Ghost broking involves unauthorized brokers selling insurance policies, often at reduced rates but with invalid coverage, posing significant risks to consumers. Insurance fraud encompasses deliberate deception to obtain illegitimate benefits from insurance companies, including false claims or misrepresentation of facts. Explore the key differences, risks, and legal implications of ghost broking and insurance fraud to safeguard your insurance investments.
Why it is important
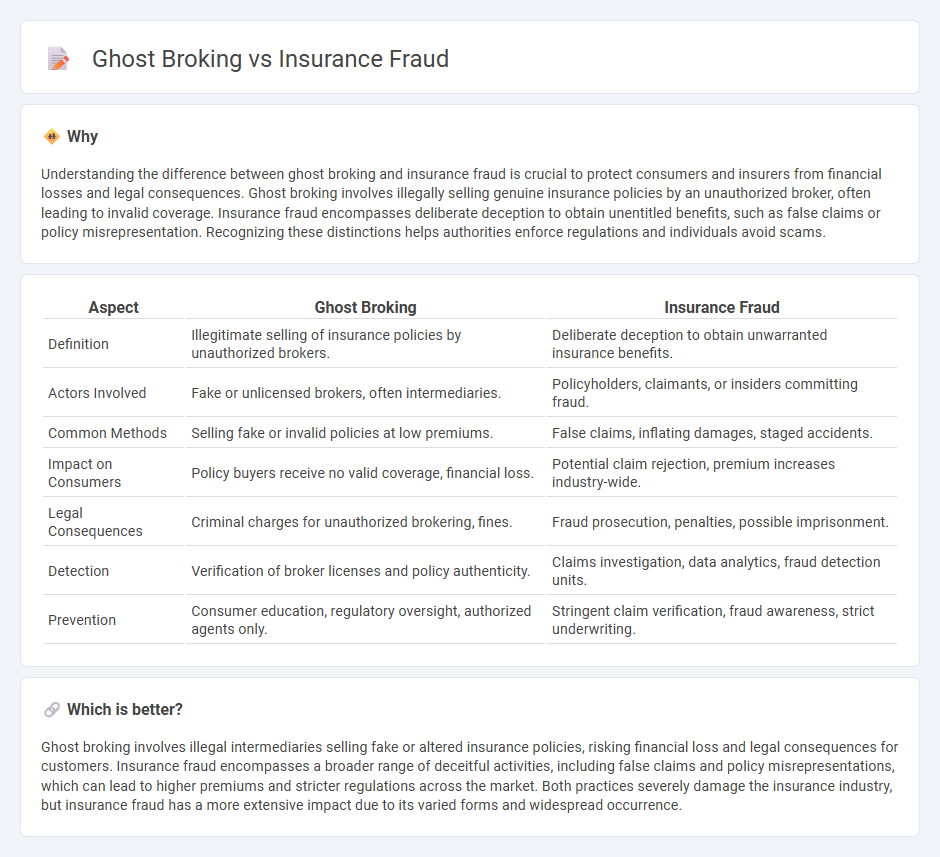
Understanding the difference between ghost broking and insurance fraud is crucial to protect consumers and insurers from financial losses and legal consequences. Ghost broking involves illegally selling genuine insurance policies by an unauthorized broker, often leading to invalid coverage. Insurance fraud encompasses deliberate deception to obtain unentitled benefits, such as false claims or policy misrepresentation. Recognizing these distinctions helps authorities enforce regulations and individuals avoid scams.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Ghost Broking | Insurance Fraud |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Illegitimate selling of insurance policies by unauthorized brokers. | Deliberate deception to obtain unwarranted insurance benefits. |
| Actors Involved | Fake or unlicensed brokers, often intermediaries. | Policyholders, claimants, or insiders committing fraud. |
| Common Methods | Selling fake or invalid policies at low premiums. | False claims, inflating damages, staged accidents. |
| Impact on Consumers | Policy buyers receive no valid coverage, financial loss. | Potential claim rejection, premium increases industry-wide. |
| Legal Consequences | Criminal charges for unauthorized brokering, fines. | Fraud prosecution, penalties, possible imprisonment. |
| Detection | Verification of broker licenses and policy authenticity. | Claims investigation, data analytics, fraud detection units. |
| Prevention | Consumer education, regulatory oversight, authorized agents only. | Stringent claim verification, fraud awareness, strict underwriting. |
Which is better?
Ghost broking involves illegal intermediaries selling fake or altered insurance policies, risking financial loss and legal consequences for customers. Insurance fraud encompasses a broader range of deceitful activities, including false claims and policy misrepresentations, which can lead to higher premiums and stricter regulations across the market. Both practices severely damage the insurance industry, but insurance fraud has a more extensive impact due to its varied forms and widespread occurrence.
Connection
Ghost broking involves fake insurance brokers who sell counterfeit or invalid insurance policies, leading to significant insurance fraud. These fraudulent activities result in financial losses for both insurance companies and genuine policyholders by exploiting claim processes and premium payments. Understanding the connection between ghost broking and insurance fraud is crucial for developing effective fraud detection and prevention strategies in the insurance industry.
Key Terms
Claims manipulation
Insurance fraud involves deliberately falsifying or exaggerating claims to receive undeserved payouts, often including staged accidents or inflated repair costs. Ghost broking specifically refers to unauthorized intermediaries selling fake or altered insurance policies to unsuspecting buyers, which leads to invalid claims and potential legal issues. Discover more about the key differences and prevention strategies in claims manipulation techniques.
Policy fabrication
Insurance fraud involves deceptive practices to obtain unauthorized benefits, often through falsifying claims or inflating damages. Ghost broking specifically refers to the fabrication of insurance policies, where fraudsters create fake or altered documents to sell non-existent or invalid coverage. Explore how policy fabrication in ghost broking undermines trust in insurance markets and the ways to detect such scams.
Unlicensed intermediary
Insurance fraud involves deliberate deception to gain unlawful benefits, while ghost broking specifically refers to unlicensed intermediaries who pose as legitimate brokers to sell fraudulent insurance policies. These unlicensed intermediaries manipulate documents or create fake policies, leaving consumers unprotected and at financial risk. Learn more about the risks and legal implications of ghost broking to safeguard your insurance investments.
Source and External Links
Types of Insurance Fraud - This webpage lists common types of insurance fraud, including auto, homeowner, health care, life and disability, and agent/industry fraud.
What is Insurance Fraud? - This webpage defines insurance fraud and explains its legal aspects, including the intent to defraud and the act that must be committed.
Insurance Fraud - This Wikipedia article provides a comprehensive overview of insurance fraud, including its definition, types, and examples across different insurance sectors.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com