Quantamental investing combines quantitative models and fundamental analysis to identify undervalued stocks with strong growth potential by analyzing large datasets and market trends. Macro investing focuses on evaluating global economic indicators, interest rates, and geopolitical events to make strategic asset allocation decisions across markets. Explore the nuances of each approach to enhance your investment strategy.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between quantamental investing and macro investing is crucial for optimizing portfolio strategies and risk management. Quantamental investing combines quantitative data analysis with fundamental research to identify stock opportunities based on specific metrics and financial health. Macro investing focuses on broad economic trends and global market dynamics to predict asset allocation and sector performance. Recognizing these distinctions enables investors to align their investment approach with their financial goals and market conditions effectively.
Comparison Table
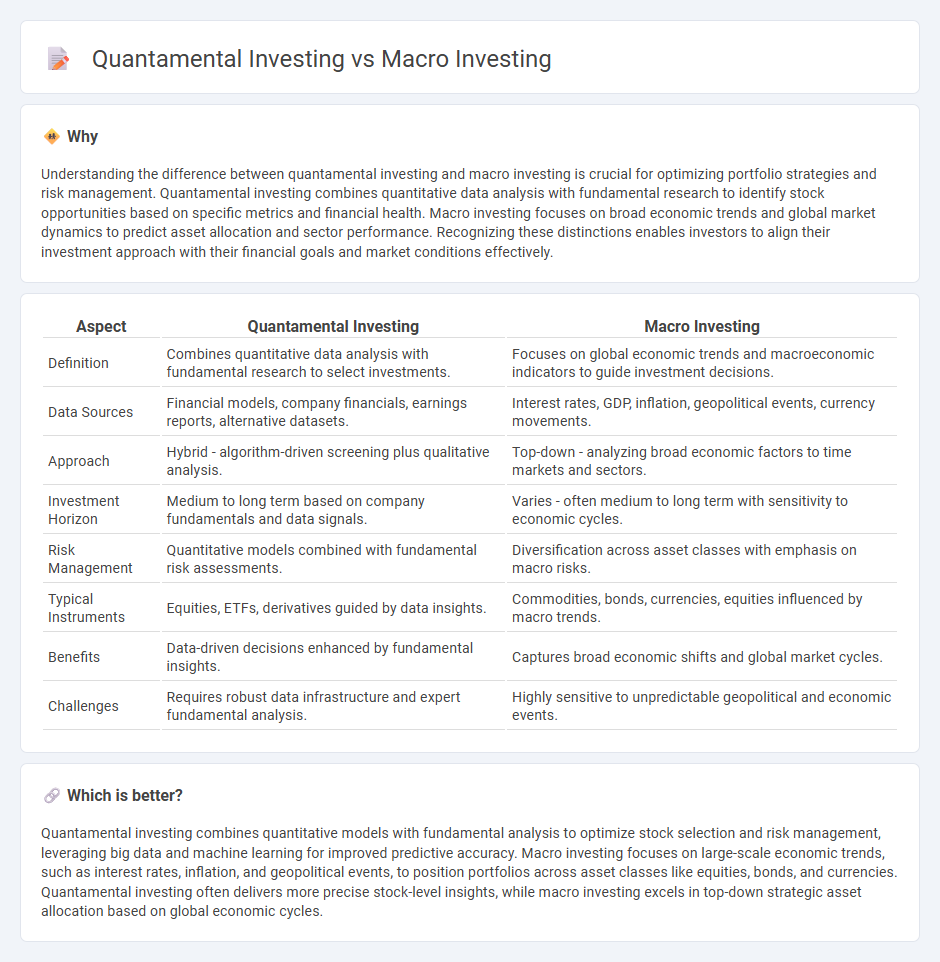
| Aspect | Quantamental Investing | Macro Investing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Combines quantitative data analysis with fundamental research to select investments. | Focuses on global economic trends and macroeconomic indicators to guide investment decisions. |
| Data Sources | Financial models, company financials, earnings reports, alternative datasets. | Interest rates, GDP, inflation, geopolitical events, currency movements. |
| Approach | Hybrid - algorithm-driven screening plus qualitative analysis. | Top-down - analyzing broad economic factors to time markets and sectors. |
| Investment Horizon | Medium to long term based on company fundamentals and data signals. | Varies - often medium to long term with sensitivity to economic cycles. |
| Risk Management | Quantitative models combined with fundamental risk assessments. | Diversification across asset classes with emphasis on macro risks. |
| Typical Instruments | Equities, ETFs, derivatives guided by data insights. | Commodities, bonds, currencies, equities influenced by macro trends. |
| Benefits | Data-driven decisions enhanced by fundamental insights. | Captures broad economic shifts and global market cycles. |
| Challenges | Requires robust data infrastructure and expert fundamental analysis. | Highly sensitive to unpredictable geopolitical and economic events. |
Which is better?
Quantamental investing combines quantitative models with fundamental analysis to optimize stock selection and risk management, leveraging big data and machine learning for improved predictive accuracy. Macro investing focuses on large-scale economic trends, such as interest rates, inflation, and geopolitical events, to position portfolios across asset classes like equities, bonds, and currencies. Quantamental investing often delivers more precise stock-level insights, while macro investing excels in top-down strategic asset allocation based on global economic cycles.
Connection
Quantamental investing integrates quantitative data analysis with fundamental research to identify investment opportunities, while macro investing focuses on broad economic trends and global market movements. Both strategies rely on analyzing financial indicators and economic data to assess market conditions and predict asset performance. Combining quantitative models with macroeconomic insights allows investors to optimize portfolio allocation and manage risk effectively across diverse financial markets.
Key Terms
**Macro Investing:**
Macro investing centers on analyzing global economic trends, such as interest rates, inflation, and geopolitical events, to make strategic investment decisions across various asset classes. Investors use macroeconomic data and models to predict market movements and allocate capital accordingly, emphasizing broad market cycles and risk management. Explore the key principles and strategies to deepen your understanding of macro investing.
Global Macro Trends
Global macro investing centers on analyzing broad economic indicators and geopolitical events to capitalize on macroeconomic trends across various asset classes worldwide. Quantamental investing blends quantitative models with fundamental analysis to identify investment opportunities by harnessing data-driven insights alongside qualitative assessments. Explore deeper distinctions and strategic advantages to optimize your investment approach.
Monetary Policy
Macro investing examines broad economic trends and monetary policy decisions, such as interest rate changes by central banks, to inform asset allocation and market timing strategies. Quantamental investing integrates quantitative models with fundamental analysis, incorporating monetary policy indicators to identify undervalued securities and optimize portfolio performance. Explore how combining monetary policy insights with quantitative and fundamental data can enhance your investment approach.
Source and External Links
Global Macro Strategy - Corporate Finance Institute - Macro investing is an investment strategy that interprets large macroeconomic events on global, regional, and national scales, using factors like interest rates, currency exchange rates, and political events to make investment decisions across currencies, interest rates, and stock indices worldwide.
Macro Investing - The Hedge Fund Journal - Macro investing is a flexible hedge fund strategy that historically performs well during market stress by using a top-down approach to preserve capital and provide portfolio diversification, though it faces challenges such as high volatility and return dispersion.
The Importance of Macro Investing | Western Asset - Macro strategies contribute significantly to portfolio alpha and help reduce volatility during market turmoil by diversifying exposures, particularly through interest rate and credit spread positioning across global portfolios.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com