating traditional insurers. Explore the differences in risk pooling dynamics to understand which insurance model aligns with your needs.
Member Ownership
Member ownership in cooperative insurance ensures policyholders have voting rights and influence over company decisions, fostering transparency and alignment with members' interests. Peer-to-peer insurance pools risk among members directly, often allowing participants to share profits or losses based on collective claims experience, enhancing engagement and trust. Discover how member ownership models impact insurance outcomes and member benefits.
Claims Sharing
Cooperative insurance pools policyholders to share risks and claims through a structured mutual system, emphasizing collective responsibility and financial stability. Peer-to-peer insurance leverages small groups of individuals who share claims among themselves, often with digital platforms enhancing transparency and reducing administrative costs. Explore how claims sharing impacts premiums and customer trust in these innovative insurance models.
Source and External Links
Co-operative Insurance Companies: Welcome - Offers flexible insurance policies tailored for farming operations, including dairy, horse, poultry, sheep, deer, emu, and tree coverage, as well as personal and commercial insurance products.
Insurance Co-ops - NCBA CLUSA - Cooperative insurance covers members' belongings and unit interiors (e.g., against burglary, fire), while insurance co-ops (mutual companies) focus on policyholder interests, providing coverage at reasonable cost without external investor pressure.
Health insurance cooperative - Wikipedia - Health insurance co-ops are member-owned non-profits that provide health coverage as an alternative to public or single-payer systems, initially receiving government investment but operating independently.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com