On-demand insurance offers flexible, pay-per-use coverage activated only when needed, contrasting with self-insurance where individuals or businesses set aside funds to cover potential losses independently. This model reduces upfront costs and adapts to varying risk levels without long-term commitments, whereas self-insurance requires sufficient capital reserves and risk management expertise. Explore the benefits and considerations of on-demand insurance compared to self-insurance to determine the best risk strategy.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between on-demand insurance and self-insurance is crucial for effective risk management and financial planning. On-demand insurance offers flexible, short-term coverage tailored to specific needs, while self-insurance involves setting aside funds to cover potential losses independently. Choosing the right approach impacts premium costs, claim processes, and overall financial security. Businesses and individuals can optimize protection and cost-efficiency by aligning their strategy with these insurance models.
Comparison Table
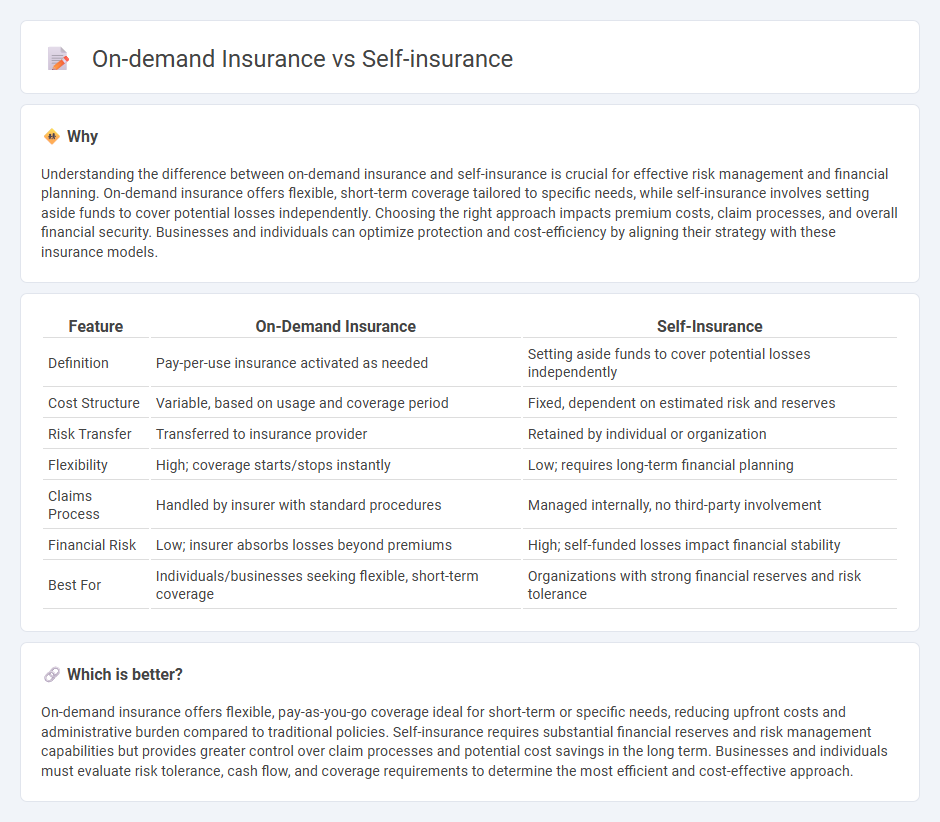
| Feature | On-Demand Insurance | Self-Insurance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Pay-per-use insurance activated as needed | Setting aside funds to cover potential losses independently |
| Cost Structure | Variable, based on usage and coverage period | Fixed, dependent on estimated risk and reserves |
| Risk Transfer | Transferred to insurance provider | Retained by individual or organization |
| Flexibility | High; coverage starts/stops instantly | Low; requires long-term financial planning |
| Claims Process | Handled by insurer with standard procedures | Managed internally, no third-party involvement |
| Financial Risk | Low; insurer absorbs losses beyond premiums | High; self-funded losses impact financial stability |
| Best For | Individuals/businesses seeking flexible, short-term coverage | Organizations with strong financial reserves and risk tolerance |
Which is better?
On-demand insurance offers flexible, pay-as-you-go coverage ideal for short-term or specific needs, reducing upfront costs and administrative burden compared to traditional policies. Self-insurance requires substantial financial reserves and risk management capabilities but provides greater control over claim processes and potential cost savings in the long term. Businesses and individuals must evaluate risk tolerance, cash flow, and coverage requirements to determine the most efficient and cost-effective approach.
Connection
On-demand insurance and self-insurance both emphasize flexibility and cost-efficiency in risk management, allowing consumers to tailor coverage to specific needs and avoid traditional long-term policies. On-demand insurance provides short-term, pay-as-you-go protection through digital platforms, while self-insurance involves setting aside funds to cover potential losses internally without transferring risk to an insurer. Both approaches reduce reliance on conventional insurance companies, empowering individuals and businesses to control their financial exposure more directly.
Key Terms
Risk Retention
Self-insurance involves an organization or individual assuming full responsibility for potential losses by retaining the risk internally, rather than transferring it to an insurer. On-demand insurance, in contrast, allows policyholders to purchase coverage only for specific risks and timeframes, reducing overall risk retention but offering flexible protection. Explore the advantages and drawbacks of risk retention strategies in self-insurance and on-demand insurance to determine the best fit for your risk management needs.
Flexibility
Self-insurance offers significant flexibility by allowing businesses to tailor coverage and manage risk internally, adapting policies to their specific needs without reliance on external providers. On-demand insurance provides dynamic and immediate coverage options, enabling individuals to purchase protection only when needed, ideal for sporadic or short-term risks. Explore the differences in flexibility between self-insurance and on-demand insurance to determine the best fit for your risk management strategy.
Premium Structure
Self-insurance involves setting aside funds to cover potential losses, resulting in lower upfront costs but requiring significant capital reserves and risk tolerance. On-demand insurance offers flexible, pay-as-you-go premiums based on actual usage or specific events, optimizing cost efficiency for sporadic or short-term coverage needs. Explore detailed comparisons to determine which premium structure best aligns with your financial goals and risk profile.
Source and External Links
Self-insurance - Self-insurance is a risk management strategy where an organization covers potential losses using its own funds rather than purchasing third-party insurance.
A Guide to Self-Insurance - This guide outlines steps to manage self-insurance, including creating a strong team, conducting a cash flow analysis, and using stop-loss insurance.
What Is the Difference between Self-Insurance and Captive Insurance - This article explains the difference between self-insurance and captive insurance, highlighting how self-insurance involves an organization setting aside funds for potential losses.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com