Ghost broking involves fraudsters selling fake or invalid insurance policies, exposing customers to financial risk and legal issues. Churning refers to the unethical practice where brokers repeatedly encourage clients to switch insurance policies to generate commissions, often resulting in unnecessary expenses and policy confusion. Explore how to identify and protect yourself from these deceptive insurance practices.
Why it is important
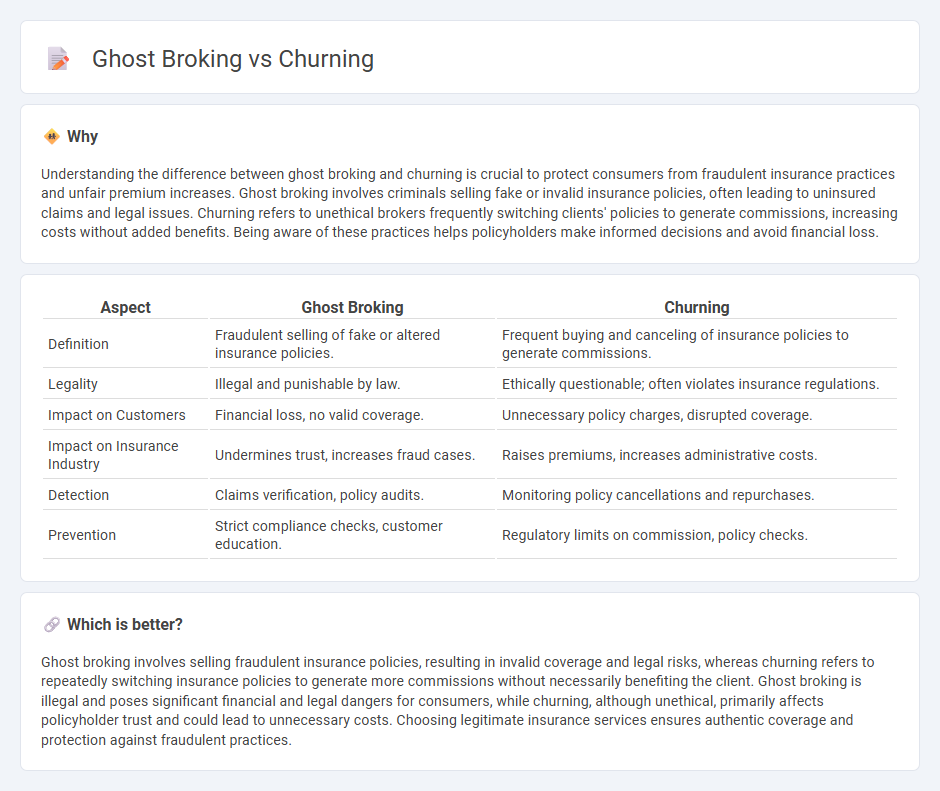
Understanding the difference between ghost broking and churning is crucial to protect consumers from fraudulent insurance practices and unfair premium increases. Ghost broking involves criminals selling fake or invalid insurance policies, often leading to uninsured claims and legal issues. Churning refers to unethical brokers frequently switching clients' policies to generate commissions, increasing costs without added benefits. Being aware of these practices helps policyholders make informed decisions and avoid financial loss.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Ghost Broking | Churning |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Fraudulent selling of fake or altered insurance policies. | Frequent buying and canceling of insurance policies to generate commissions. |
| Legality | Illegal and punishable by law. | Ethically questionable; often violates insurance regulations. |
| Impact on Customers | Financial loss, no valid coverage. | Unnecessary policy charges, disrupted coverage. |
| Impact on Insurance Industry | Undermines trust, increases fraud cases. | Raises premiums, increases administrative costs. |
| Detection | Claims verification, policy audits. | Monitoring policy cancellations and repurchases. |
| Prevention | Strict compliance checks, customer education. | Regulatory limits on commission, policy checks. |
Which is better?
Ghost broking involves selling fraudulent insurance policies, resulting in invalid coverage and legal risks, whereas churning refers to repeatedly switching insurance policies to generate more commissions without necessarily benefiting the client. Ghost broking is illegal and poses significant financial and legal dangers for consumers, while churning, although unethical, primarily affects policyholder trust and could lead to unnecessary costs. Choosing legitimate insurance services ensures authentic coverage and protection against fraudulent practices.
Connection
Ghost broking involves fraudulent intermediaries selling fake or misleading insurance policies, while churning refers to repeatedly switching policies to generate commissions without client benefit. Both practices exploit insurance markets by undermining policyholder trust and inflating costs. Regulatory bodies actively combat these schemes to protect consumers and maintain market integrity.
Key Terms
Policy Replacement
Churning involves frequent policy cancellations and replacements to generate commissions, often leading to unnecessary policy switching without added benefits for the customer. Ghost broking entails fraudulent activity where intermediaries sell fake or invalid insurance policies, putting clients at significant financial risk and legal liability. Explore how these practices impact insurance policies and consumer protection measures.
Misrepresentation
Churning involves excessive trading to generate commissions, often misleading clients about the necessity and risks, while ghost broking entails selling fraudulent insurance policies by impersonating legitimate brokers, resulting in significant misrepresentation of coverage validity. Both practices undermine client trust and violate regulatory standards, causing financial and legal repercussions. Explore more to understand the differences and protect yourself from such deceptive schemes.
Unauthorized Intermediary
Unauthorized intermediaries in the insurance sector engage in practices such as churning and ghost broking, both of which compromise policyholder protection and market integrity. Churning involves repeatedly switching policies to generate excessive commissions, while ghost broking entails the fraudulent creation or sale of insurance policies by unlicensed dealers. Explore more to understand the risks associated with unauthorized intermediaries and how to safeguard yourself.
Source and External Links
churning | Wex | US Law | LII / Legal Information Institute - Churning is the illegal practice by brokers of excessively buying and selling securities in a client's account primarily to generate commissions rather than to benefit the client, violating federal securities law and fiduciary duty.
Churning (finance) - Wikipedia - Churning is the frequent trading within an investment account by brokers to earn commissions, often leading to diminished investment value, and is considered securities fraud in many jurisdictions.
What Is Credit Card Churning? | Discover - Credit card churning refers to repeatedly opening and closing credit card accounts to gain sign-up bonuses and rewards, which can negatively impact credit scores and risk debt.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com