Liquidity staking allows investors to earn rewards by locking their cryptocurrency assets while maintaining access to liquidity through tokenized representations. Treasury bills, issued by governments, are short-term debt instruments offering fixed returns with high safety and liquidity. Explore further to understand which financial instrument aligns best with your investment strategy.
Why it is important
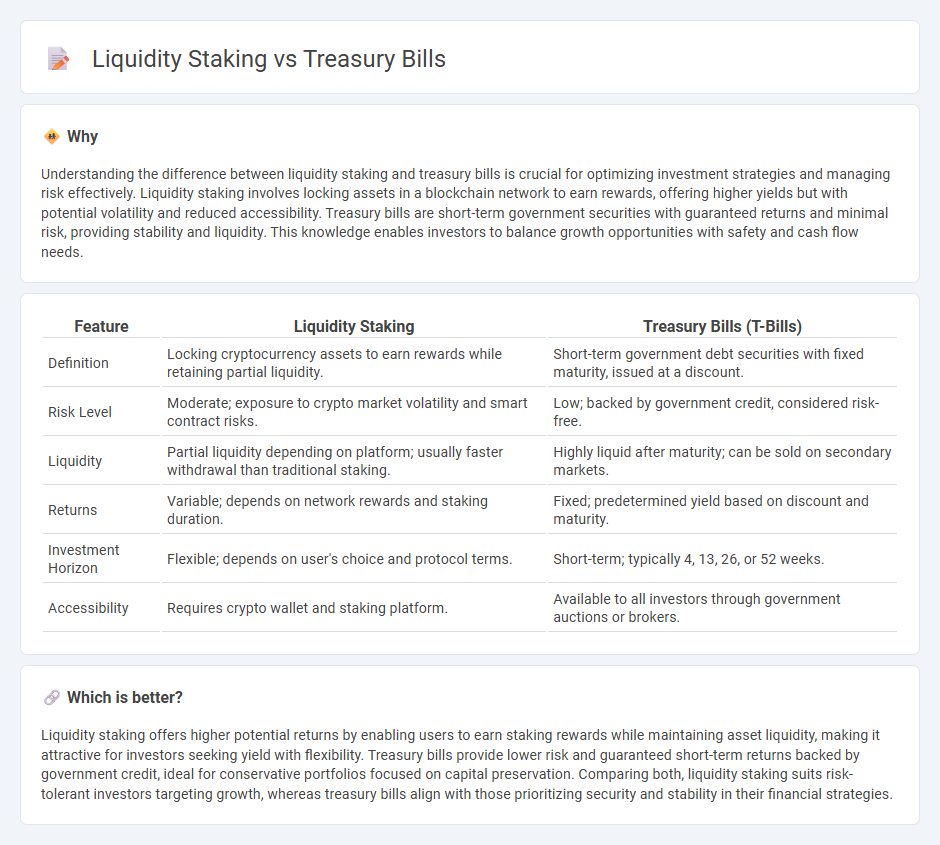
Understanding the difference between liquidity staking and treasury bills is crucial for optimizing investment strategies and managing risk effectively. Liquidity staking involves locking assets in a blockchain network to earn rewards, offering higher yields but with potential volatility and reduced accessibility. Treasury bills are short-term government securities with guaranteed returns and minimal risk, providing stability and liquidity. This knowledge enables investors to balance growth opportunities with safety and cash flow needs.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Liquidity Staking | Treasury Bills (T-Bills) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Locking cryptocurrency assets to earn rewards while retaining partial liquidity. | Short-term government debt securities with fixed maturity, issued at a discount. |
| Risk Level | Moderate; exposure to crypto market volatility and smart contract risks. | Low; backed by government credit, considered risk-free. |
| Liquidity | Partial liquidity depending on platform; usually faster withdrawal than traditional staking. | Highly liquid after maturity; can be sold on secondary markets. |
| Returns | Variable; depends on network rewards and staking duration. | Fixed; predetermined yield based on discount and maturity. |
| Investment Horizon | Flexible; depends on user's choice and protocol terms. | Short-term; typically 4, 13, 26, or 52 weeks. |
| Accessibility | Requires crypto wallet and staking platform. | Available to all investors through government auctions or brokers. |
Which is better?
Liquidity staking offers higher potential returns by enabling users to earn staking rewards while maintaining asset liquidity, making it attractive for investors seeking yield with flexibility. Treasury bills provide lower risk and guaranteed short-term returns backed by government credit, ideal for conservative portfolios focused on capital preservation. Comparing both, liquidity staking suits risk-tolerant investors targeting growth, whereas treasury bills align with those prioritizing security and stability in their financial strategies.
Connection
Liquidity staking enhances capital efficiency by allowing investors to earn staking rewards while retaining liquidity through tokenized assets, which can be used to purchase safe instruments like treasury bills. Treasury bills, short-term government securities with low risk and high liquidity, provide a secure investment avenue for funds generated or unlocked via liquidity staking. This synergy supports portfolio diversification, balancing yield generation from staking with the stability and predictability of treasury bill returns.
Key Terms
Maturity
Treasury bills typically have fixed short-term maturities ranging from a few days up to one year, offering predictable returns upon maturity. Liquidity staking, however, often involves flexible or indefinite lock-up periods depending on the platform, affecting the timing of asset accessibility. Explore the nuances of maturity structures to determine which option aligns best with your investment strategy.
Yield
Treasury bills offer a fixed, low-risk yield backed by government securities, typically ranging from 1% to 5% annually depending on market conditions. Liquidity staking provides potentially higher yields, often between 8% and 20%, by locking tokens in decentralized finance protocols to facilitate transactions and earn rewards. Explore more about yield optimization strategies by comparing risk profiles and return potentials of both investment options.
Risk
Treasury bills (T-bills) are short-term government securities with minimal risk due to their backing by the government, offering predictable returns and high liquidity. Liquidity staking involves locking cryptocurrency assets to earn rewards but carries higher risks related to price volatility, potential slashing penalties, and smart contract vulnerabilities. Explore the risk profiles of these investment options further to choose the best strategy for your financial goals.
Source and External Links
Treasury Bills | FRED | St. Louis Fed - Treasury bills data include interest rates on US Treasury bills in various maturities with historical daily, weekly, monthly, and annual rates available from 1958 onwards.
Interest Rate Statistics | U.S. Department of the Treasury - Provides daily Treasury Bill rates reflecting market bid quotations on recently auctioned Treasury bills updated each business day.
Treasury Notes -- TreasuryDirect - Describes Treasury Notes which pay fixed interest every six months with maturities from 2 to 10 years; different from Treasury Bills which are short-term discount securities.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com