Credit life insurance specifically covers outstanding loan balances in case of the policyholder's death, providing peace of mind for lenders and borrowers alike. Term life insurance offers broader financial protection by paying a death benefit to beneficiaries if the insured dies within a specified term, allowing for greater flexibility in coverage amounts and duration. Discover how these life insurance types can safeguard your financial future based on your unique needs.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between Credit Life Insurance and Term Life Insurance is crucial for selecting the appropriate coverage based on financial goals and obligations. Credit Life Insurance specifically pays off outstanding debts if the insured dies during the loan term, protecting creditors but not beneficiaries. Term Life Insurance provides a death benefit to beneficiaries for a specified period, offering broader financial security to families. Choosing the right policy ensures effective risk management and financial protection tailored to individual needs.
Comparison Table
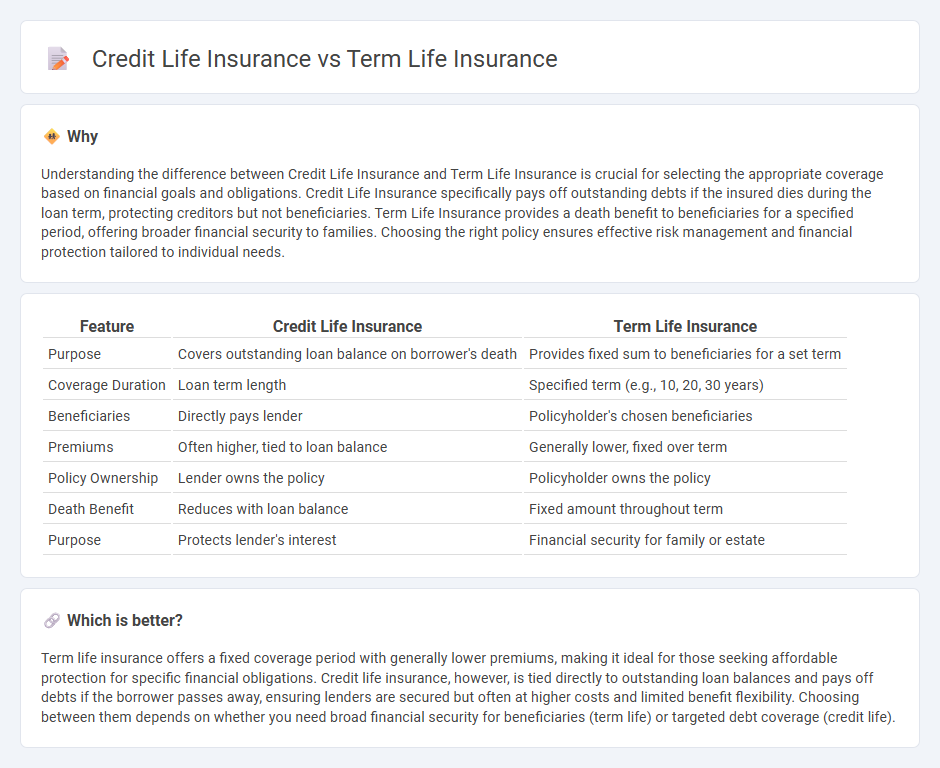
| Feature | Credit Life Insurance | Term Life Insurance |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Covers outstanding loan balance on borrower's death | Provides fixed sum to beneficiaries for a set term |
| Coverage Duration | Loan term length | Specified term (e.g., 10, 20, 30 years) |
| Beneficiaries | Directly pays lender | Policyholder's chosen beneficiaries |
| Premiums | Often higher, tied to loan balance | Generally lower, fixed over term |
| Policy Ownership | Lender owns the policy | Policyholder owns the policy |
| Death Benefit | Reduces with loan balance | Fixed amount throughout term |
| Purpose | Protects lender's interest | Financial security for family or estate |
Which is better?
Term life insurance offers a fixed coverage period with generally lower premiums, making it ideal for those seeking affordable protection for specific financial obligations. Credit life insurance, however, is tied directly to outstanding loan balances and pays off debts if the borrower passes away, ensuring lenders are secured but often at higher costs and limited benefit flexibility. Choosing between them depends on whether you need broad financial security for beneficiaries (term life) or targeted debt coverage (credit life).
Connection
Credit life insurance and term life insurance both provide financial protection by paying a death benefit upon the insured's death; however, credit life insurance specifically covers outstanding debt such as loans or mortgages, while term life insurance offers broader coverage for a fixed period. Both types of insurance reduce financial risk for beneficiaries, ensuring debts are settled and income replacement is secured during the policy term. The connection lies in their focus on providing temporary life coverage with death benefits designed to protect financial obligations.
Key Terms
Coverage Duration
Term life insurance provides coverage for a specified period, typically 10, 20, or 30 years, offering financial protection to beneficiaries if the insured passes away during the term. Credit life insurance is designed to cover the balance of a specific debt, such as a mortgage or loan, and coverage duration aligns with the loan term, decreasing as the debt is paid down. Explore further to understand which insurance type best suits your financial protection needs.
Beneficiary
Term life insurance allows policyholders to designate any beneficiary, providing flexibility in financial protection for loved ones or entities such as trusts or charities. Credit life insurance, on the other hand, typically names the lender or creditor as the beneficiary, ensuring loan repayment in case of the borrower's death. Explore the differences further to determine the best option for your financial needs.
Premium Structure
Term life insurance features fixed premiums payable throughout the policy term, offering predictable costs and potential renewal options without increases based on changing credit status. Credit life insurance premiums are typically tied to the outstanding loan balance, decreasing as the debt diminishes, which can make payments variable and sometimes higher upfront. Explore detailed comparisons to understand which premium structure suits your financial goals and credit obligations best.
Source and External Links
What is Term Life Insurance | Banner Life | Legal & General - Term life insurance provides affordable death coverage for a set term, typically 10 to 30 years, with level premiums and death benefit staying the same during the term to cover temporary financial obligations like mortgages or income replacement.
What Is a Term Life Insurance Policy? - Term life insurance offers fixed death benefit protection for a chosen period (10 to 30 years), generally at lower cost than permanent policies, with fixed payments and often includes options to convert to permanent insurance without a medical exam.
Term Life Insurance -- Types and How it Works - Term life insurance policies are straightforward, providing coverage for a specific term with fixed or annually renewable premiums, including options such as return of premium or guaranteed issue; they offer affordable, flexible coverage that can convert to permanent insurance.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com