Robo advisory leverages advanced algorithms and AI to provide personalized investment management with low fees and automated portfolio rebalancing. Passive investing focuses on tracking market indexes, offering broad diversification and cost efficiency by minimizing active decision-making. Explore the differences to determine which strategy aligns best with your financial goals.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between robo advisory and passive investing is crucial for optimizing portfolio management strategies and aligning investment goals with risk tolerance. Robo advisors use algorithm-driven models to offer automated, personalized financial advice and portfolio rebalancing, while passive investing focuses on tracking market indices with minimal trading. Knowing these distinctions helps investors minimize fees, improve diversification, and enhance long-term returns. Choosing the right approach impacts financial planning efficiency and wealth accumulation over time.
Comparison Table
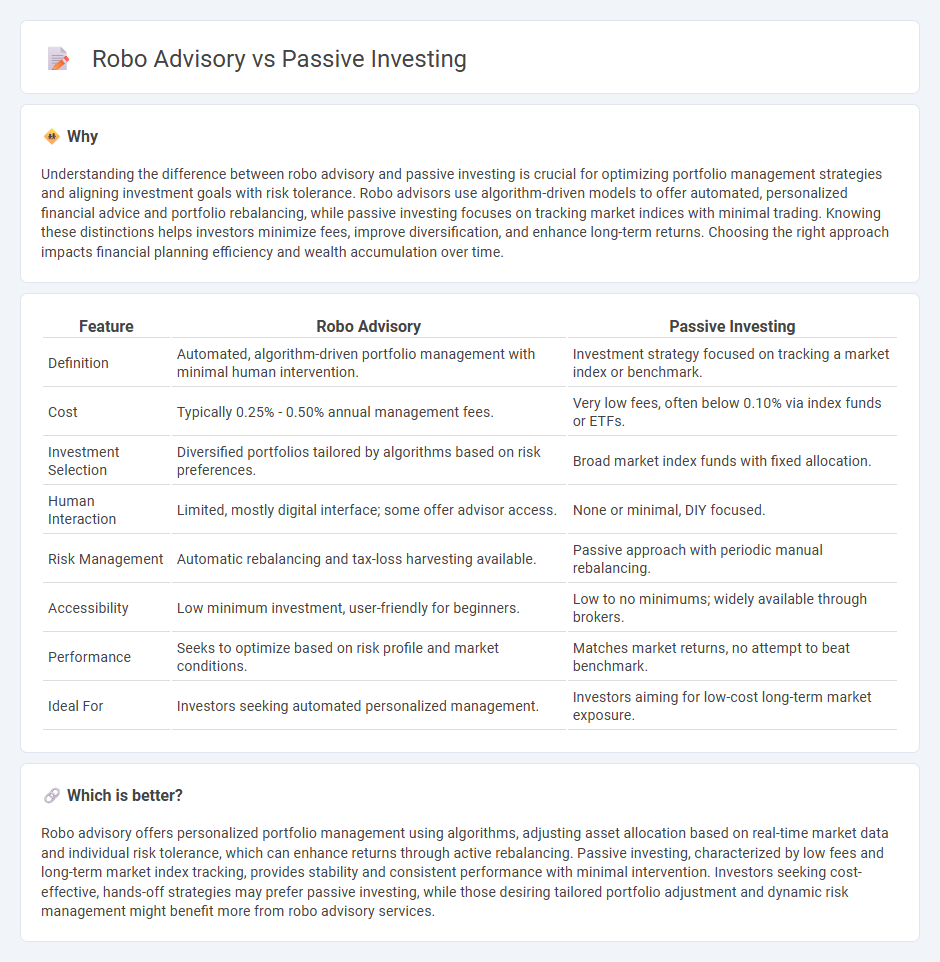
| Feature | Robo Advisory | Passive Investing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Automated, algorithm-driven portfolio management with minimal human intervention. | Investment strategy focused on tracking a market index or benchmark. |
| Cost | Typically 0.25% - 0.50% annual management fees. | Very low fees, often below 0.10% via index funds or ETFs. |
| Investment Selection | Diversified portfolios tailored by algorithms based on risk preferences. | Broad market index funds with fixed allocation. |
| Human Interaction | Limited, mostly digital interface; some offer advisor access. | None or minimal, DIY focused. |
| Risk Management | Automatic rebalancing and tax-loss harvesting available. | Passive approach with periodic manual rebalancing. |
| Accessibility | Low minimum investment, user-friendly for beginners. | Low to no minimums; widely available through brokers. |
| Performance | Seeks to optimize based on risk profile and market conditions. | Matches market returns, no attempt to beat benchmark. |
| Ideal For | Investors seeking automated personalized management. | Investors aiming for low-cost long-term market exposure. |
Which is better?
Robo advisory offers personalized portfolio management using algorithms, adjusting asset allocation based on real-time market data and individual risk tolerance, which can enhance returns through active rebalancing. Passive investing, characterized by low fees and long-term market index tracking, provides stability and consistent performance with minimal intervention. Investors seeking cost-effective, hands-off strategies may prefer passive investing, while those desiring tailored portfolio adjustment and dynamic risk management might benefit more from robo advisory services.
Connection
Robo advisory platforms utilize algorithm-driven technology to create and manage passive investment portfolios, optimizing asset allocation based on individual risk tolerance and financial goals. Passive investing typically involves low-cost index funds or ETFs, which robo advisors select and rebalance automatically to maximize returns while minimizing fees. This synergy enables investors to achieve diversified, long-term growth with minimal active portfolio management.
Key Terms
Index Funds
Index funds are a cornerstone of passive investing, offering low-cost, diversified exposure to broad market segments by tracking specific indices like the S&P 500. Robo advisory platforms leverage algorithms to allocate investments primarily in index funds, providing automated portfolio management tailored to individual risk profiles and financial goals. Explore how combining index funds with robo advisory can optimize your passive investment strategy.
Automated Portfolio Management
Automated portfolio management leverages algorithm-driven platforms to execute passive investing strategies, minimizing human intervention while optimizing asset allocation based on market data and investor profiles. Robo advisors provide scalable, cost-effective solutions that continuously rebalance portfolios to maintain risk tolerance and investment goals. Explore how automated portfolio management can streamline your passive investment approach and enhance portfolio efficiency.
Expense Ratios
Expense ratios play a crucial role in passive investing and robo advisory services, directly impacting net returns for investors. Passive investment funds typically have lower expense ratios, often averaging around 0.03% to 0.10%, whereas robo advisors include management fees that can range from 0.20% to 0.50%, reflecting the cost of automated portfolio management and personalized services. Explore detailed comparisons and performance insights to understand how expense ratios influence long-term investment outcomes.
Source and External Links
What is Passive Investing & How it Works? | TD Direct Investing - Passive investing is a long-term strategy focused on buying and holding a diverse portfolio that mirrors a market index, aiming to build wealth gradually over time with lower fees and less trading than active investing.
Passive management - Wikipedia - Passive investing tracks market-weighted indexes through vehicles like index funds and ETFs, offering low fees, tax efficiency, and less hands-on management compared to active strategies.
Active vs. Passive Investing | FINRA.org - Passive investing, also known as "buy and hold," aims to replicate overall market performance over time and involves fewer trades and reduced portfolio intervention than active investing.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com