Quantamental investing combines quantitative analysis with fundamental research to select stocks, aiming for higher returns and risk management compared to passive investing, which tracks market indices without stock-picking. This hybrid strategy leverages algorithms and human judgment to identify undervalued securities, offering potential to outperform broad market benchmarks. Discover more about how quantamental investing can enhance your portfolio compared to traditional passive approaches.
Why it is important
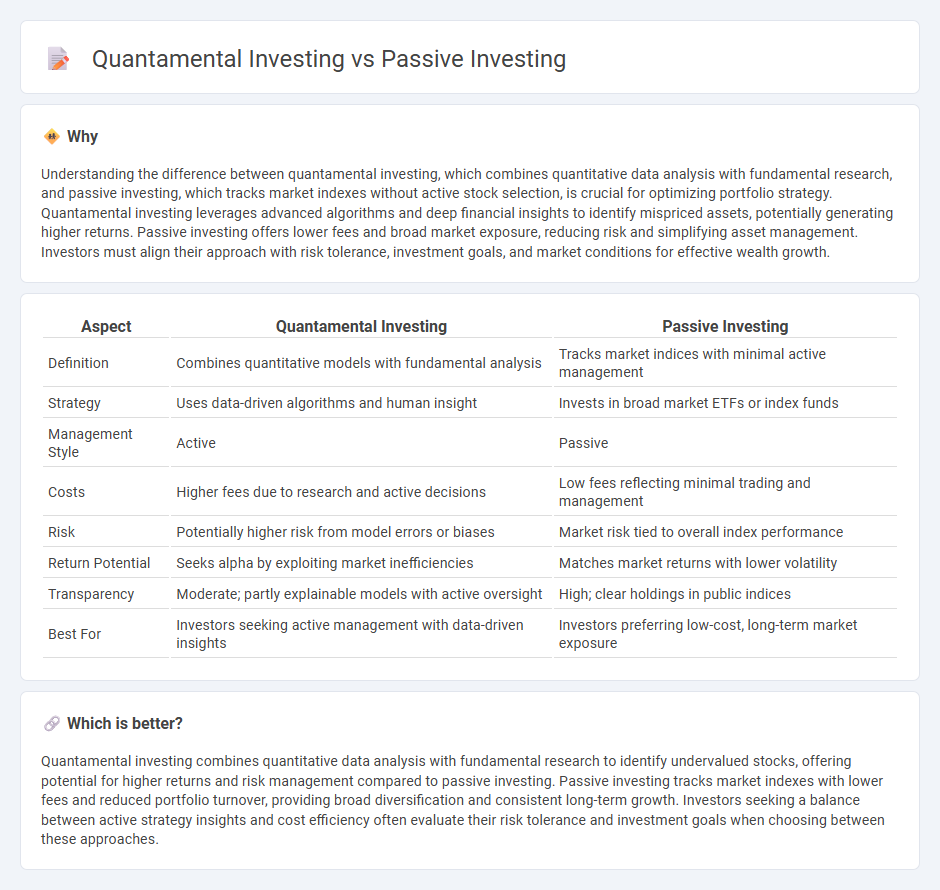
Understanding the difference between quantamental investing, which combines quantitative data analysis with fundamental research, and passive investing, which tracks market indexes without active stock selection, is crucial for optimizing portfolio strategy. Quantamental investing leverages advanced algorithms and deep financial insights to identify mispriced assets, potentially generating higher returns. Passive investing offers lower fees and broad market exposure, reducing risk and simplifying asset management. Investors must align their approach with risk tolerance, investment goals, and market conditions for effective wealth growth.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Quantamental Investing | Passive Investing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Combines quantitative models with fundamental analysis | Tracks market indices with minimal active management |
| Strategy | Uses data-driven algorithms and human insight | Invests in broad market ETFs or index funds |
| Management Style | Active | Passive |
| Costs | Higher fees due to research and active decisions | Low fees reflecting minimal trading and management |
| Risk | Potentially higher risk from model errors or biases | Market risk tied to overall index performance |
| Return Potential | Seeks alpha by exploiting market inefficiencies | Matches market returns with lower volatility |
| Transparency | Moderate; partly explainable models with active oversight | High; clear holdings in public indices |
| Best For | Investors seeking active management with data-driven insights | Investors preferring low-cost, long-term market exposure |
Which is better?
Quantamental investing combines quantitative data analysis with fundamental research to identify undervalued stocks, offering potential for higher returns and risk management compared to passive investing. Passive investing tracks market indexes with lower fees and reduced portfolio turnover, providing broad diversification and consistent long-term growth. Investors seeking a balance between active strategy insights and cost efficiency often evaluate their risk tolerance and investment goals when choosing between these approaches.
Connection
Quantamental investing combines quantitative analysis with fundamental research to identify high-quality stocks, enhancing portfolio performance through data-driven insights. Passive investing focuses on replicating market indices, providing broad diversification and low costs. Integrating quantamental strategies within passive frameworks can optimize asset selection and risk management while maintaining passive investment benefits.
Key Terms
Index Funds
Index funds exemplify passive investing by tracking market benchmarks with minimal active management, emphasizing broad market exposure and low fees. Quantamental investing combines quantitative data analysis with fundamental research to select stocks, aiming to outperform traditional passive strategies. Discover how integrating these methods can enhance your investment portfolio.
Factor Models
Passive investing relies on broad market indices to achieve diversification with minimal costs, aiming to replicate market returns without active decision-making. Quantamental investing combines quantitative factor models with fundamental analysis to identify securities with superior growth, value, momentum, or quality characteristics, enhancing alpha generation. Explore deeper insights into how factor models drive performance differences between passive and quantamental strategies.
Fundamental Analysis
Passive investing relies on broad market index funds to achieve diversified exposure with minimal trading, prioritizing long-term market returns rather than stock selection based on fundamentals. Quantamental investing combines quantitative models and algorithmic strategies with in-depth fundamental analysis, leveraging data like earnings, cash flow, and valuation metrics to enhance stock selection and portfolio performance. Explore detailed comparisons and strategies to understand how integrating fundamental analysis can optimize your investment approach.
Source and External Links
What is Passive Investing & How it Works? | TD Direct Investing - Passive investing is a long-term strategy focused on buying and holding a diversified portfolio that mimics a market index to build wealth gradually, usually at lower costs compared to active investing.
Active vs. Passive Investing | FINRA.org - Passive investing, also called "buy and hold," aims to mirror market performance over time using funds like index funds, involving less frequent trading and intervention than active strategies.
Passive management - Wikipedia - Passive investing involves tracking a market-weighted index through vehicles such as index funds, ETFs, and index futures, focusing on replicating market returns with minimal active management.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com