Payment for order flow (PFOF) involves brokers receiving compensation for directing client orders to specific market makers, enhancing liquidity and reducing transaction costs. Alternative Trading Systems (ATS) operate as non-exchange trading venues providing additional avenues for order execution, often offering increased transparency and flexibility. Explore how PFOF and ATS impact market efficiency and investor outcomes.
Why it is important
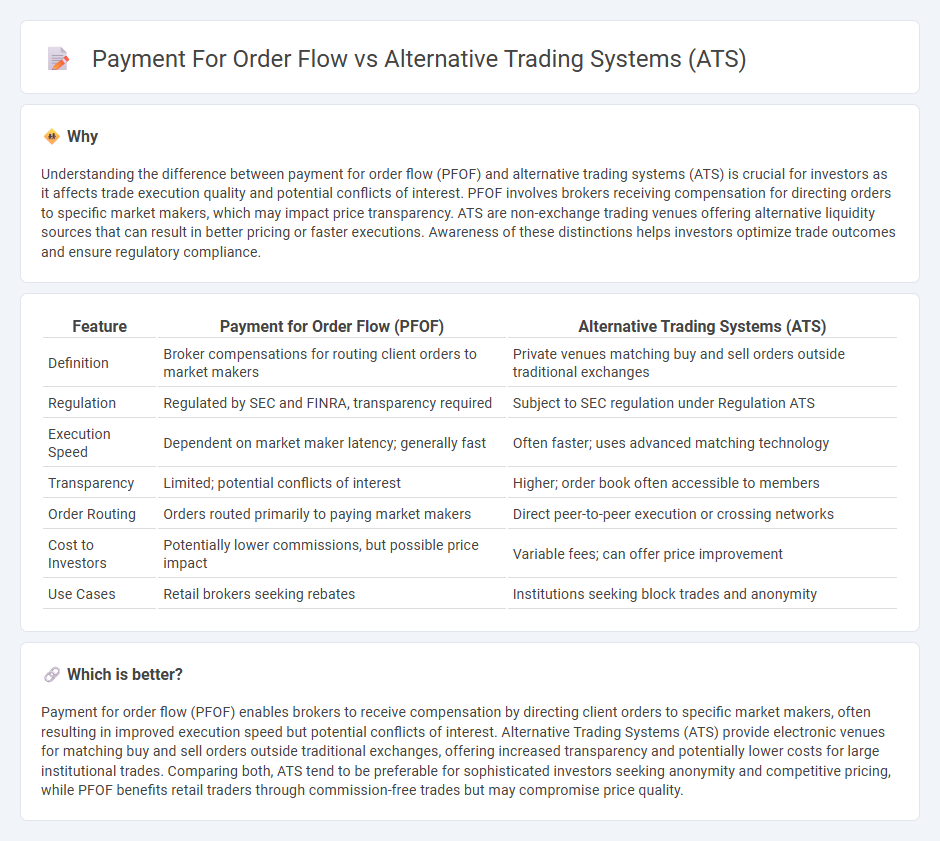
Understanding the difference between payment for order flow (PFOF) and alternative trading systems (ATS) is crucial for investors as it affects trade execution quality and potential conflicts of interest. PFOF involves brokers receiving compensation for directing orders to specific market makers, which may impact price transparency. ATS are non-exchange trading venues offering alternative liquidity sources that can result in better pricing or faster executions. Awareness of these distinctions helps investors optimize trade outcomes and ensure regulatory compliance.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Payment for Order Flow (PFOF) | Alternative Trading Systems (ATS) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Broker compensations for routing client orders to market makers | Private venues matching buy and sell orders outside traditional exchanges |
| Regulation | Regulated by SEC and FINRA, transparency required | Subject to SEC regulation under Regulation ATS |
| Execution Speed | Dependent on market maker latency; generally fast | Often faster; uses advanced matching technology |
| Transparency | Limited; potential conflicts of interest | Higher; order book often accessible to members |
| Order Routing | Orders routed primarily to paying market makers | Direct peer-to-peer execution or crossing networks |
| Cost to Investors | Potentially lower commissions, but possible price impact | Variable fees; can offer price improvement |
| Use Cases | Retail brokers seeking rebates | Institutions seeking block trades and anonymity |
Which is better?
Payment for order flow (PFOF) enables brokers to receive compensation by directing client orders to specific market makers, often resulting in improved execution speed but potential conflicts of interest. Alternative Trading Systems (ATS) provide electronic venues for matching buy and sell orders outside traditional exchanges, offering increased transparency and potentially lower costs for large institutional trades. Comparing both, ATS tend to be preferable for sophisticated investors seeking anonymity and competitive pricing, while PFOF benefits retail traders through commission-free trades but may compromise price quality.
Connection
Payment for order flow (PFOF) directly influences the operational dynamics of alternative trading systems (ATS) by incentivizing brokers to route client orders to these platforms for execution. ATS entities leverage PFOF arrangements to attract increased order flow, enhancing liquidity and potentially providing tighter bid-ask spreads compared to traditional exchanges. This symbiotic relationship impacts market transparency and execution quality, raising regulatory considerations around fair order routing and best execution practices.
Key Terms
Dark Pools
Alternative Trading Systems (ATS), particularly dark pools, facilitate private, non-public trading venues where large orders execute without market impact, preserving anonymity and minimizing price slippage. Payment for Order Flow (PFOF) involves brokerages routing client orders to specific market makers for compensation, potentially raising conflicts of interest and transparency concerns. Explore the operational differences and regulatory implications of dark pools versus PFOF to understand their roles in modern equity markets.
Liquidity Providers
Alternative Trading Systems (ATS) function as private trading venues facilitating direct matching of buy and sell orders, thereby enhancing market liquidity without routing through traditional exchanges. Payment for Order Flow (PFOF) involves brokers receiving compensation from liquidity providers like market makers for directing client orders to them, aiming to improve execution quality and spread efficiency. Discover how liquidity providers leverage ATS and PFOF to optimize trade execution and market access.
Order Routing
Alternative Trading Systems (ATS) provide electronic platforms for matching buy and sell orders, offering transparency and often lower costs compared to traditional exchanges, while Payment for Order Flow (PFOF) involves brokers routing orders to specific market makers in exchange for fees, potentially affecting best execution. ATS rely on order routing to aggregate liquidity from multiple sources, enhancing price discovery and reducing execution costs, whereas PFOF can present conflicts of interest by prioritizing venue payments over optimal order execution. Explore the differences in order routing mechanisms and their impact on trade quality to understand how ATS and PFOF shape modern securities trading.
Source and External Links
Alternative trading system - An ATS is a US and Canadian regulatory term for a non-exchange trading venue that matches buyers and sellers, regulated as broker-dealers rather than exchanges, providing alternative access to liquidity and often involving electronic platforms like dark pools or ECNs.
Alternative Trading System (ATS) - Definition, Examples - ATSs are trading venues that are not regulated as exchanges but connect buyers and sellers, often used for large trades to avoid market price impact, including forms like electronic communication networks, dark pools, and crossing networks.
Alternative Trading System (ATS) Regulation and Requirements - ATSs include diverse types such as dark pools (anonymous large block trades), ECNs (automated order matching), crossing networks (scheduled trades), broker-dealers' internal systems, and call markets, each catering to different trading strategies and liquidity needs outside traditional exchanges.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com