Decoupled insurance separates the insurance product from the underlying purchase, allowing consumers to independently select coverage tailored to their specific needs. Embedded insurance integrates coverage directly into the purchase process, streamlining protection and enhancing convenience by bundling insurance with the product or service. Explore the differences between decoupled and embedded insurance models to understand which approach best suits your risk management strategy.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between decoupled insurance and embedded insurance is crucial for consumers and businesses to optimize coverage, control costs, and ensure transparency in policy terms. Decoupled insurance offers standalone policies allowing tailored risk management, while embedded insurance integrates coverage within product purchases, enhancing convenience but potentially limiting customization. Recognizing these distinctions helps stakeholders make informed decisions aligned with their financial goals and risk tolerance. Accurate knowledge also aids regulators and insurers in designing appropriate frameworks and products that meet market needs efficiently.
Comparison Table
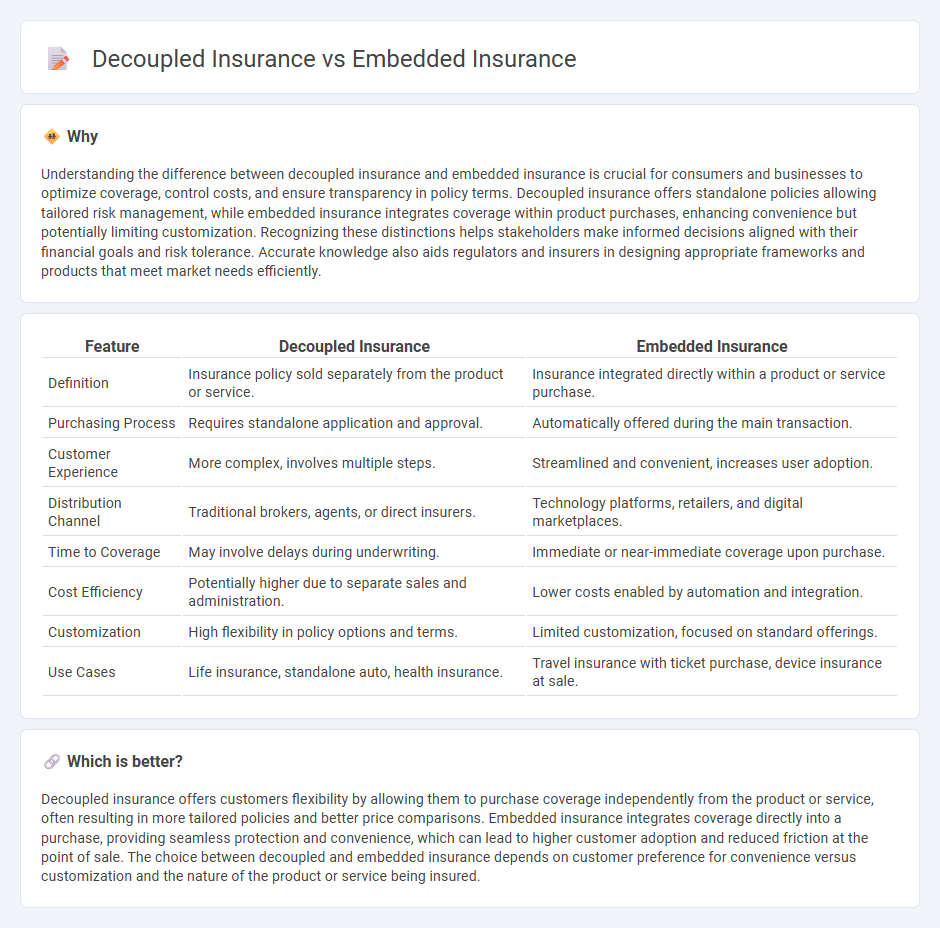
| Feature | Decoupled Insurance | Embedded Insurance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Insurance policy sold separately from the product or service. | Insurance integrated directly within a product or service purchase. |
| Purchasing Process | Requires standalone application and approval. | Automatically offered during the main transaction. |
| Customer Experience | More complex, involves multiple steps. | Streamlined and convenient, increases user adoption. |
| Distribution Channel | Traditional brokers, agents, or direct insurers. | Technology platforms, retailers, and digital marketplaces. |
| Time to Coverage | May involve delays during underwriting. | Immediate or near-immediate coverage upon purchase. |
| Cost Efficiency | Potentially higher due to separate sales and administration. | Lower costs enabled by automation and integration. |
| Customization | High flexibility in policy options and terms. | Limited customization, focused on standard offerings. |
| Use Cases | Life insurance, standalone auto, health insurance. | Travel insurance with ticket purchase, device insurance at sale. |
Which is better?
Decoupled insurance offers customers flexibility by allowing them to purchase coverage independently from the product or service, often resulting in more tailored policies and better price comparisons. Embedded insurance integrates coverage directly into a purchase, providing seamless protection and convenience, which can lead to higher customer adoption and reduced friction at the point of sale. The choice between decoupled and embedded insurance depends on customer preference for convenience versus customization and the nature of the product or service being insured.
Connection
Embedded insurance integrates insurance products directly into the purchase process of goods and services, simplifying customer access and increasing policy uptake. Decoupled insurance, in contrast, separates insurance products from the primary transaction, allowing consumers to buy coverage independently on digital platforms. Both models leverage digital technology to enhance consumer choice and streamline insurance distribution, catering to diverse preferences for purchasing insurance.
Key Terms
Distribution channel
Embedded insurance integrates coverage seamlessly within the purchase of a product or service, leveraging direct distribution channels such as e-commerce platforms and point-of-sale systems to enhance customer convenience and streamline policy acquisition. Decoupled insurance relies on traditional brokers or independent agents, employing separate distribution channels that may limit immediacy but offer personalized advisory services. Explore the evolving strategies in insurance distribution to determine which model best aligns with customer engagement and market trends.
Customer journey
Embedded insurance integrates coverage seamlessly into the purchase process, enhancing customer convenience by reducing friction and providing instant protection at the point of sale. Decoupled insurance requires separate engagement, often leading to longer decision times and potential drop-off due to additional research and comparison needed. Discover more about optimizing insurance strategies to improve customer experience and conversion rates.
Product integration
Embedded insurance integrates coverage directly within a product or service offering, providing seamless protection without requiring separate purchase processes, enhancing customer convenience and reducing friction. Decoupled insurance, by contrast, operates independently from the primary product, necessitating separate transactions and often resulting in lower engagement rates and customer awareness. Explore deeper insights into how product integration influences consumer adoption and business strategy in insurance.
Source and External Links
What is Embedded Insurance | Chubb - Embedded insurance allows businesses to integrate risk protection into their customers' purchase journeys, offering personalized protection at competitive rates.
Embedded Insurance: Definition, Types, Benefits - Endava - Embedded insurance is seamlessly integrated into a customer's buying experience, providing immediate coverage at the point of sale, unlike traditional insurance which is purchased separately.
This Is Why The Future of Insurance Distribution Is Embedded - Embedded insurance emerging as a new way to distribute insurance services by bundling coverage within the purchase of a product or service itself, offered in real-time or at the point of sale.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com