Climate-linked derivatives provide financial instruments that hedge risks associated with environmental factors such as carbon prices or weather variations, enabling investors to manage climate-induced uncertainties. Social bonds direct capital towards projects with positive social outcomes, addressing issues like affordable housing or community development while offering investors targeted impact opportunities. Explore the distinct roles and benefits of these innovative financial tools in advancing sustainable finance.
Why it is important
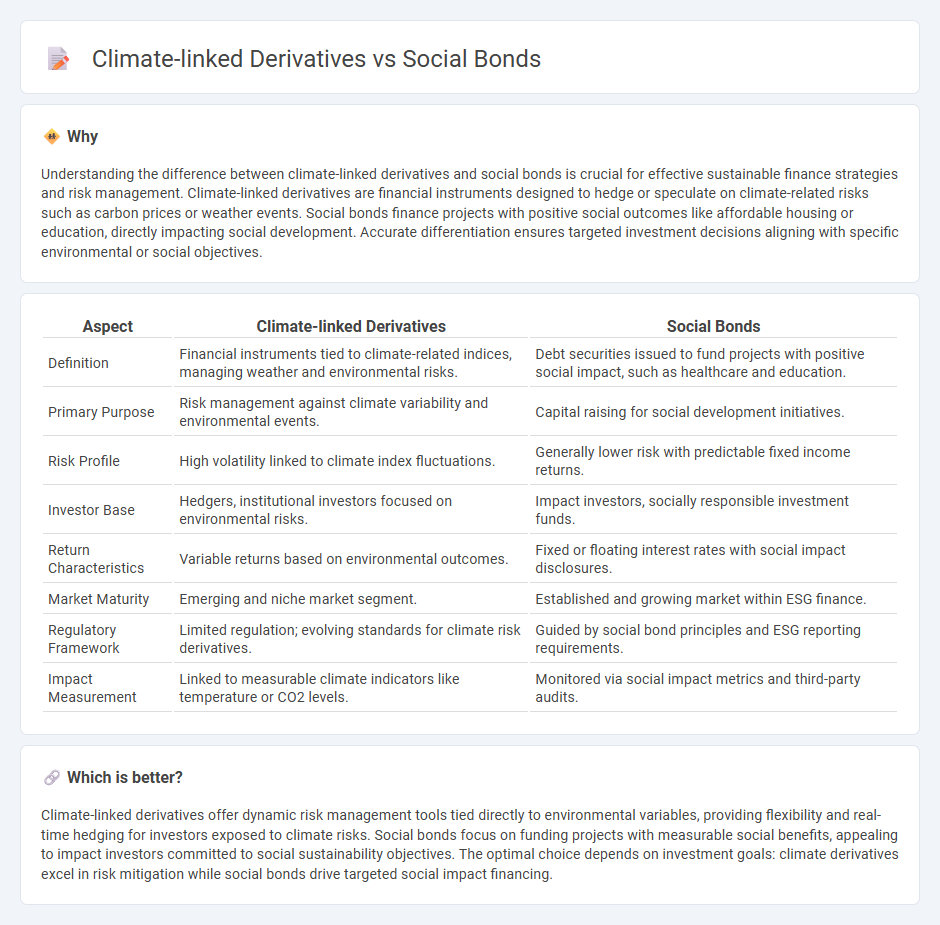
Understanding the difference between climate-linked derivatives and social bonds is crucial for effective sustainable finance strategies and risk management. Climate-linked derivatives are financial instruments designed to hedge or speculate on climate-related risks such as carbon prices or weather events. Social bonds finance projects with positive social outcomes like affordable housing or education, directly impacting social development. Accurate differentiation ensures targeted investment decisions aligning with specific environmental or social objectives.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Climate-linked Derivatives | Social Bonds |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Financial instruments tied to climate-related indices, managing weather and environmental risks. | Debt securities issued to fund projects with positive social impact, such as healthcare and education. |
| Primary Purpose | Risk management against climate variability and environmental events. | Capital raising for social development initiatives. |
| Risk Profile | High volatility linked to climate index fluctuations. | Generally lower risk with predictable fixed income returns. |
| Investor Base | Hedgers, institutional investors focused on environmental risks. | Impact investors, socially responsible investment funds. |
| Return Characteristics | Variable returns based on environmental outcomes. | Fixed or floating interest rates with social impact disclosures. |
| Market Maturity | Emerging and niche market segment. | Established and growing market within ESG finance. |
| Regulatory Framework | Limited regulation; evolving standards for climate risk derivatives. | Guided by social bond principles and ESG reporting requirements. |
| Impact Measurement | Linked to measurable climate indicators like temperature or CO2 levels. | Monitored via social impact metrics and third-party audits. |
Which is better?
Climate-linked derivatives offer dynamic risk management tools tied directly to environmental variables, providing flexibility and real-time hedging for investors exposed to climate risks. Social bonds focus on funding projects with measurable social benefits, appealing to impact investors committed to social sustainability objectives. The optimal choice depends on investment goals: climate derivatives excel in risk mitigation while social bonds drive targeted social impact financing.
Connection
Climate-linked derivatives and social bonds both serve as financial instruments aimed at addressing environmental and social challenges by channeling capital towards sustainable projects. Climate-linked derivatives provide risk management tools linked to climate variables, enabling investors and companies to hedge against climate-related risks, while social bonds raise funds for initiatives that promote social welfare, including climate resilience. The integration of these instruments supports a comprehensive approach to financing sustainable development by aligning risk mitigation with impact-driven investment.
Key Terms
Impact Measurement
Social bonds fund projects targeting positive social outcomes, with impact measurement centered on metrics such as job creation, affordable housing units, and community health improvements. Climate-linked derivatives measure environmental impact by quantifying carbon emission reductions, renewable energy production, and climate risk mitigation effectiveness. Explore deeper insights into these financial instruments and their role in driving measurable social and environmental change.
Use of Proceeds
Social bonds channel funds exclusively towards projects that generate measurable social benefits, such as affordable housing or education, ensuring transparency and accountability in the utilization of proceeds. Climate-linked derivatives, on the other hand, are financial instruments designed to hedge risks related to climate variables, where the use of proceeds is tied to risk management rather than direct project financing. Explore the distinctions further to understand their roles in sustainable finance.
Risk Hedging
Social bonds provide targeted financing for social impact projects, offering investors an opportunity to support community development while potentially mitigating reputational risks. Climate-linked derivatives serve as financial instruments designed to hedge against climate-related risks by allowing stakeholders to transfer or manage exposure to extreme weather events or regulatory changes. Explore how these instruments innovate risk management and investment strategies in the evolving sustainability landscape.
Source and External Links
Building Social Bonds | NIH News in Health - Social bonds are the strong relationships between people--such as family, friends, and colleagues--that promote mental, emotional, and physical well-being and are linked to reduced stress, better heart health, and longer life.
Social Bonds: Definition & Benefits - Nasdaq - Social bonds are fixed-income investment instruments issued to fund projects with direct social benefits, like affordable housing, healthcare, and education, as part of the responsible investing movement (ESG).
Social impact bond - Wikipedia - Social impact bonds are a form of outcomes-based contracting where private investors fund social programs and are repaid by the government only if predefined social outcomes are achieved.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com