On-demand insurance offers flexible, pay-as-you-go coverage ideal for short-term or specific needs, contrasting with captive insurance, which is a self-owned risk management solution allowing businesses to tailor policies to their unique risks. Businesses leveraging captive insurance gain greater control over claims, underwriting, and risk exposure, often resulting in cost efficiencies and customized risk strategies. Explore our in-depth analysis to determine which insurance model aligns best with your financial goals and risk management approach.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between on-demand insurance and captive insurance is crucial for optimizing risk management and cost efficiency. On-demand insurance offers flexible, pay-as-you-go coverage ideal for sporadic or short-term needs, while captive insurance involves creating a private insurance company to manage long-term risk and potentially reduce premiums. Choosing the appropriate type can impact a business's financial stability and insurance claims process. Informed decisions based on these differences help businesses tailor coverage to their specific risk profiles and operational strategies.
Comparison Table
| Feature | On-Demand Insurance | Captive Insurance |
|---|---|---|
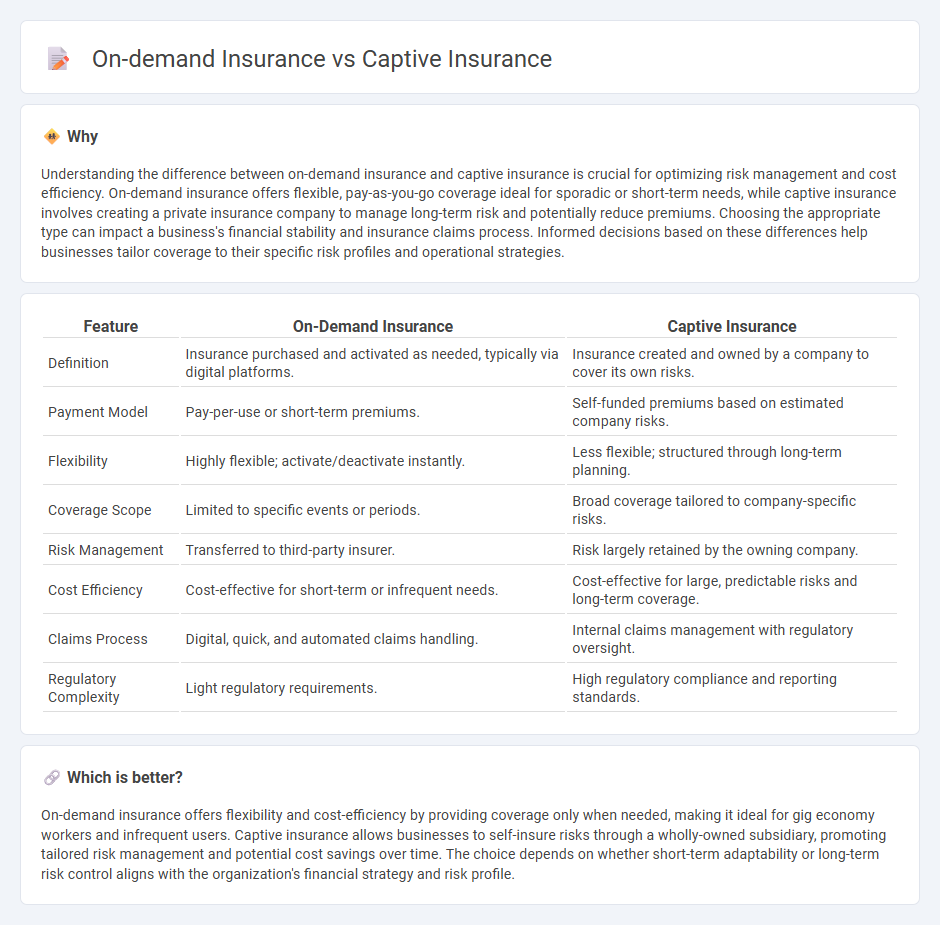
| Definition | Insurance purchased and activated as needed, typically via digital platforms. | Insurance created and owned by a company to cover its own risks. |
| Payment Model | Pay-per-use or short-term premiums. | Self-funded premiums based on estimated company risks. |
| Flexibility | Highly flexible; activate/deactivate instantly. | Less flexible; structured through long-term planning. |
| Coverage Scope | Limited to specific events or periods. | Broad coverage tailored to company-specific risks. |
| Risk Management | Transferred to third-party insurer. | Risk largely retained by the owning company. |
| Cost Efficiency | Cost-effective for short-term or infrequent needs. | Cost-effective for large, predictable risks and long-term coverage. |
| Claims Process | Digital, quick, and automated claims handling. | Internal claims management with regulatory oversight. |
| Regulatory Complexity | Light regulatory requirements. | High regulatory compliance and reporting standards. |
Which is better?
On-demand insurance offers flexibility and cost-efficiency by providing coverage only when needed, making it ideal for gig economy workers and infrequent users. Captive insurance allows businesses to self-insure risks through a wholly-owned subsidiary, promoting tailored risk management and potential cost savings over time. The choice depends on whether short-term adaptability or long-term risk control aligns with the organization's financial strategy and risk profile.
Connection
On-demand insurance and captive insurance are connected through their focus on customized risk management solutions tailored to specific needs. On-demand insurance offers flexible, usage-based coverage ideal for dynamic exposure scenarios, while captive insurance enables companies to self-insure and control risks internally. Both models enhance cost efficiency and risk control by leveraging innovation and tailored policy structures.
Key Terms
Risk Retention
Captive insurance allows companies to retain risk internally by creating a wholly owned insurance subsidiary, providing customized coverage and potential cost savings. On-demand insurance offers flexible, pay-as-you-go policies for specific risks, transferring risk externally with minimal upfront commitment. Explore how risk retention strategies vary between these models to optimize your asset protection.
Flexibility
Captive insurance allows companies to tailor policies precisely to their risk profiles, offering extensive flexibility in coverage and claims management. On-demand insurance provides quick, short-term protection that adapitates instantly to the insured's needs, ideal for fluctuating risks and usage patterns. Explore how these flexible solutions can transform your risk management strategy.
Ownership
Captive insurance involves a company owning an insurance subsidiary to manage its own risks internally, providing greater control and customization over policies and claims. On-demand insurance is typically owned by third-party providers offering flexible, pay-as-you-go coverage for specific needs without long-term commitments. Explore the distinctions in ownership models to determine which insurance type aligns best with your risk management strategy.
Source and External Links
Captive insurance - Wikipedia - Captive insurance is an alternative to self-insurance where insured parties form a licensed insurance company for their own use, offering tailored risk coverage, pricing near cost, tax benefits, and more control over insurance management.
What Is Captive Insurance? - A captive insurer is wholly owned by its insureds and provides stable, tailored coverage often unavailable or expensive in the commercial market, with owners assuming their own risk and controlling their insurer to achieve broader coverage and pricing stability.
Captive Insurance Companies - NAIC - Captives are self-insurance subsidiaries owned by the insured, designed for unique risk needs and tax benefits, widely used by major corporations and regulated like commercial insurers; over 7,000 captives exist globally across many domiciles including Bermuda and Vermont.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com