Peer-to-peer insurance leverages community pooling of risks, allowing members to share premiums and claim benefits directly, reducing overhead and improving transparency. Direct-to-consumer insurance eliminates intermediaries by offering policies directly from insurers to customers, enhancing convenience and potentially lowering costs. Discover how each model transforms traditional insurance by exploring their unique benefits and limitations.
Why it is important
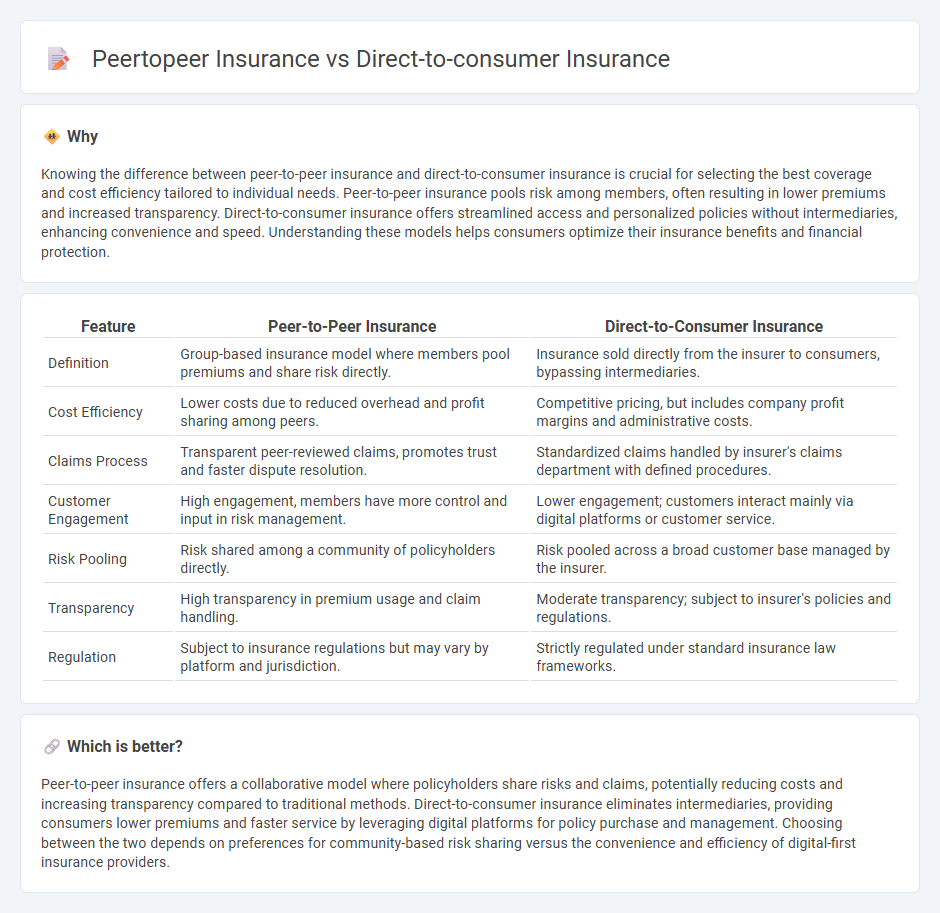
Knowing the difference between peer-to-peer insurance and direct-to-consumer insurance is crucial for selecting the best coverage and cost efficiency tailored to individual needs. Peer-to-peer insurance pools risk among members, often resulting in lower premiums and increased transparency. Direct-to-consumer insurance offers streamlined access and personalized policies without intermediaries, enhancing convenience and speed. Understanding these models helps consumers optimize their insurance benefits and financial protection.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Peer-to-Peer Insurance | Direct-to-Consumer Insurance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Group-based insurance model where members pool premiums and share risk directly. | Insurance sold directly from the insurer to consumers, bypassing intermediaries. |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower costs due to reduced overhead and profit sharing among peers. | Competitive pricing, but includes company profit margins and administrative costs. |
| Claims Process | Transparent peer-reviewed claims, promotes trust and faster dispute resolution. | Standardized claims handled by insurer's claims department with defined procedures. |
| Customer Engagement | High engagement, members have more control and input in risk management. | Lower engagement; customers interact mainly via digital platforms or customer service. |
| Risk Pooling | Risk shared among a community of policyholders directly. | Risk pooled across a broad customer base managed by the insurer. |
| Transparency | High transparency in premium usage and claim handling. | Moderate transparency; subject to insurer's policies and regulations. |
| Regulation | Subject to insurance regulations but may vary by platform and jurisdiction. | Strictly regulated under standard insurance law frameworks. |
Which is better?
Peer-to-peer insurance offers a collaborative model where policyholders share risks and claims, potentially reducing costs and increasing transparency compared to traditional methods. Direct-to-consumer insurance eliminates intermediaries, providing consumers lower premiums and faster service by leveraging digital platforms for policy purchase and management. Choosing between the two depends on preferences for community-based risk sharing versus the convenience and efficiency of digital-first insurance providers.
Connection
Peer-to-peer insurance and direct-to-consumer insurance share a foundation in leveraging technology to reduce intermediaries and enhance transparency between insurers and policyholders. Both models emphasize cost-efficiency and user control by eliminating traditional brokers, allowing consumers to directly manage policies and claims through digital platforms. This connection fosters a more personalized insurance experience, driven by data analytics and community risk-sharing mechanisms.
Key Terms
Distribution Channel
Direct-to-consumer insurance leverages digital platforms to sell policies directly to customers, eliminating intermediaries and reducing distribution costs. Peer-to-peer insurance groups individuals with similar risk profiles to pool premiums and share claims, often facilitated through app-based platforms that emphasize community and transparency. Explore the advantages and challenges of each distribution channel to determine the best fit for your insurance needs.
Risk Pooling
Direct-to-consumer insurance offers personalized policies directly from providers, streamlining the customer experience and reducing administrative costs. Peer-to-peer insurance emphasizes risk pooling by grouping individuals with similar risk profiles to collectively share claims, promoting transparency and potential cost savings. Explore how these models impact risk distribution and premiums to make informed insurance decisions.
Underwriting
Direct-to-consumer insurance leverages advanced data analytics and AI-driven underwriting processes to offer personalized policies without intermediaries, enhancing speed and accuracy. Peer-to-peer insurance relies on collective risk pooling and community-based underwriting methods, promoting transparency and potential cost savings by aligning member interests. Explore how these underwriting models impact pricing, risk assessment, and customer experience in the evolving insurance landscape.
Source and External Links
Direct-to-Consumer Insurance: Benefits, Challenges, and How to Get It Right - The direct-to-consumer (D2C or DTC) insurance model enables companies to sell insurance policies directly to customers online, bypassing brokers and agents, and relies heavily on digital platforms to deliver fast, seamless experiences.
The Future of Direct-to-Consumer Insurance Sales - D2C insurance allows insurers to sell directly to policyholders without intermediaries, potentially lowering costs for consumers while presenting both opportunities and challenges for insurers adapting to digital sales.
How Direct to Consumer Insurance Works - In the direct-to-consumer model, customers purchase insurance directly from the carrier's website, expecting a streamlined, self-service experience without needing to interact with agents or third parties.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com