Silent cyber coverage addresses cyber risks that are unintentionally included or excluded within traditional insurance policies, often leading to ambiguity in claims involving cyber incidents. Affirmative cyber coverage explicitly defines and insures cyber-related exposures, offering clear protection against data breaches, ransomware attacks, and business interruptions caused by cyber threats. Explore the differences and benefits of each coverage type to strengthen your organization's cyber risk management strategy.
Why it is important
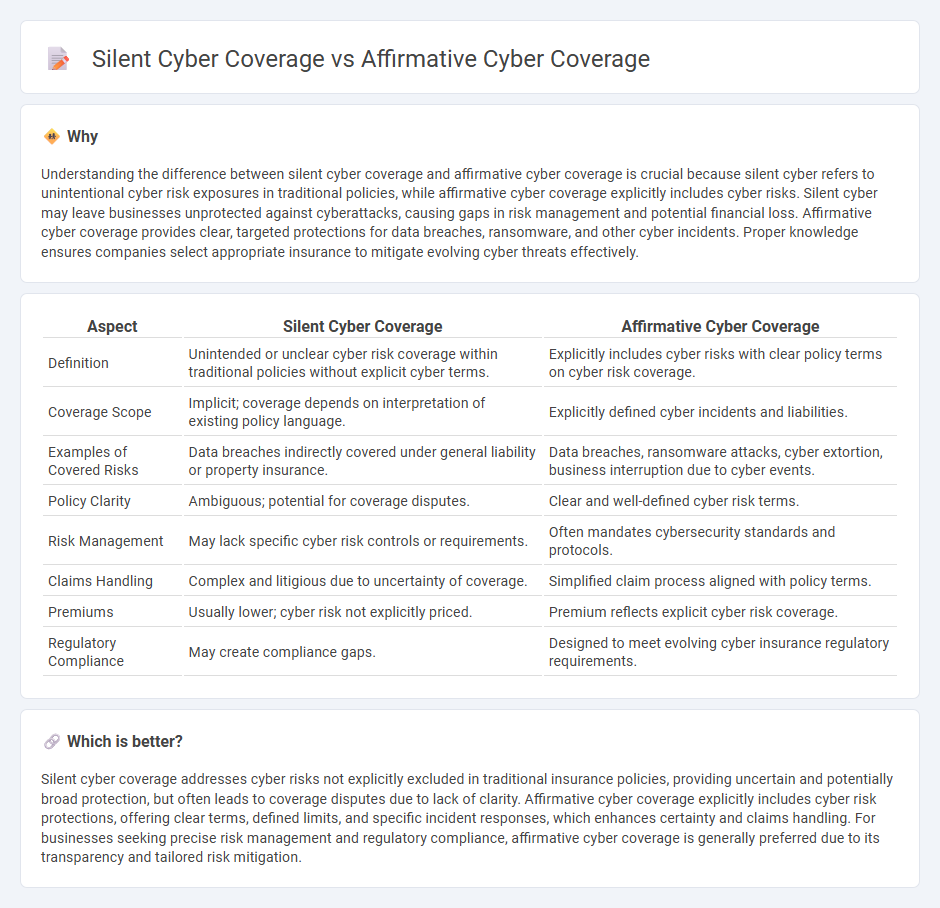
Understanding the difference between silent cyber coverage and affirmative cyber coverage is crucial because silent cyber refers to unintentional cyber risk exposures in traditional policies, while affirmative cyber coverage explicitly includes cyber risks. Silent cyber may leave businesses unprotected against cyberattacks, causing gaps in risk management and potential financial loss. Affirmative cyber coverage provides clear, targeted protections for data breaches, ransomware, and other cyber incidents. Proper knowledge ensures companies select appropriate insurance to mitigate evolving cyber threats effectively.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Silent Cyber Coverage | Affirmative Cyber Coverage |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Unintended or unclear cyber risk coverage within traditional policies without explicit cyber terms. | Explicitly includes cyber risks with clear policy terms on cyber risk coverage. |
| Coverage Scope | Implicit; coverage depends on interpretation of existing policy language. | Explicitly defined cyber incidents and liabilities. |
| Examples of Covered Risks | Data breaches indirectly covered under general liability or property insurance. | Data breaches, ransomware attacks, cyber extortion, business interruption due to cyber events. |
| Policy Clarity | Ambiguous; potential for coverage disputes. | Clear and well-defined cyber risk terms. |
| Risk Management | May lack specific cyber risk controls or requirements. | Often mandates cybersecurity standards and protocols. |
| Claims Handling | Complex and litigious due to uncertainty of coverage. | Simplified claim process aligned with policy terms. |
| Premiums | Usually lower; cyber risk not explicitly priced. | Premium reflects explicit cyber risk coverage. |
| Regulatory Compliance | May create compliance gaps. | Designed to meet evolving cyber insurance regulatory requirements. |
Which is better?
Silent cyber coverage addresses cyber risks not explicitly excluded in traditional insurance policies, providing uncertain and potentially broad protection, but often leads to coverage disputes due to lack of clarity. Affirmative cyber coverage explicitly includes cyber risk protections, offering clear terms, defined limits, and specific incident responses, which enhances certainty and claims handling. For businesses seeking precise risk management and regulatory compliance, affirmative cyber coverage is generally preferred due to its transparency and tailored risk mitigation.
Connection
Silent cyber coverage and affirmative cyber coverage intersect in the landscape of cyber insurance by addressing different aspects of cyber risk exposure in insurance policies. Silent cyber coverage pertains to unintentional cyber risk embedded within traditional insurance products, often without explicit mention, while affirmative cyber coverage involves explicit policy terms targeting cyber-related incidents. Both approaches aim to manage the financial impact of cyberattacks but differ in clarity of coverage scope and policyholder awareness, influencing risk assessment and underwriting strategies in insurance markets.
Key Terms
Explicit Clause
Affirmative cyber coverage explicitly includes cyber risks through a clearly defined clause in insurance policies, ensuring coverage for cyberattacks and data breaches. Silent cyber coverage arises when traditional policies unintentionally provide protection against cyber incidents without explicitly mentioning cyber risks, leading to ambiguity and potential disputes. Explore detailed distinctions between affirmative and silent cyber coverage clauses to fully understand their implications.
Policy Exclusion
Affirmative cyber coverage explicitly includes cyber risks within an insurance policy, ensuring clear protection against cyber incidents. Silent cyber coverage refers to unintentional exposure to cyber risks in traditional policies without explicit inclusion or exclusion, often leading to ambiguity during claims. Explore the differences in policy exclusions to better understand coverage gaps and enhance risk management strategies.
Triggering Event
Affirmative cyber coverage explicitly defines triggering events related to cyber incidents, clearly outlining when the insurer's liability begins, typically covering data breaches, ransomware, and network interruptions. Silent cyber coverage arises unintentionally within traditional policies not designed for cyber risks, often leading to ambiguous triggering events and coverage gaps during cyber-related losses. Explore more to understand how insurers manage these distinct cyber coverage triggers and mitigate potential risks.
Source and External Links
Affirmative Cyber | AIG US - Affirmative cyber coverage is insurance policy language that explicitly covers or excludes cyber-related losses, helping organizations understand how their policies respond to cyber events and integrate insurance into their cyber risk management plans to address evolving cyber threats.
Coalition Adds Affirmative AI Endorsement to Cyber Policies - Affirmative cyber coverage can also include endorsements like Coalition's Affirmative AI Endorsement, which clarifies cyber insurance coverage related to AI-driven security failures and fraudulent activities, enhancing clarity and protection against emerging digital risks.
Understanding your business's silent cyber risk cover | MMA - Affirmative cyber coverage refers to explicit cyber risk insurance typically provided by standalone policies or endorsements, distinguishing it from non-affirmative or "silent cyber," where traditional insurance policies may implicitly cover cyber-related losses without explicit reference.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com