Social prescribing insurance focuses on covering non-medical interventions such as community activities and wellness programs to improve overall health and reduce healthcare costs. Long-term care insurance provides financial support for extended services like nursing home care, home health aides, and assisted living for individuals with chronic illnesses or disabilities. Explore the differences and benefits of these insurance types to find the best fit for your healthcare needs.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between social prescribing insurance and long-term care insurance is crucial because social prescribing insurance covers non-medical interventions like mental health support and community activities, while long-term care insurance provides financial assistance for extended personal and healthcare services due to chronic illness or disability. Knowing these distinctions ensures appropriate coverage for either wellness-focused services or long-term medical care, preventing gaps in healthcare funding. Proper knowledge helps individuals choose policies that best match their health needs and financial planning strategies. This clarity optimizes resource allocation and safeguards against unexpected medical expenses.
Comparison Table
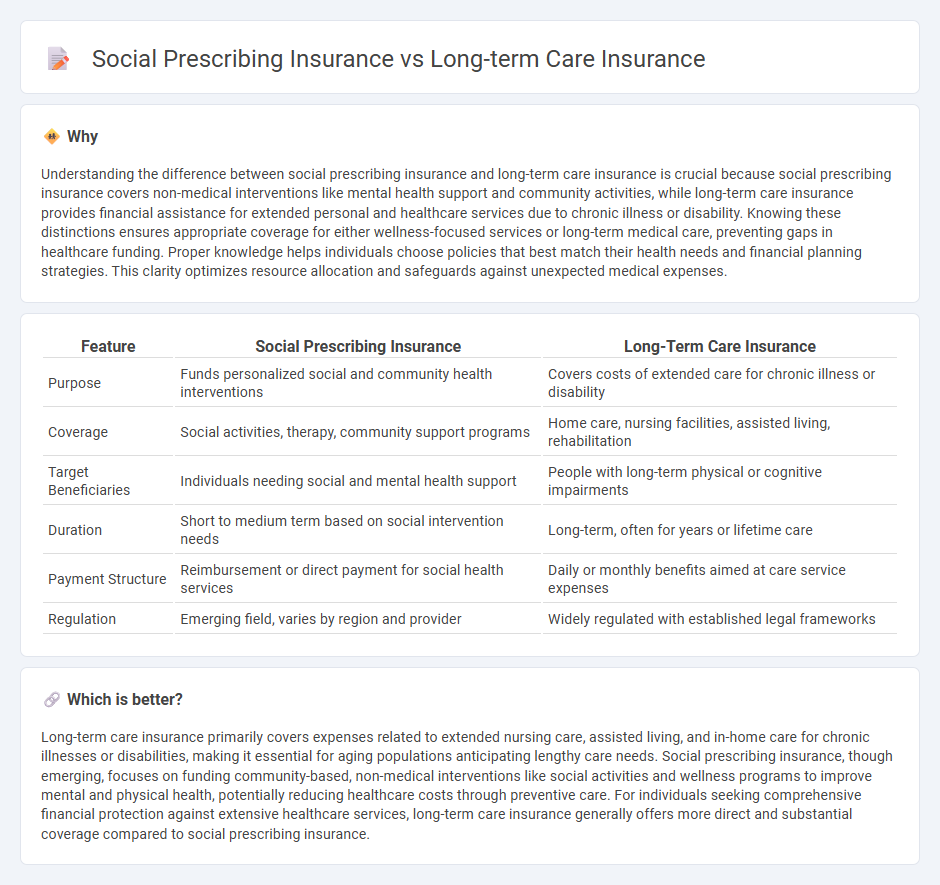
| Feature | Social Prescribing Insurance | Long-Term Care Insurance |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Funds personalized social and community health interventions | Covers costs of extended care for chronic illness or disability |
| Coverage | Social activities, therapy, community support programs | Home care, nursing facilities, assisted living, rehabilitation |
| Target Beneficiaries | Individuals needing social and mental health support | People with long-term physical or cognitive impairments |
| Duration | Short to medium term based on social intervention needs | Long-term, often for years or lifetime care |
| Payment Structure | Reimbursement or direct payment for social health services | Daily or monthly benefits aimed at care service expenses |
| Regulation | Emerging field, varies by region and provider | Widely regulated with established legal frameworks |
Which is better?
Long-term care insurance primarily covers expenses related to extended nursing care, assisted living, and in-home care for chronic illnesses or disabilities, making it essential for aging populations anticipating lengthy care needs. Social prescribing insurance, though emerging, focuses on funding community-based, non-medical interventions like social activities and wellness programs to improve mental and physical health, potentially reducing healthcare costs through preventive care. For individuals seeking comprehensive financial protection against extensive healthcare services, long-term care insurance generally offers more direct and substantial coverage compared to social prescribing insurance.
Connection
Social prescribing insurance complements long-term care insurance by funding non-clinical interventions such as community activities and support services that improve mental and physical health, potentially reducing the need for extensive long-term care. Both types of insurance aim to enhance overall well-being and manage chronic conditions, ultimately lowering healthcare costs and delaying institutionalization. Integrating social prescribing with long-term care insurance promotes holistic care approaches, addressing social determinants of health alongside medical needs.
Key Terms
Coverage scope
Long-term care insurance primarily covers services such as nursing home care, home health care, and personal care assistance for chronic illnesses or disabilities. Social prescribing insurance typically funds non-medical interventions including community activities, wellness programs, and social support services aimed at improving mental and physical well-being. Explore in-depth comparisons to understand how each insurance type supports different aspects of health and care needs.
Benefit triggers
Long-term care insurance primarily activates benefits when policyholders experience significant physical or cognitive impairments requiring assistance with daily living activities, while social prescribing insurance focuses on funding non-medical interventions that improve social determinants of health, such as community engagement and mental wellbeing. Benefit triggers for long-term care insurance often include formal medical assessments and documented functional limitations, whereas social prescribing insurance relies on referrals from healthcare providers and evidence of social or psychological needs. Explore further to understand how these distinct benefit triggers impact coverage and patient outcomes.
Service integration
Long-term care insurance primarily covers personal and medical support services for elderly or disabled individuals over extended periods, while social prescribing insurance emphasizes holistic well-being by funding community-based interventions like social activities and support networks. Service integration in long-term care insurance often involves coordination between healthcare providers, caregivers, and insurers to ensure seamless care delivery. Explore how innovative service integration is transforming both insurance models by enhancing patient outcomes and reducing healthcare costs.
Source and External Links
Long-Term Care Insurance Explained - NerdWallet - Long-term care insurance helps cover care costs when you can't perform at least two of six daily activities, reimburses after waiting periods, and policies often cap daily and lifetime benefits.
Long-term care costs & options - Fidelity Investments - Long-term care can be paid through government programs, traditional insurance, hybrid insurance, or personal savings; Medicare generally does not cover long-term care costs.
What is Long-term Care Insurance? - It covers personal and custodial care services in various settings, with premiums based on age, coverage limits, and optional benefits; medical underwriting typically applies.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com