Tokenized treasury bills offer a secure, government-backed digital asset enabling investors to access short-term debt instruments through blockchain technology, providing transparency and liquidity. In contrast, Decentralized Finance (DeFi) lending platforms facilitate peer-to-peer borrowing and lending without intermediaries, leveraging smart contracts for automation and higher yields but with increased risk. Explore the nuances and benefits of both to optimize your investment strategy in the evolving finance landscape.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between tokenized treasury bills and Decentralized Finance (DeFi) lending is crucial for informed investment decisions due to their distinct risk profiles and regulatory frameworks. Tokenized treasury bills represent government-backed securities on a blockchain, offering low-risk, stable returns and enhanced liquidity. DeFi lending platforms facilitate peer-to-peer lending through smart contracts, often with higher risk and potential for greater yields due to market volatility and decentralized governance. Knowing these differences helps investors optimize portfolio diversification and risk management strategies in the evolving digital finance landscape.
Comparison Table
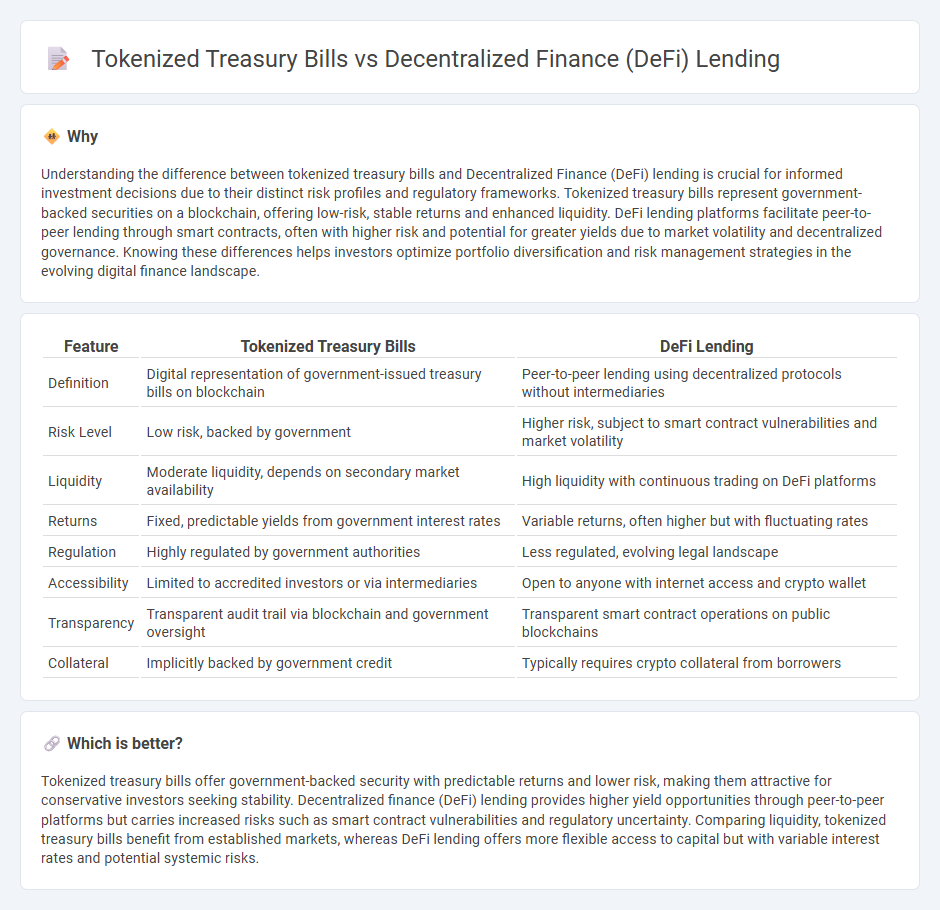
| Feature | Tokenized Treasury Bills | DeFi Lending |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Digital representation of government-issued treasury bills on blockchain | Peer-to-peer lending using decentralized protocols without intermediaries |
| Risk Level | Low risk, backed by government | Higher risk, subject to smart contract vulnerabilities and market volatility |
| Liquidity | Moderate liquidity, depends on secondary market availability | High liquidity with continuous trading on DeFi platforms |
| Returns | Fixed, predictable yields from government interest rates | Variable returns, often higher but with fluctuating rates |
| Regulation | Highly regulated by government authorities | Less regulated, evolving legal landscape |
| Accessibility | Limited to accredited investors or via intermediaries | Open to anyone with internet access and crypto wallet |
| Transparency | Transparent audit trail via blockchain and government oversight | Transparent smart contract operations on public blockchains |
| Collateral | Implicitly backed by government credit | Typically requires crypto collateral from borrowers |
Which is better?
Tokenized treasury bills offer government-backed security with predictable returns and lower risk, making them attractive for conservative investors seeking stability. Decentralized finance (DeFi) lending provides higher yield opportunities through peer-to-peer platforms but carries increased risks such as smart contract vulnerabilities and regulatory uncertainty. Comparing liquidity, tokenized treasury bills benefit from established markets, whereas DeFi lending offers more flexible access to capital but with variable interest rates and potential systemic risks.
Connection
Tokenized treasury bills enable fractional ownership and increased liquidity by representing government debt as digital assets on a blockchain. Decentralized finance (DeFi) lending platforms utilize these tokenized assets as collateral to facilitate transparent, permissionless borrowing and lending without traditional intermediaries. This integration enhances market access, reduces settlement times, and increases capital efficiency within the DeFi ecosystem.
Key Terms
Smart Contracts
DeFi lending leverages smart contracts to automate loan issuance, repayment schedules, and collateral management, ensuring transparency and reducing reliance on traditional intermediaries. Tokenized treasury bills utilize smart contracts to represent government debt securely on blockchain, enabling fractional ownership, instantaneous settlement, and enhanced liquidity. Explore the transformative potential of smart contracts in decentralized finance and tokenized assets to understand their impact on modern financial systems.
Collateralization
DeFi lending platforms utilize over-collateralization to mitigate the risk of borrower default, requiring users to lock assets exceeding the loan value, often around 150% collateral ratio. Tokenized treasury bills represent government debt secured by the sovereign credit, offering a low-risk asset backed by real-world collateral but lacking over-collateralization dynamics. Explore the mechanisms of risk management and collateralization in both systems to understand their unique financial security models.
Yield
Decentralized finance (DeFi) lending platforms offer variable yields often exceeding traditional finance rates due to direct peer-to-peer transactions and liquidity incentives. Tokenized treasury bills provide a more stable, government-backed yield, typically lower but with minimal risk and higher liquidity compared to conventional treasury investments. Explore deeper insights into yield dynamics and risk profiles between these innovative financial instruments to optimize your portfolio strategy.
Source and External Links
How Does DeFi Lending Work? - Webisoft Blog - DeFi lending allows individuals to lend and borrow digital assets without intermediaries by using collateralized loans managed through smart contracts, enabling transparency, accessibility, and potentially higher interest rates for lenders.
How DeFi Works for Lending and Borrowing Markets - Stellar - DeFi lending operates via decentralized protocols where users deposit assets into lending pools as liquidity providers earning interest, and borrowers provide collateral in other digital assets to access loans, with terms governed by smart contracts balancing supply and demand.
The Rise of DeFi Lending and How to Get Involved - Hedera - DeFi lending empowers users to lend on chosen money markets to earn interest based on yields, relying on concepts like over-collateralization and smart contracts, with a rapidly growing user base and billions locked in digital assets.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com