Tokenization transforms traditional financial assets into digital tokens on a blockchain, enhancing liquidity and accessibility by enabling fractional ownership and seamless transfers. Bearer bonds are physical certificates that grant ownership to whoever holds them, lacking digital traceability and posing higher risks of loss or theft. Explore how tokenization is revolutionizing asset management and compares to conventional bearer bonds.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between tokenization and bearer bonds is crucial in finance as tokenization digitizes asset ownership, enabling seamless, transparent, and secure trading on blockchain platforms, while bearer bonds represent physical certificates that grant ownership to the holder without registration. Tokenization increases liquidity, reduces settlement times, and minimizes counterparty risk compared to traditional bearer bonds, which carry risks such as loss, theft, and lack of traceability. Knowing these distinctions helps investors and financial institutions adopt modern digital asset management practices while mitigating legal and operational risks associated with bearer instruments. This knowledge is vital for leveraging blockchain technology to enhance financial market efficiency and compliance.
Comparison Table
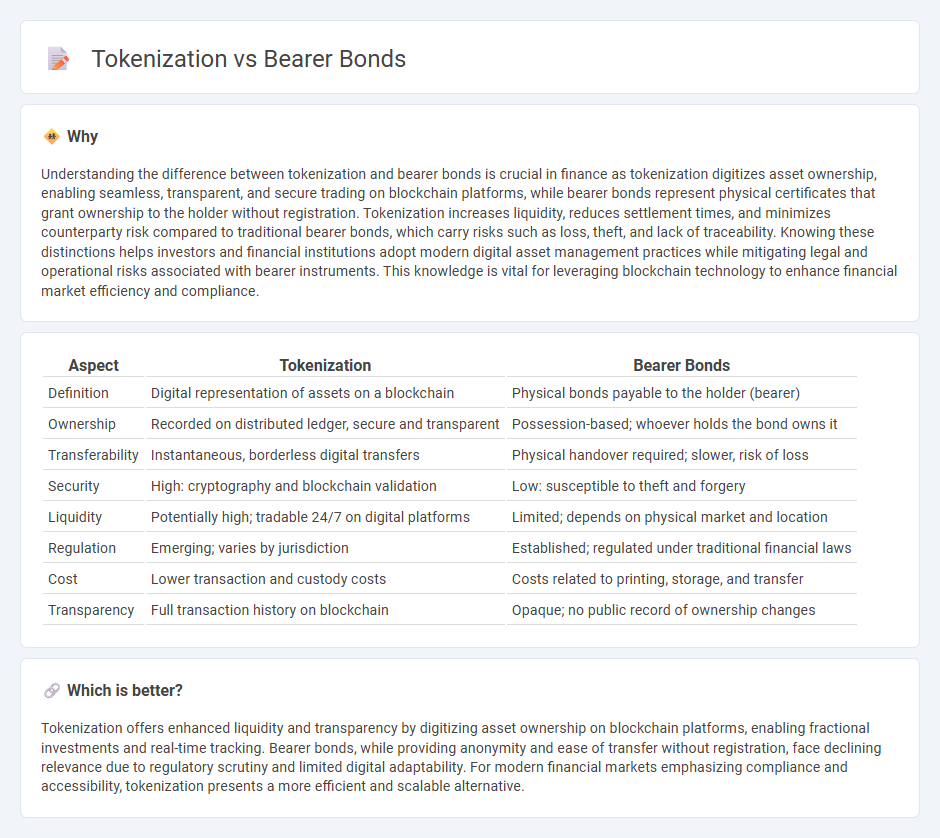
| Aspect | Tokenization | Bearer Bonds |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Digital representation of assets on a blockchain | Physical bonds payable to the holder (bearer) |
| Ownership | Recorded on distributed ledger, secure and transparent | Possession-based; whoever holds the bond owns it |
| Transferability | Instantaneous, borderless digital transfers | Physical handover required; slower, risk of loss |
| Security | High: cryptography and blockchain validation | Low: susceptible to theft and forgery |
| Liquidity | Potentially high; tradable 24/7 on digital platforms | Limited; depends on physical market and location |
| Regulation | Emerging; varies by jurisdiction | Established; regulated under traditional financial laws |
| Cost | Lower transaction and custody costs | Costs related to printing, storage, and transfer |
| Transparency | Full transaction history on blockchain | Opaque; no public record of ownership changes |
Which is better?
Tokenization offers enhanced liquidity and transparency by digitizing asset ownership on blockchain platforms, enabling fractional investments and real-time tracking. Bearer bonds, while providing anonymity and ease of transfer without registration, face declining relevance due to regulatory scrutiny and limited digital adaptability. For modern financial markets emphasizing compliance and accessibility, tokenization presents a more efficient and scalable alternative.
Connection
Tokenization transforms financial assets into digital tokens on a blockchain, enhancing liquidity and transferability similarly to bearer bonds, which represent ownership to the holder without registered ownership. Both enable easy and secure transfer of assets without intermediaries, but tokenization offers improved transparency, traceability, and fractional ownership. The synergy between tokenization and bearer bonds modernizes asset management by combining the benefits of digital technology with traditional bearer instruments.
Key Terms
Anonymity
Bearer bonds provide complete anonymity as ownership is transferred by physical possession without registration, making transactions untraceable and ideal for privacy-focused investors. Tokenization replaces physical certificates with digital tokens on a blockchain, offering enhanced security and transparency but typically requiring identity verification, thus reducing anonymity. Explore further to understand how these financial instruments balance privacy and compliance in modern markets.
Ownership Transfer
Bearer bonds allow direct and anonymous ownership transfer by physical delivery, enabling quick, unregistered transactions without intermediaries. Tokenization digitizes ownership into blockchain-based tokens, enhancing security, transparency, and traceability while facilitating seamless and programmable transfers. Explore how each method transforms ownership transfer in modern finance.
Digital Ledger
Bearer bonds represent physical certificates granting ownership to the holder, lacking recorded ownership data, while tokenization converts these assets into digital tokens on a Digital Ledger Technology (DLT) platform, enhancing transparency, security, and transferability. Digital Ledger offers immutable records and decentralized verification, significantly reducing risks of fraud and improving liquidity in asset management. Explore how Digital Ledger revolutionizes asset tokenization and transforms traditional bearer bonds for modern finance.
Source and External Links
Bearer Bonds Explained: Unraveling The Complexities - Cbonds - Bearer bonds are fixed-income securities owned by whoever physically holds them, featuring attached coupons for interest payments that must be presented to a bank or financial institution to collect, and their use has declined sharply due to risks of theft and illicit activities.
What Are Bearer Bonds? Explanation & How to Redeem - Annuity.org - Bearer bonds are rare debt instruments where ownership and the right to cash flows belong solely to the physical holder of the bond certificate, with no central record of ownership, making them nearly obsolete in modern financial markets due to concerns over fraud and criminal misuse.
Bearer bond - Wikipedia - Bearer bonds are debt securities issued by governments or corporations to the bearer (holder), but U.S. tax law changes in 1982 effectively ended new issues by removing tax benefits, and a 1988 Supreme Court case upheld these restrictions, marking the virtual end of U.S. municipal bearer bonds.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com