Flood risk modeling focuses on predicting potential damages and frequency of flood events by analyzing hydrological data, terrain, and weather patterns, while catastrophe risk modeling assesses the impact of a wide range of disasters, including floods, earthquakes, and hurricanes, by simulating extreme scenarios and their financial consequences for insurers. Both models utilize probabilistic techniques and extensive datasets to estimate losses and improve underwriting accuracy in insurance portfolios. Explore more to understand how these models shape risk management strategies and policy pricing.
Why it is important
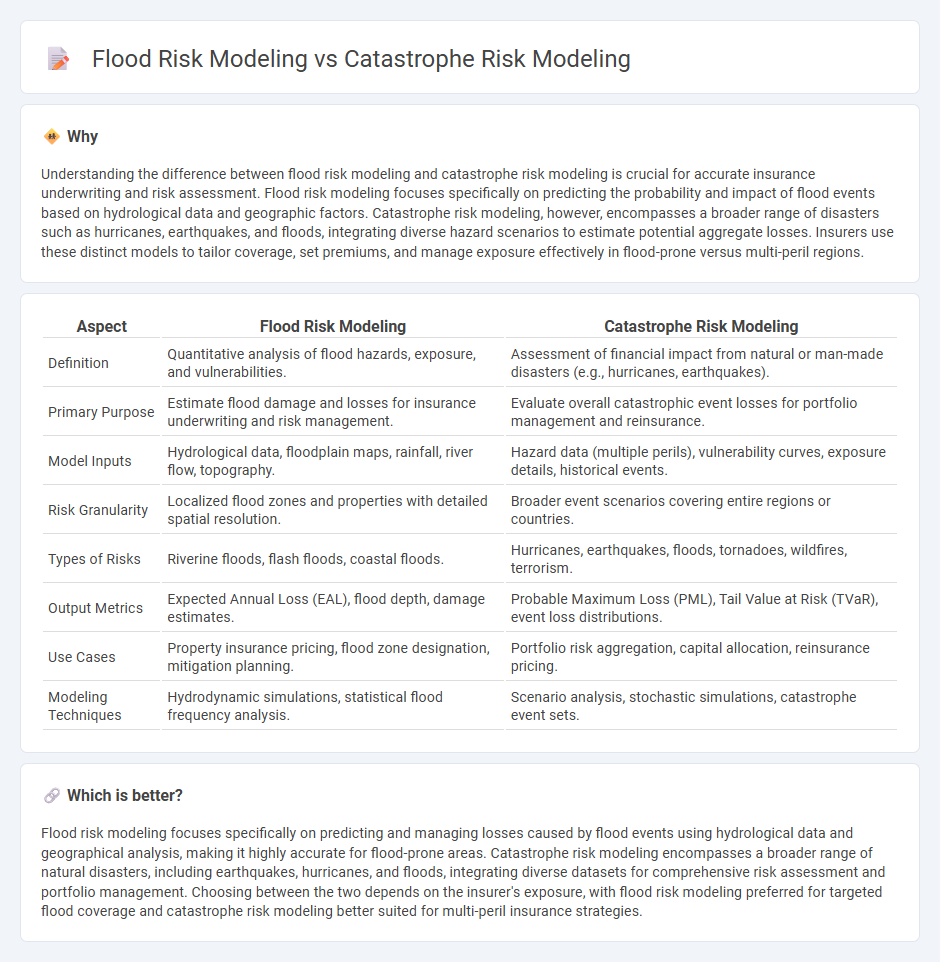
Understanding the difference between flood risk modeling and catastrophe risk modeling is crucial for accurate insurance underwriting and risk assessment. Flood risk modeling focuses specifically on predicting the probability and impact of flood events based on hydrological data and geographic factors. Catastrophe risk modeling, however, encompasses a broader range of disasters such as hurricanes, earthquakes, and floods, integrating diverse hazard scenarios to estimate potential aggregate losses. Insurers use these distinct models to tailor coverage, set premiums, and manage exposure effectively in flood-prone versus multi-peril regions.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Flood Risk Modeling | Catastrophe Risk Modeling |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Quantitative analysis of flood hazards, exposure, and vulnerabilities. | Assessment of financial impact from natural or man-made disasters (e.g., hurricanes, earthquakes). |
| Primary Purpose | Estimate flood damage and losses for insurance underwriting and risk management. | Evaluate overall catastrophic event losses for portfolio management and reinsurance. |
| Model Inputs | Hydrological data, floodplain maps, rainfall, river flow, topography. | Hazard data (multiple perils), vulnerability curves, exposure details, historical events. |
| Risk Granularity | Localized flood zones and properties with detailed spatial resolution. | Broader event scenarios covering entire regions or countries. |
| Types of Risks | Riverine floods, flash floods, coastal floods. | Hurricanes, earthquakes, floods, tornadoes, wildfires, terrorism. |
| Output Metrics | Expected Annual Loss (EAL), flood depth, damage estimates. | Probable Maximum Loss (PML), Tail Value at Risk (TVaR), event loss distributions. |
| Use Cases | Property insurance pricing, flood zone designation, mitigation planning. | Portfolio risk aggregation, capital allocation, reinsurance pricing. |
| Modeling Techniques | Hydrodynamic simulations, statistical flood frequency analysis. | Scenario analysis, stochastic simulations, catastrophe event sets. |
Which is better?
Flood risk modeling focuses specifically on predicting and managing losses caused by flood events using hydrological data and geographical analysis, making it highly accurate for flood-prone areas. Catastrophe risk modeling encompasses a broader range of natural disasters, including earthquakes, hurricanes, and floods, integrating diverse datasets for comprehensive risk assessment and portfolio management. Choosing between the two depends on the insurer's exposure, with flood risk modeling preferred for targeted flood coverage and catastrophe risk modeling better suited for multi-peril insurance strategies.
Connection
Flood risk modeling and catastrophe risk modeling are interconnected through their shared objective of assessing and quantifying potential losses from natural disasters. Flood risk modeling focuses specifically on predicting flood events by analyzing hydrological data, topography, and climate patterns, while catastrophe risk modeling incorporates flood risk along with other hazards like earthquakes and hurricanes to evaluate overall insurance portfolio vulnerabilities. Insurers leverage both models to develop accurate risk assessments, set premiums, and ensure adequate capital reserves for extreme weather events and large-scale catastrophes.
Key Terms
**Catastrophe Risk Modeling:**
Catastrophe risk modeling encompasses a broad spectrum of natural disasters including hurricanes, earthquakes, and floods, utilizing complex simulations to estimate potential losses and inform insurance underwriting. It integrates hazard assessment, vulnerability analysis, and exposure data to predict both direct and indirect economic impacts with high precision. Explore more to understand how advanced catastrophe models enhance risk management and resilience strategies.
Exposure
Catastrophe risk modeling encompasses a broad spectrum of natural disasters, including earthquakes, hurricanes, and floods, with exposure analysis addressing the total value and distribution of assets at risk. Flood risk modeling specifically narrows this scope, emphasizing hydrological data and floodplain mapping to accurately assess the exposure of properties within vulnerable zones. Explore the detailed methodologies and data integration techniques to better understand exposure in both catastrophe and flood risk assessments.
Event Frequency
Catastrophe risk modeling often involves analyzing a wide range of perils including hurricanes, earthquakes, and floods, where event frequency considers the likelihood of multiple disaster types impacting a region within a given timeframe. Flood risk modeling specifically quantifies event frequency by examining historical hydrological data, precipitation patterns, and river flow rates to predict flood occurrences and their potential severity. Explore in-depth methodologies and predictive analytics used in flood and catastrophe risk modeling to enhance risk assessment accuracy and disaster preparedness.
Source and External Links
KatRisk: Catastrophe Risk Modeling - Catastrophe risk models transform theoretical disaster scenarios into actionable metrics like Exceedance Probability curves and Annual Average Loss, empowering insurers and financial institutions to better understand and plan for extreme weather and disasters.
Insurance Topics | Catastrophe Models (Property) - Catastrophe models consist of four key components: hazard (event catalog and frequency), vulnerability (damage functions), exposure (insurance portfolio data), and financial modules that calculate expected losses under various scenarios.
About Catastrophe Modeling | AIR Worldwide - Catastrophe models use scientific data and simulation techniques to estimate the frequency, intensity, and financial impact of natural and man-made disasters to help organizations prepare and manage catastrophe risks worldwide.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com