Peer-to-peer insurance leverages community pooling of resources to share risks directly among participants, reducing administrative costs and increasing transparency. Captive insurance involves a company creating its own insurance subsidiary to underwrite its risks, offering greater control and potential cost savings on premiums. Discover how these innovative insurance models can transform risk management strategies for businesses and individuals.
Why it is important
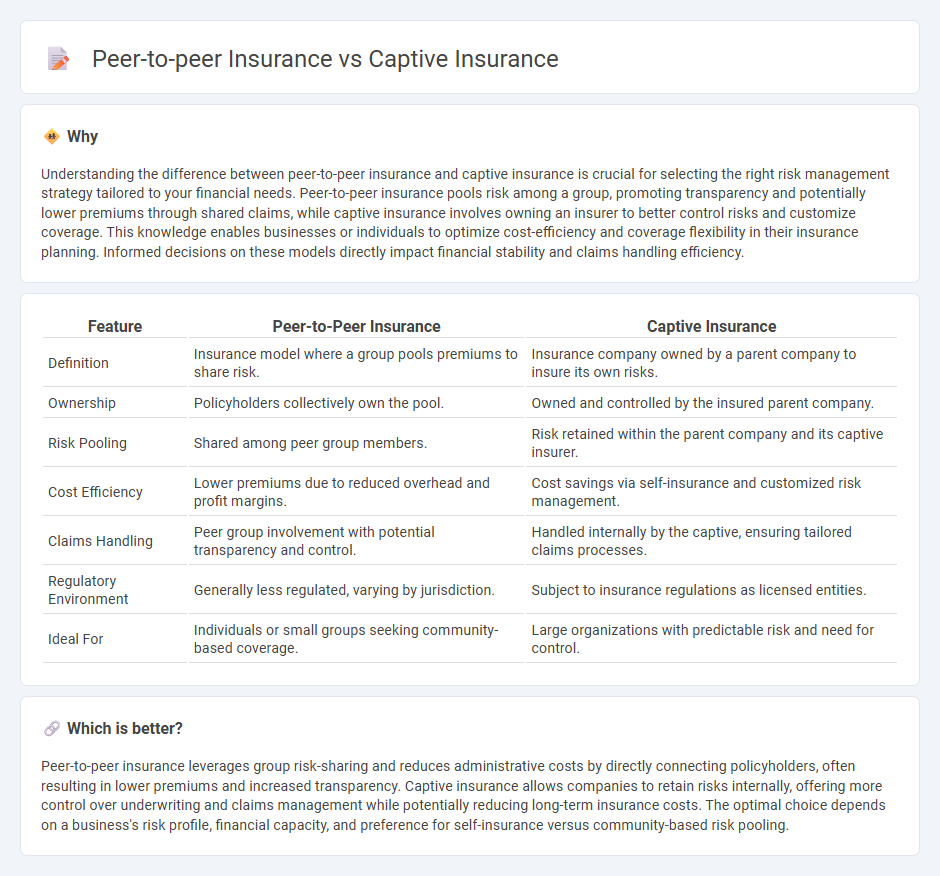
Understanding the difference between peer-to-peer insurance and captive insurance is crucial for selecting the right risk management strategy tailored to your financial needs. Peer-to-peer insurance pools risk among a group, promoting transparency and potentially lower premiums through shared claims, while captive insurance involves owning an insurer to better control risks and customize coverage. This knowledge enables businesses or individuals to optimize cost-efficiency and coverage flexibility in their insurance planning. Informed decisions on these models directly impact financial stability and claims handling efficiency.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Peer-to-Peer Insurance | Captive Insurance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Insurance model where a group pools premiums to share risk. | Insurance company owned by a parent company to insure its own risks. |
| Ownership | Policyholders collectively own the pool. | Owned and controlled by the insured parent company. |
| Risk Pooling | Shared among peer group members. | Risk retained within the parent company and its captive insurer. |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower premiums due to reduced overhead and profit margins. | Cost savings via self-insurance and customized risk management. |
| Claims Handling | Peer group involvement with potential transparency and control. | Handled internally by the captive, ensuring tailored claims processes. |
| Regulatory Environment | Generally less regulated, varying by jurisdiction. | Subject to insurance regulations as licensed entities. |
| Ideal For | Individuals or small groups seeking community-based coverage. | Large organizations with predictable risk and need for control. |
Which is better?
Peer-to-peer insurance leverages group risk-sharing and reduces administrative costs by directly connecting policyholders, often resulting in lower premiums and increased transparency. Captive insurance allows companies to retain risks internally, offering more control over underwriting and claims management while potentially reducing long-term insurance costs. The optimal choice depends on a business's risk profile, financial capacity, and preference for self-insurance versus community-based risk pooling.
Connection
Peer-to-peer insurance and captive insurance both represent alternative risk management models that shift control from traditional insurers to policyholders or organizations. Peer-to-peer insurance pools premiums among members to cover losses collectively, reducing administrative costs and aligning interests, while captive insurance involves a company creating its own insurance subsidiary to manage risks internally and customize coverage. Both approaches enhance risk retention, improve cost efficiency, and provide tailored protection by leveraging direct stakeholder involvement and minimizing reliance on conventional insurance markets.
Key Terms
Risk Pooling
Captive insurance allows companies to create a self-owned risk pool to manage and finance their specific risks, offering tailored coverage and cost control. Peer-to-peer insurance pools premiums from members sharing similar risk profiles to reduce administrative costs and improve transparency. Explore more about how different risk pooling methods impact insurance efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Ownership Structure
Captive insurance involves a company creating its own insurance subsidiary to manage risks internally, ensuring complete ownership and control over policies and claims management. Peer-to-peer insurance relies on groups of individuals pooling resources to insure each other, fostering shared ownership and risk distribution without a centralized insurer. Discover the key differences and benefits in ownership structures between these models for tailored risk management solutions.
Profit Distribution
Captive insurance allows companies to retain underwriting profits internally, enhancing financial control and risk management efficiency. Peer-to-peer insurance distributes profits back to members based on claims performance, promoting transparency and mutual benefit among participants. Explore the differences in profit distribution strategies to determine the best model for your risk management needs.
Source and External Links
Captive insurance - Wikipedia - Captive insurance is an alternative to self-insurance where insured parties create licensed insurance companies to insure their own risks, offering tax benefits, pricing near cost, and more control over risk management, with types including single-parent, group, and sponsored captives.
What Is Captive Insurance? - Captive.com - A captive insurer is a wholly owned insurance company controlled by its insureds that provides tailored coverage for difficult risks, price stability, and direct control over claims and loss control tailored to participants' needs.
What is Captive Insurance? - Alliant - Captive insurance companies are licensed firms owned by their insureds, allowing organizations to manage risk, stabilize premiums, access reinsurance directly, and share in underwriting profits while reducing reliance on commercial markets.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com