Zero day options offer traders the ability to capitalize on price movements within the final trading day before expiration, providing high leverage and rapid returns. Volatility index options, such as those on the VIX, allow investors to hedge or speculate on market volatility independent of directional price movement. Explore the strategic uses and risk profiles of these distinct financial instruments to enhance your trading approach.
Why it is important
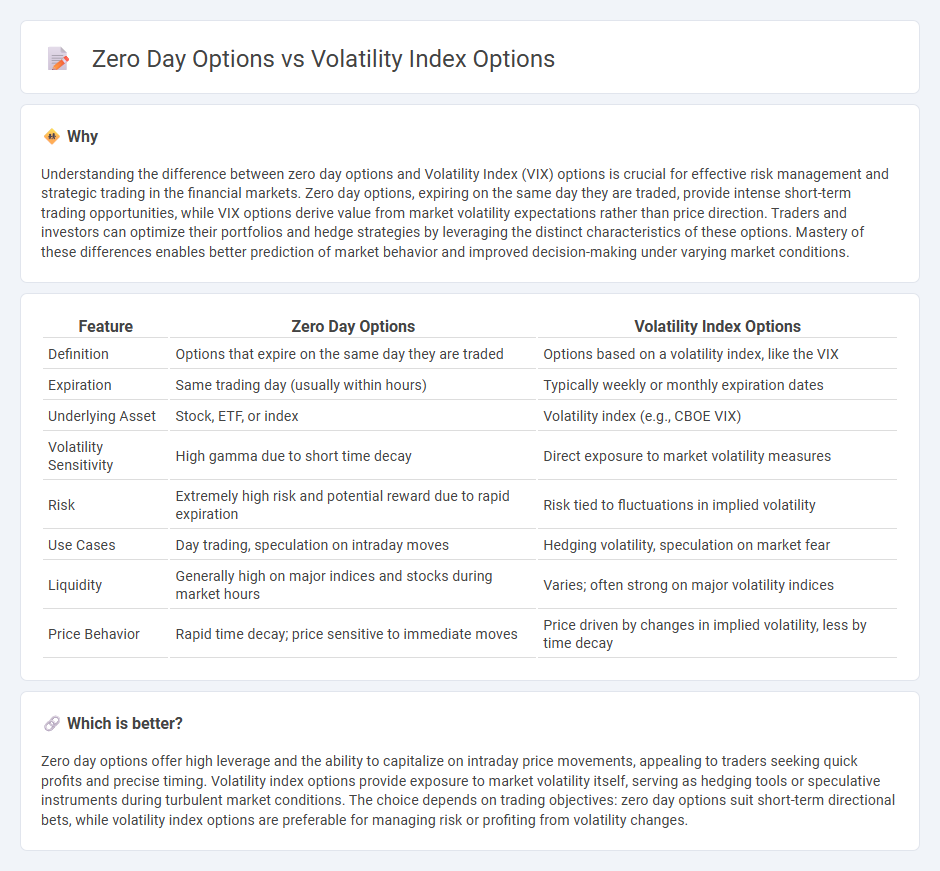
Understanding the difference between zero day options and Volatility Index (VIX) options is crucial for effective risk management and strategic trading in the financial markets. Zero day options, expiring on the same day they are traded, provide intense short-term trading opportunities, while VIX options derive value from market volatility expectations rather than price direction. Traders and investors can optimize their portfolios and hedge strategies by leveraging the distinct characteristics of these options. Mastery of these differences enables better prediction of market behavior and improved decision-making under varying market conditions.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Zero Day Options | Volatility Index Options |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Options that expire on the same day they are traded | Options based on a volatility index, like the VIX |
| Expiration | Same trading day (usually within hours) | Typically weekly or monthly expiration dates |
| Underlying Asset | Stock, ETF, or index | Volatility index (e.g., CBOE VIX) |
| Volatility Sensitivity | High gamma due to short time decay | Direct exposure to market volatility measures |
| Risk | Extremely high risk and potential reward due to rapid expiration | Risk tied to fluctuations in implied volatility |
| Use Cases | Day trading, speculation on intraday moves | Hedging volatility, speculation on market fear |
| Liquidity | Generally high on major indices and stocks during market hours | Varies; often strong on major volatility indices |
| Price Behavior | Rapid time decay; price sensitive to immediate moves | Price driven by changes in implied volatility, less by time decay |
Which is better?
Zero day options offer high leverage and the ability to capitalize on intraday price movements, appealing to traders seeking quick profits and precise timing. Volatility index options provide exposure to market volatility itself, serving as hedging tools or speculative instruments during turbulent market conditions. The choice depends on trading objectives: zero day options suit short-term directional bets, while volatility index options are preferable for managing risk or profiting from volatility changes.
Connection
Zero day options and Volatility Index (VIX) options are interconnected through their focus on short-term market volatility and risk pricing. Zero day options, expiring within the same trading day, offer traders the opportunity to speculate on immediate price fluctuations, while VIX options provide hedging and speculative tools based on expected market volatility over a slightly longer timeframe. Both instruments serve as critical tools for managing uncertainty and capturing rapid shifts in investor sentiment within financial markets.
Key Terms
Implied Volatility
Volatility index options primarily reflect the market's expectation of future volatility through implied volatility metrics, offering traders the ability to hedge or speculate on volatility changes over days or weeks. Zero day options, expiring on the same day, possess heightened sensitivity to implied volatility shifts, creating unique opportunities for intraday volatility trading and rapid time decay exploitation. Explore detailed strategies and risk profiles to better understand how implied volatility dynamics impact these distinct option types.
Time Decay (Theta)
Volatility index options, such as those on the VIX, experience time decay (Theta) at a rate influenced by underlying market volatility and their expiration timeline, generally exhibiting smoother Theta decay compared to zero day options, which lose value rapidly as expiration approaches. Zero day options have accelerated time decay due to their extremely short lifespan, with Theta often peaking on the day of expiration, making them highly sensitive to time erosion and ideal for traders seeking quick, high-risk rewards. Explore further to understand how time decay dynamics impact your trading strategies in volatility and zero day options.
Hedging
Volatility index options provide traders with a strategic tool to hedge against market fluctuations by capturing implied volatility trends over specified periods, while zero day options offer highly granular protection on the exact day of expiration, ideal for managing extreme short-term market risks. Hedging with volatility index options tends to smooth portfolio volatility through broader market sentiment, whereas zero day options require precise timing and understanding of immediate price movements to effectively mitigate sudden losses. Explore deeper insights into optimizing hedging strategies with volatility and zero day options for tailored risk management.
Source and External Links
Understanding VIX or Volatility Index - TD Bank - The Volatility Index (VIX) reflects the annualized implied volatility of a hypothetical S&P 500 option with 30 days to expiration, calculated from near-term S&P 500 options prices, and is often called the market's "fear gauge" because it rises when market fear increases.
VIX Options Product Specification - Cboe Global Markets - VIX options trade on the Chicago Board Options Exchange and are based on the Cboe Volatility Index, which measures expected 30-day volatility of the S&P 500 using SPX options; these options have standardized strike prices, monthly and weekly expirations, and a $100 multiplier.
VIX - Wikipedia - The VIX is calculated as a weighted average of the prices of out-of-the-money puts and calls on the S&P 500, representing the market's 30-day expected volatility derived from SPX options pricing.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com