Yield farming generates passive income by staking or lending cryptocurrencies to earn rewards, leveraging DeFi protocols for optimized returns. Borrowing in finance involves obtaining funds with the obligation to repay, often used for leveraging investments or managing liquidity needs. Explore the differences and benefits of yield farming versus borrowing to maximize your financial strategy.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between yield farming and borrowing is crucial in finance because yield farming involves earning interest through liquidity provision while borrowing entails taking loans with interest obligations, affecting risk and return profiles. Yield farming can generate passive income by leveraging decentralized finance (DeFi) protocols, whereas borrowing increases leverage and potential debt exposure. Misunderstanding these concepts can lead to financial losses or missed opportunities in managing assets effectively. Accurate knowledge aids in optimizing investment strategies and managing financial risk appropriately.
Comparison Table
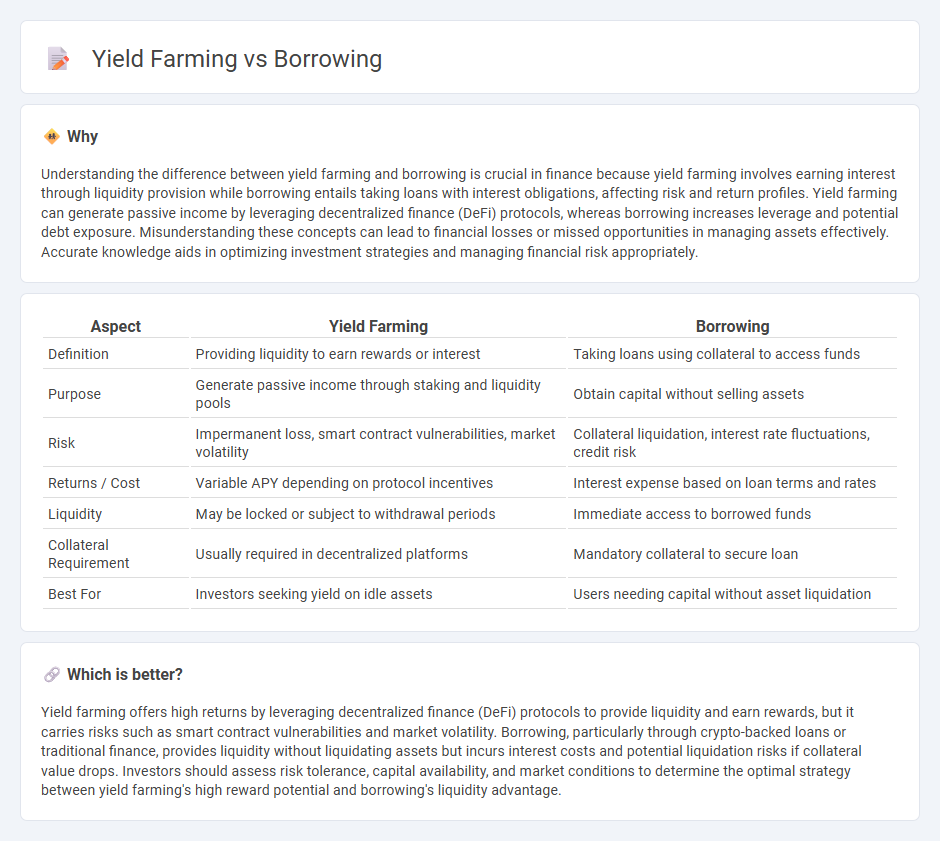
| Aspect | Yield Farming | Borrowing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Providing liquidity to earn rewards or interest | Taking loans using collateral to access funds |
| Purpose | Generate passive income through staking and liquidity pools | Obtain capital without selling assets |
| Risk | Impermanent loss, smart contract vulnerabilities, market volatility | Collateral liquidation, interest rate fluctuations, credit risk |
| Returns / Cost | Variable APY depending on protocol incentives | Interest expense based on loan terms and rates |
| Liquidity | May be locked or subject to withdrawal periods | Immediate access to borrowed funds |
| Collateral Requirement | Usually required in decentralized platforms | Mandatory collateral to secure loan |
| Best For | Investors seeking yield on idle assets | Users needing capital without asset liquidation |
Which is better?
Yield farming offers high returns by leveraging decentralized finance (DeFi) protocols to provide liquidity and earn rewards, but it carries risks such as smart contract vulnerabilities and market volatility. Borrowing, particularly through crypto-backed loans or traditional finance, provides liquidity without liquidating assets but incurs interest costs and potential liquidation risks if collateral value drops. Investors should assess risk tolerance, capital availability, and market conditions to determine the optimal strategy between yield farming's high reward potential and borrowing's liquidity advantage.
Connection
Yield farming and borrowing are interconnected through decentralized finance (DeFi) protocols, where users often borrow assets to maximize yield opportunities by leveraging capital. Borrowing enables farmers to increase liquidity, thereby enhancing returns through compounded interest and rewards from liquidity pools. The synergy between borrowing and yield farming drives higher capital efficiency and risk diversification in crypto asset management.
Key Terms
Interest Rate
Borrowing in decentralized finance (DeFi) involves taking out loans at fixed or variable interest rates, which are influenced by market demand and collateralization levels. Yield farming focuses on earning returns by staking or lending assets, often providing higher but more volatile interest rates due to incentive tokens and liquidity pool rewards. Explore the dynamics of interest rates in both strategies to optimize your DeFi investment decisions.
Collateral
Borrowing involves using collateral assets to secure a loan, allowing users to leverage their holdings without selling them, whereas yield farming typically requires locking collateral into liquidity pools to earn rewards through interest or token incentives. In borrowing, the choice and valuation of collateral directly impact loan-to-value ratios and liquidation risks, while yield farming collateral focuses on maximizing reward yield and minimizing impermanent loss. Explore deeper insights into how collateral strategies differ in borrowing and yield farming to optimize your DeFi investment approach.
Liquidity
Borrowing in decentralized finance (DeFi) involves obtaining assets by locking collateral, enhancing liquidity without selling holdings, while yield farming maximizes returns by providing liquidity to protocols in exchange for rewards or interest. Liquidity in borrowing maintains asset availability for trading and leveraging, whereas yield farming actively contributes to protocol liquidity pools, boosting transaction efficiency and network stability. Explore deeper insights into how borrowing and yield farming strategies impact overall DeFi liquidity dynamics.
Source and External Links
Understanding the Basics of Borrowing - Borrowing money involves obtaining funds from a lender with an agreement to repay later, often with interest and fees, and can be used to achieve financial goals such as buying a home, investing, or managing cash flow, but requires careful risk assessment and repayment planning.
Borrowing money - Borrowing can help you reach goals like buying a home or paying for education by assessing credit, financial situation, and making informed decisions about repayment and debt management.
BORROWING | definition in the Cambridge English Dictionary - Borrowing refers to taking money temporarily, especially from banks or other institutions, often involving costs that have increased recently, and is a common financial activity used to cover deficits or finance expenditures.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com