Cyber risk underwriting focuses on assessing and pricing policies that protect businesses from digital threats such as data breaches, ransomware, and cyberattacks, requiring expertise in IT security and evolving cyber threats. Environmental liability underwriting evaluates risks related to pollution, contamination, and environmental damage, demanding knowledge of environmental laws, cleanup costs, and potential long-term liabilities. Explore the distinct methodologies and key factors influencing these specialized underwriting practices to understand their impact on risk management strategies.
Why it is important
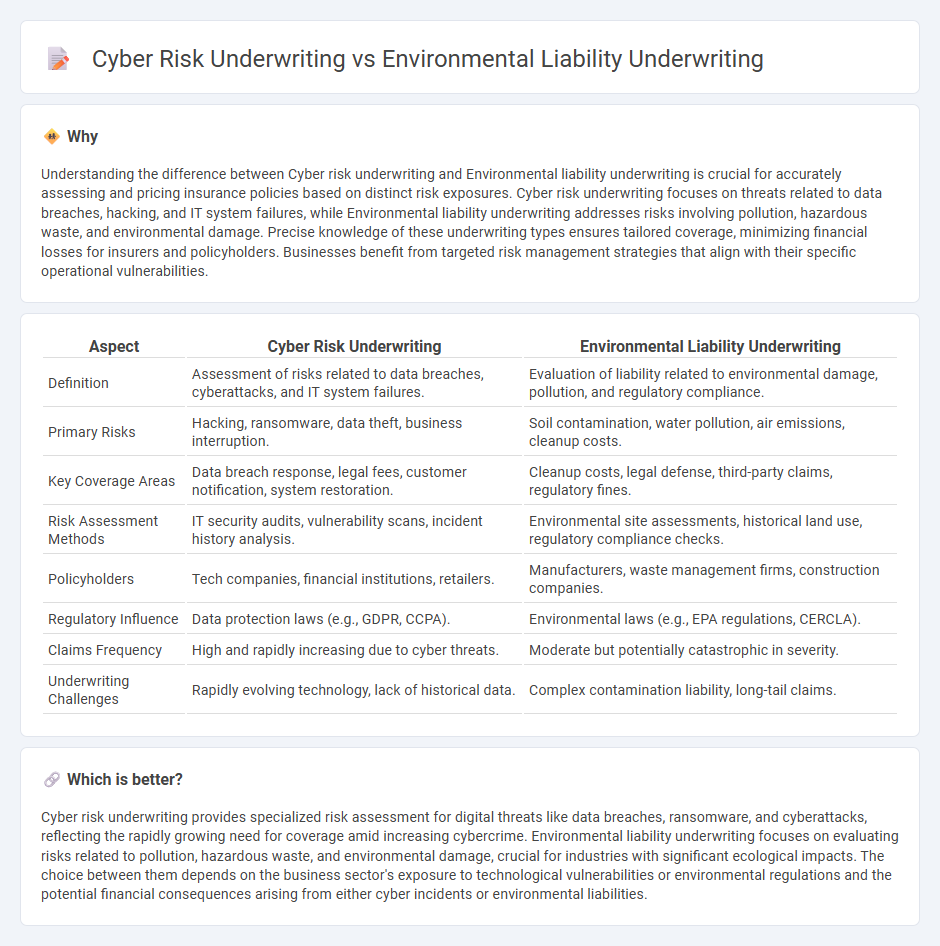
Understanding the difference between Cyber risk underwriting and Environmental liability underwriting is crucial for accurately assessing and pricing insurance policies based on distinct risk exposures. Cyber risk underwriting focuses on threats related to data breaches, hacking, and IT system failures, while Environmental liability underwriting addresses risks involving pollution, hazardous waste, and environmental damage. Precise knowledge of these underwriting types ensures tailored coverage, minimizing financial losses for insurers and policyholders. Businesses benefit from targeted risk management strategies that align with their specific operational vulnerabilities.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Cyber Risk Underwriting | Environmental Liability Underwriting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Assessment of risks related to data breaches, cyberattacks, and IT system failures. | Evaluation of liability related to environmental damage, pollution, and regulatory compliance. |
| Primary Risks | Hacking, ransomware, data theft, business interruption. | Soil contamination, water pollution, air emissions, cleanup costs. |
| Key Coverage Areas | Data breach response, legal fees, customer notification, system restoration. | Cleanup costs, legal defense, third-party claims, regulatory fines. |
| Risk Assessment Methods | IT security audits, vulnerability scans, incident history analysis. | Environmental site assessments, historical land use, regulatory compliance checks. |
| Policyholders | Tech companies, financial institutions, retailers. | Manufacturers, waste management firms, construction companies. |
| Regulatory Influence | Data protection laws (e.g., GDPR, CCPA). | Environmental laws (e.g., EPA regulations, CERCLA). |
| Claims Frequency | High and rapidly increasing due to cyber threats. | Moderate but potentially catastrophic in severity. |
| Underwriting Challenges | Rapidly evolving technology, lack of historical data. | Complex contamination liability, long-tail claims. |
Which is better?
Cyber risk underwriting provides specialized risk assessment for digital threats like data breaches, ransomware, and cyberattacks, reflecting the rapidly growing need for coverage amid increasing cybercrime. Environmental liability underwriting focuses on evaluating risks related to pollution, hazardous waste, and environmental damage, crucial for industries with significant ecological impacts. The choice between them depends on the business sector's exposure to technological vulnerabilities or environmental regulations and the potential financial consequences arising from either cyber incidents or environmental liabilities.
Connection
Cyber risk underwriting and environmental liability underwriting intersect through the assessment of emerging risks related to digital systems and environmental impact. Both underwriting processes analyze data on potential damages--such as cybersecurity breaches causing environmental harm or operational disruptions affecting ecological liabilities. Integrating cyber risk and environmental liability frameworks enhances insurers' ability to quantify combined threats and develop comprehensive coverage solutions.
Key Terms
**Environmental Liability Underwriting:**
Environmental liability underwriting involves assessing risks related to pollution, hazardous waste, and environmental damage caused by businesses or property owners. Underwriters evaluate factors such as regulatory compliance, historical contamination, and the potential cost of cleanup and legal claims. Explore more about how environmental liability underwriting protects organizations from costly ecological risks and liabilities.
Pollution Exclusion
Environmental liability underwriting rigorously assesses risks related to pollution damage, with a critical emphasis on pollution exclusion clauses that limit insurer responsibility for contamination events. Cyber risk underwriting, in contrast, focuses on data breaches and system failures, typically excluding physical pollution damages while addressing network security threats. Explore our comprehensive analysis to understand how pollution exclusions distinctly impact these underwriting practices.
Site Assessment
Environmental liability underwriting emphasizes thorough site assessments to identify contamination risks, focusing on soil, groundwater, and historical land use to estimate potential cleanup costs and regulatory liabilities. Cyber risk underwriting relies on evaluating a company's IT infrastructure, security protocols, and vulnerability assessments to predict breach likelihood and potential financial losses. Discover detailed strategies and key differences in site assessment approaches between these underwriting specialties.
Source and External Links
Environmental Liability Insurance | The Hartford - Provides environmental liability coverage for pollution incidents, including bodily injury, property damage, and cleanup costs, with extensive underwriting expertise.
Environmental Liability Insurance - NFP - Offers environmental insurance solutions to mitigate risks associated with development and construction projects, addressing both direct and indirect environmental liabilities.
Environmental Liability Insurance - Allianz Commercial - Provides customized Environmental Impairment Liability Insurance tailored to companies' specific needs, addressing potential environmental damages.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com