Blockchain rollups increase transaction throughput by bundling multiple transactions into a single batch, reducing on-chain data load and cutting costs while maintaining security through on-chain validation. State channels enable off-chain transactions between participants by locking funds in a multi-signature contract, offering near-instant finality and minimal fees with on-chain settlement only when channels close. Explore the detailed mechanisms and use cases to understand which layer 2 solution aligns best with your financial application needs.
Why it is important
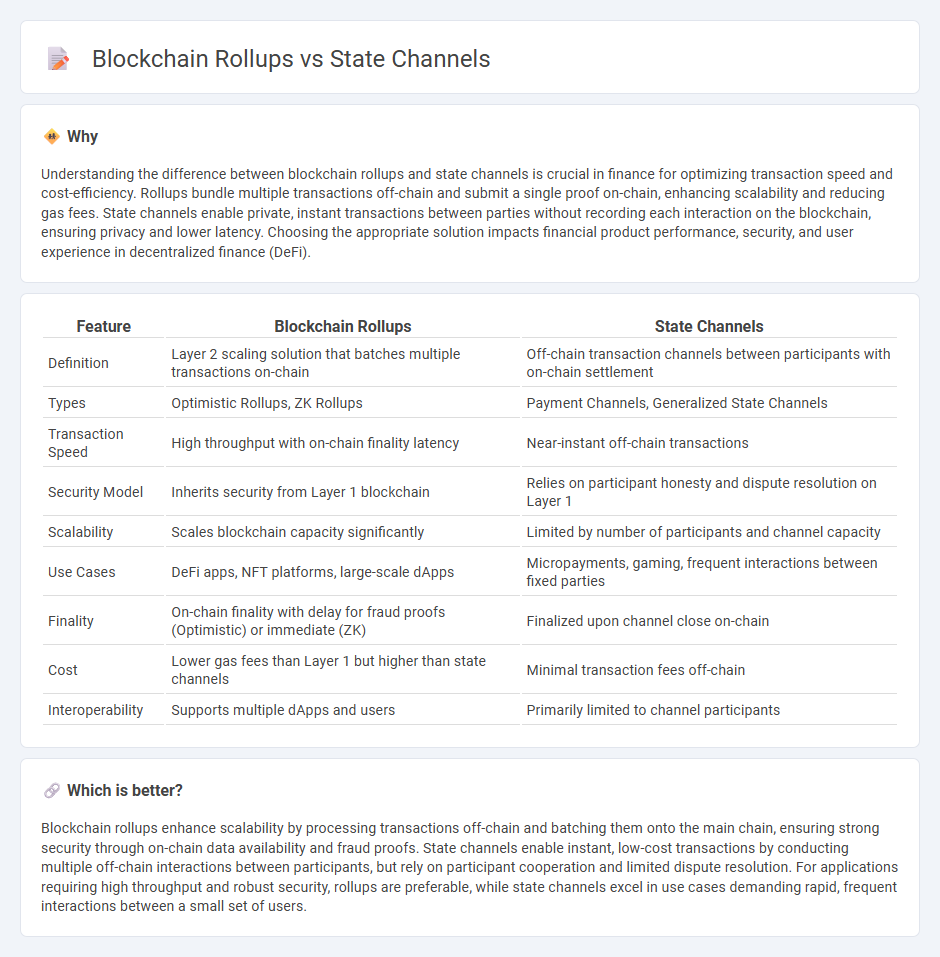
Understanding the difference between blockchain rollups and state channels is crucial in finance for optimizing transaction speed and cost-efficiency. Rollups bundle multiple transactions off-chain and submit a single proof on-chain, enhancing scalability and reducing gas fees. State channels enable private, instant transactions between parties without recording each interaction on the blockchain, ensuring privacy and lower latency. Choosing the appropriate solution impacts financial product performance, security, and user experience in decentralized finance (DeFi).
Comparison Table
| Feature | Blockchain Rollups | State Channels |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Layer 2 scaling solution that batches multiple transactions on-chain | Off-chain transaction channels between participants with on-chain settlement |
| Types | Optimistic Rollups, ZK Rollups | Payment Channels, Generalized State Channels |
| Transaction Speed | High throughput with on-chain finality latency | Near-instant off-chain transactions |
| Security Model | Inherits security from Layer 1 blockchain | Relies on participant honesty and dispute resolution on Layer 1 |
| Scalability | Scales blockchain capacity significantly | Limited by number of participants and channel capacity |
| Use Cases | DeFi apps, NFT platforms, large-scale dApps | Micropayments, gaming, frequent interactions between fixed parties |
| Finality | On-chain finality with delay for fraud proofs (Optimistic) or immediate (ZK) | Finalized upon channel close on-chain |
| Cost | Lower gas fees than Layer 1 but higher than state channels | Minimal transaction fees off-chain |
| Interoperability | Supports multiple dApps and users | Primarily limited to channel participants |
Which is better?
Blockchain rollups enhance scalability by processing transactions off-chain and batching them onto the main chain, ensuring strong security through on-chain data availability and fraud proofs. State channels enable instant, low-cost transactions by conducting multiple off-chain interactions between participants, but rely on participant cooperation and limited dispute resolution. For applications requiring high throughput and robust security, rollups are preferable, while state channels excel in use cases demanding rapid, frequent interactions between a small set of users.
Connection
Blockchain rollups and state channels both enhance scalability by processing multiple transactions off-chain while maintaining security through on-chain data anchors. Rollups aggregate batches of transactions into a single proof submitted on-chain, reducing congestion and gas fees on networks like Ethereum. State channels enable participants to transact privately off-chain, settling final states on-chain only upon completion, minimizing blockchain interaction and increasing transaction speed.
Key Terms
Off-chain transactions
State channels enable instant off-chain transactions by allowing participants to transact directly and only settle final balances on the blockchain, reducing on-chain congestion and fees. Blockchain rollups batch multiple transactions off-chain but post aggregated data on-chain, ensuring security through on-chain fraud proofs or validity proofs. Explore the advantages and technical nuances of off-chain transaction solutions to optimize blockchain scalability.
Aggregation
State channels aggregate multiple off-chain transactions into a single on-chain settlement, reducing blockchain congestion and enhancing scalability. Blockchain rollups batch numerous transactions and execute them off-chain, then submit compressed proofs to the main chain, optimizing data storage and processing. Explore deeper insights into how these aggregation techniques impact blockchain efficiency and user experience.
Finality
State channels enable near-instant transaction finality by allowing off-chain interactions that settle only the net outcome on the main blockchain. Blockchain rollups bundle multiple transactions into a single batch, achieving scalability with delayed but secure finality anchored on the base layer. Explore further to understand how finality impacts efficiency and security in Layer 2 solutions.
Source and External Links
State Channels - Instant P2P Ethereum Transactions - State channels are a scalability technology for Ethereum enabling instant and free peer-to-peer Ethereum transactions off-chain, reducing on-chain transaction load.
State Channels - EthHub - State channels operate by locking blockchain state in a multisig contract among participants who then exchange off-chain signed transactions, only settling the final state on-chain to achieve scalability and instant interaction.
State Channels - Ethereum.org - Participants open a channel by committing funds to a smart contract, transact freely off-chain by signing and exchanging state updates, and close the channel by submitting the final state to the blockchain, minimizing mainnet interaction and ensuring security through dispute resolution.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com