Inflation swaps and inflation-linked bonds serve as key instruments for managing inflation risk by offering protection against rising consumer prices. Inflation swaps provide customizable inflation exposure through derivative contracts, while inflation-linked bonds deliver direct principal and interest payments adjusted for inflation. Explore the detailed mechanics and comparative advantages of these tools to optimize your inflation risk strategy.
Why it is important
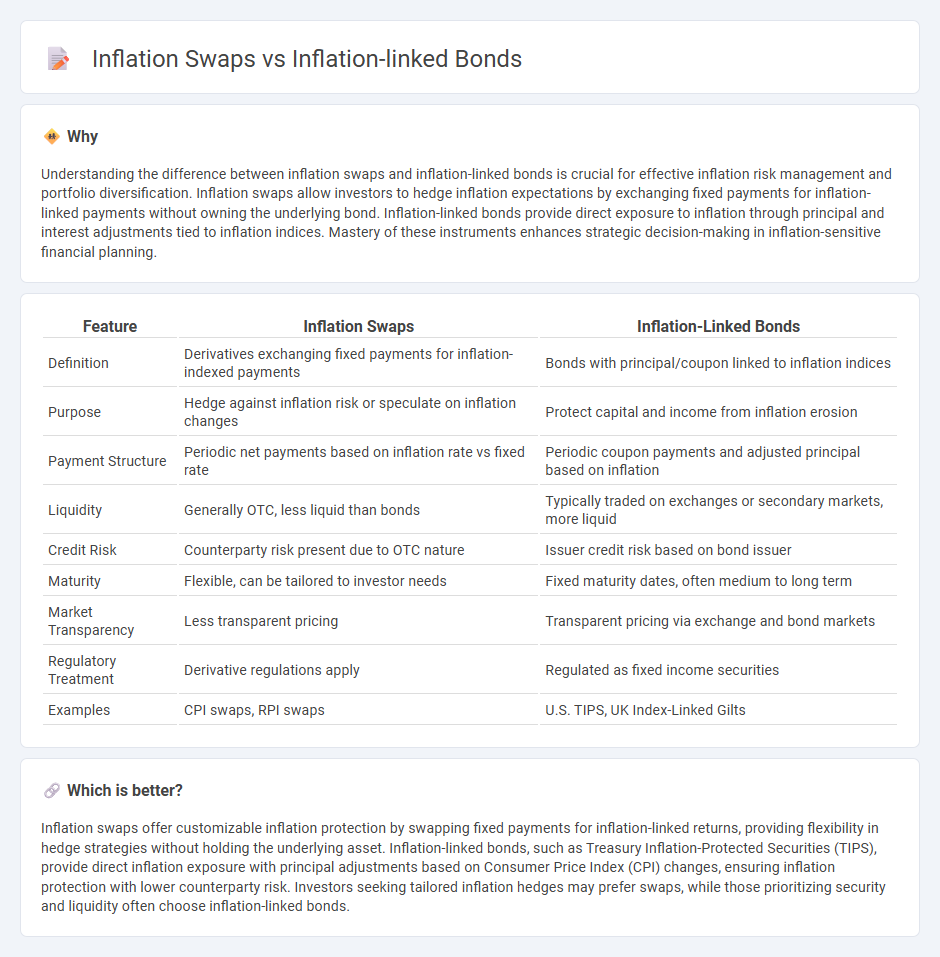
Understanding the difference between inflation swaps and inflation-linked bonds is crucial for effective inflation risk management and portfolio diversification. Inflation swaps allow investors to hedge inflation expectations by exchanging fixed payments for inflation-linked payments without owning the underlying bond. Inflation-linked bonds provide direct exposure to inflation through principal and interest adjustments tied to inflation indices. Mastery of these instruments enhances strategic decision-making in inflation-sensitive financial planning.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Inflation Swaps | Inflation-Linked Bonds |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Derivatives exchanging fixed payments for inflation-indexed payments | Bonds with principal/coupon linked to inflation indices |
| Purpose | Hedge against inflation risk or speculate on inflation changes | Protect capital and income from inflation erosion |
| Payment Structure | Periodic net payments based on inflation rate vs fixed rate | Periodic coupon payments and adjusted principal based on inflation |
| Liquidity | Generally OTC, less liquid than bonds | Typically traded on exchanges or secondary markets, more liquid |
| Credit Risk | Counterparty risk present due to OTC nature | Issuer credit risk based on bond issuer |
| Maturity | Flexible, can be tailored to investor needs | Fixed maturity dates, often medium to long term |
| Market Transparency | Less transparent pricing | Transparent pricing via exchange and bond markets |
| Regulatory Treatment | Derivative regulations apply | Regulated as fixed income securities |
| Examples | CPI swaps, RPI swaps | U.S. TIPS, UK Index-Linked Gilts |
Which is better?
Inflation swaps offer customizable inflation protection by swapping fixed payments for inflation-linked returns, providing flexibility in hedge strategies without holding the underlying asset. Inflation-linked bonds, such as Treasury Inflation-Protected Securities (TIPS), provide direct inflation exposure with principal adjustments based on Consumer Price Index (CPI) changes, ensuring inflation protection with lower counterparty risk. Investors seeking tailored inflation hedges may prefer swaps, while those prioritizing security and liquidity often choose inflation-linked bonds.
Connection
Inflation swaps and inflation-linked bonds are connected through their shared function of managing inflation risk, with inflation swaps allowing counterparties to exchange fixed payments for inflation-indexed returns based on a specific inflation measure. Inflation-linked bonds, such as Treasury Inflation-Protected Securities (TIPS), provide investors with principal and interest payments adjusted according to inflation, serving as underlying assets or benchmarks in inflation swap contracts. Both instruments are essential tools in inflation risk hedging strategies, enabling investors and institutions to align their cash flows with actual inflation rates.
Key Terms
Principal Adjustment (for inflation-linked bonds)
Inflation-linked bonds adjust their principal value based on the Consumer Price Index (CPI), ensuring investors' capital keeps pace with inflation and preserves purchasing power over time. Inflation swaps, in contrast, exchange fixed payments for floating inflation-linked payments without principal adjustment, focusing on hedging inflation risk rather than capital preservation. Discover detailed strategies and comparative advantages of principal adjustments in inflation-linked bonds for optimized inflation risk management.
Floating Leg (for inflation swaps)
Inflation-linked bonds provide fixed interest payments adjusted for inflation, offering investors protection through principal and coupon linked to Consumer Price Index (CPI). The floating leg of inflation swaps reflects actual inflation rates, typically calculated as the realized CPI over the swap period, allowing counterparties to exchange fixed inflation expectations for actual inflation outcomes. Explore the mechanics and benefits of inflation swaps' floating legs to better understand their role in inflation risk management.
Real Yield
Inflation-linked bonds provide investors with a fixed real yield adjusted by the inflation rate, preserving purchasing power through principal and coupon adjustments indexed to inflation. Inflation swaps allow parties to exchange fixed real yields for floating inflation rates, enabling customization of inflation exposure without holding the underlying bond. Explore detailed comparisons to understand strategic advantages and risks associated with real yield management in inflation-linked instruments.
Source and External Links
Risks and Rewards of Inflation-Linked Bonds - Inflation-linked bonds are fixed-income securities with principal and coupons tied to price indices, designed to eliminate inflation risk, offering strategic long-term inflation hedging, with returns influenced by breakeven inflation and real yield dynamics.
Inflation-linked bond ETFs: how they protect you against ... - Inflation-linked bonds increase their principal and coupon payments in line with inflation indices, providing effective protection against rising prices and preserving portfolio wealth by ensuring returns keep pace with inflation.
Understanding Inflation-Linked Bonds - Inflation-linked bonds are primarily government-issued securities that adjust principal and interest payments in line with inflation to protect investors' purchasing power against the eroding effects of inflation.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com