Cyber risk underwriting focuses on evaluating digital vulnerabilities related to data breaches, network security, and cyber-attacks, using specialized algorithms to assess potential financial losses in the technology sector. Automobile underwriting involves analyzing driver history, vehicle type, and accident risk to determine premiums and coverage for physical damage and liability. Explore the unique criteria and methods behind each underwriting type to understand their critical roles in risk management.
Why it is important
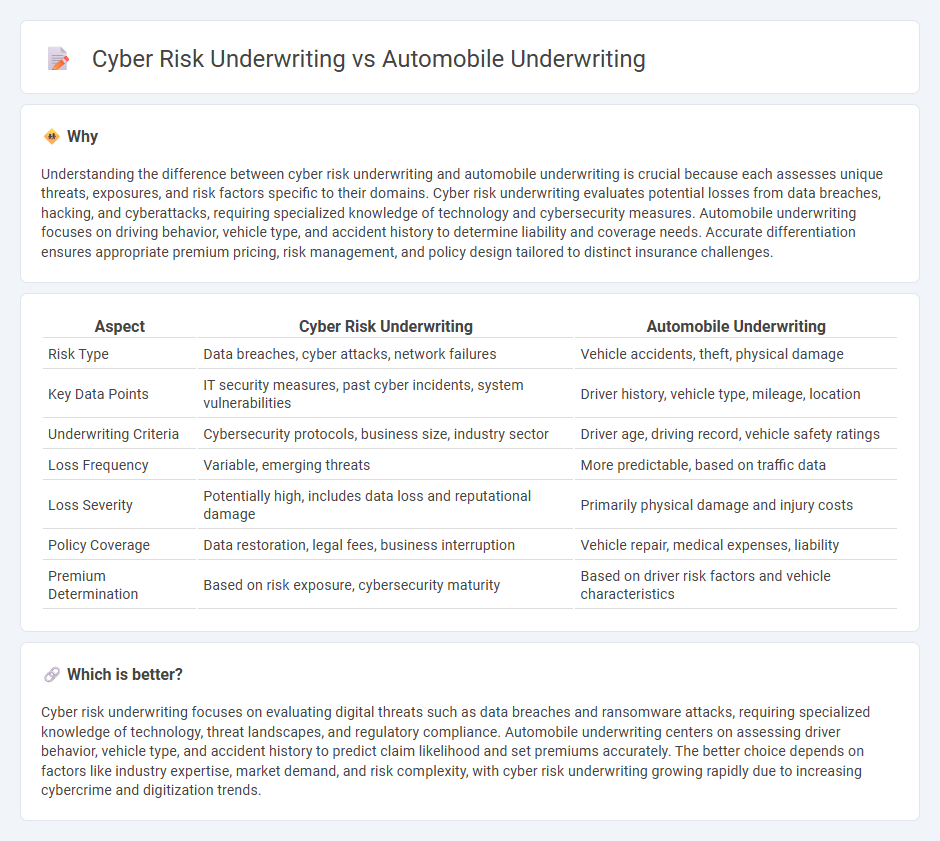
Understanding the difference between cyber risk underwriting and automobile underwriting is crucial because each assesses unique threats, exposures, and risk factors specific to their domains. Cyber risk underwriting evaluates potential losses from data breaches, hacking, and cyberattacks, requiring specialized knowledge of technology and cybersecurity measures. Automobile underwriting focuses on driving behavior, vehicle type, and accident history to determine liability and coverage needs. Accurate differentiation ensures appropriate premium pricing, risk management, and policy design tailored to distinct insurance challenges.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Cyber Risk Underwriting | Automobile Underwriting |
|---|---|---|
| Risk Type | Data breaches, cyber attacks, network failures | Vehicle accidents, theft, physical damage |
| Key Data Points | IT security measures, past cyber incidents, system vulnerabilities | Driver history, vehicle type, mileage, location |
| Underwriting Criteria | Cybersecurity protocols, business size, industry sector | Driver age, driving record, vehicle safety ratings |
| Loss Frequency | Variable, emerging threats | More predictable, based on traffic data |
| Loss Severity | Potentially high, includes data loss and reputational damage | Primarily physical damage and injury costs |
| Policy Coverage | Data restoration, legal fees, business interruption | Vehicle repair, medical expenses, liability |
| Premium Determination | Based on risk exposure, cybersecurity maturity | Based on driver risk factors and vehicle characteristics |
Which is better?
Cyber risk underwriting focuses on evaluating digital threats such as data breaches and ransomware attacks, requiring specialized knowledge of technology, threat landscapes, and regulatory compliance. Automobile underwriting centers on assessing driver behavior, vehicle type, and accident history to predict claim likelihood and set premiums accurately. The better choice depends on factors like industry expertise, market demand, and risk complexity, with cyber risk underwriting growing rapidly due to increasing cybercrime and digitization trends.
Connection
Cyber risk underwriting and automobile underwriting intersect through the increasing integration of connected vehicle technologies, where cybersecurity vulnerabilities directly impact automobile insurance risk assessments. Insurers analyzing these risks incorporate data on software threats, potential cyberattacks on vehicle systems, and the likelihood of remote hacks, influencing coverage terms and premium pricing in automobile policies. This convergence drives the need for comprehensive risk models combining both cyber threat intelligence and traditional automotive risk factors to accurately underwrite connected car insurance.
Key Terms
**Automobile Underwriting:**
Automobile underwriting involves assessing risk factors such as driver history, vehicle type, usage patterns, and regional accident rates to determine insurance premiums and coverage limits. Underwriters utilize telematics data, repair cost trends, and claims frequency to accurately price policies and minimize losses. Discover more about how advanced analytics shape automobile underwriting decisions.
Driver history
Automobile underwriting heavily relies on driver history to assess risk, analyzing past accidents, traffic violations, and claims to determine insurance premiums. In contrast, cyber risk underwriting evaluates organizational cybersecurity measures, breach history, and vulnerability exposures rather than individual behavior patterns. Discover how these underwriting approaches differ in detail to better manage insurance risks.
Vehicle type
Automobile underwriting involves assessing risks based on vehicle type, including factors like make, model, age, and usage patterns, which directly impact premium calculation and coverage terms. Cyber risk underwriting, however, prioritizes the type of digital assets, network infrastructure, and the nature of cyber threats over physical vehicle characteristics. Discover more about how distinct underwriting criteria shape risk evaluation in both fields.
Source and External Links
How Does Car Insurance Underwriting Work? - Automobile underwriting is the process by which insurers analyze and assess the risk of insuring a particular individual or vehicle, taking into account factors like car usage, location, coverage level, and personal driving history to determine appropriate premiums and coverage eligibility.
ALDOI - Underwriting and Rating - Underwriting sorts applicants into groups with similar risk characteristics to accept, deny, or limit coverage while rating sets the price based on expected claim costs, considering factors like geographic location, vehicle type, lifestyle, and driving behavior.
Auto and home policy underwriting: Learn how companies ... - Insurance companies evaluate your driving record, car usage, location, vehicle type, and sometimes credit score during underwriting to decide if they will offer you a policy and at what premium.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com