Impact investing focuses on generating measurable social and environmental benefits alongside financial returns by funding innovative projects and sustainable enterprises. Community investing directs capital to underserved communities, supporting affordable housing, small businesses, and essential services to promote economic development and equity. Explore more to understand how these investment strategies drive positive change in diverse ways.
Why it is important
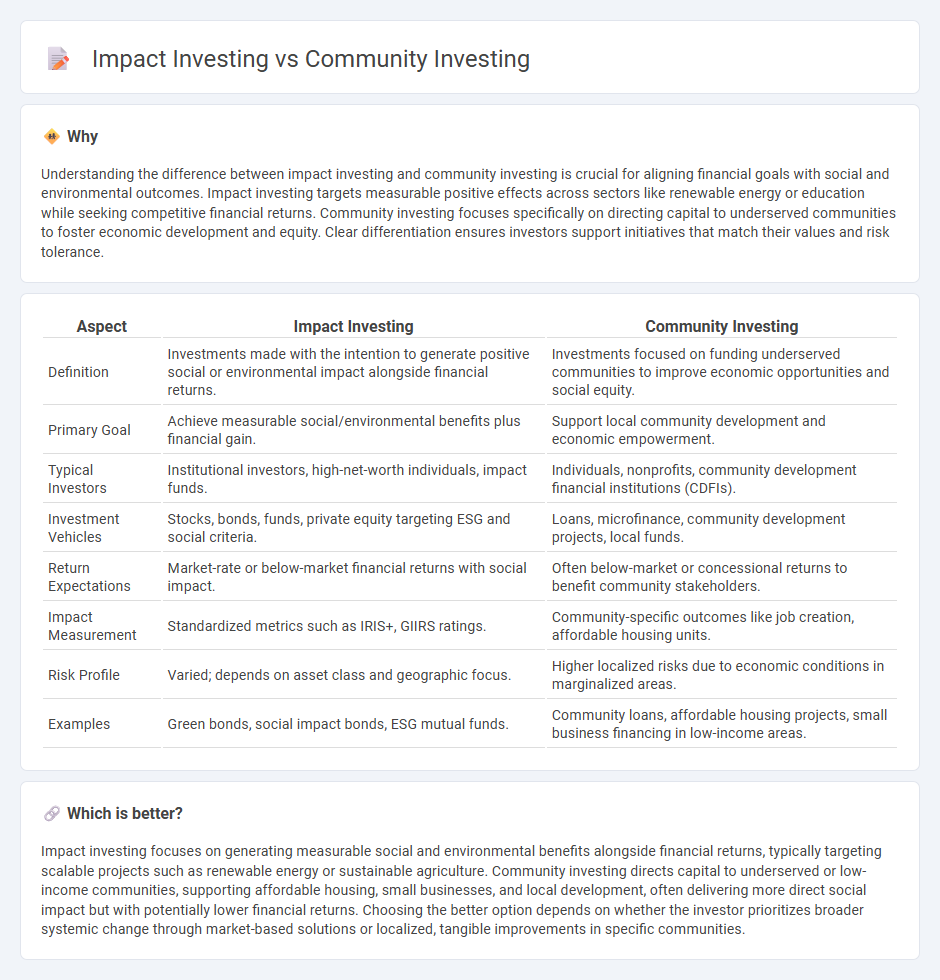
Understanding the difference between impact investing and community investing is crucial for aligning financial goals with social and environmental outcomes. Impact investing targets measurable positive effects across sectors like renewable energy or education while seeking competitive financial returns. Community investing focuses specifically on directing capital to underserved communities to foster economic development and equity. Clear differentiation ensures investors support initiatives that match their values and risk tolerance.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Impact Investing | Community Investing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Investments made with the intention to generate positive social or environmental impact alongside financial returns. | Investments focused on funding underserved communities to improve economic opportunities and social equity. |
| Primary Goal | Achieve measurable social/environmental benefits plus financial gain. | Support local community development and economic empowerment. |
| Typical Investors | Institutional investors, high-net-worth individuals, impact funds. | Individuals, nonprofits, community development financial institutions (CDFIs). |
| Investment Vehicles | Stocks, bonds, funds, private equity targeting ESG and social criteria. | Loans, microfinance, community development projects, local funds. |
| Return Expectations | Market-rate or below-market financial returns with social impact. | Often below-market or concessional returns to benefit community stakeholders. |
| Impact Measurement | Standardized metrics such as IRIS+, GIIRS ratings. | Community-specific outcomes like job creation, affordable housing units. |
| Risk Profile | Varied; depends on asset class and geographic focus. | Higher localized risks due to economic conditions in marginalized areas. |
| Examples | Green bonds, social impact bonds, ESG mutual funds. | Community loans, affordable housing projects, small business financing in low-income areas. |
Which is better?
Impact investing focuses on generating measurable social and environmental benefits alongside financial returns, typically targeting scalable projects such as renewable energy or sustainable agriculture. Community investing directs capital to underserved or low-income communities, supporting affordable housing, small businesses, and local development, often delivering more direct social impact but with potentially lower financial returns. Choosing the better option depends on whether the investor prioritizes broader systemic change through market-based solutions or localized, tangible improvements in specific communities.
Connection
Impact investing and community investing both prioritize generating positive social or environmental outcomes alongside financial returns, fostering sustainable economic development. Impact investing often targets scalable projects with measurable benefits, while community investing directs capital toward underserved local entities, supporting affordable housing, small businesses, and community services. Together, they drive inclusive growth by channeling funds into initiatives that address social inequities and promote long-term community resilience.
Key Terms
Social return
Community investing directs capital to underserved communities, emphasizing measurable social returns such as improved housing, education, and local business development. Impact investing targets both social and financial returns by funding enterprises that address social issues, often with scalable solutions and rigorous impact metrics. Explore how these investment strategies can align with your values and drive meaningful social change.
Financial inclusion
Community investing directly channels capital into underserved communities to promote financial inclusion by supporting local businesses, affordable housing, and social services. Impact investing also aims for financial inclusion but emphasizes measurable social and environmental returns alongside financial gains. Explore how each strategy uniquely drives inclusive economic growth and empowers marginalized populations.
Environmental outcomes
Community investing targets local projects that support sustainable housing, renewable energy, and conservation efforts to enhance environmental quality within underserved areas. Impact investing prioritizes measurable environmental outcomes across diverse sectors, including clean technology, climate risk mitigation, and sustainable agriculture to drive scalable ecological benefits. Explore the distinctions and synergies between these investment approaches to maximize your environmental impact strategy.
Source and External Links
Community Investment Trusts - Small Business Anti-Displacement - Community investment trusts are for-profit entities that enable neighborhood residents and stakeholders to pool resources to buy community-owned real estate, helping build equity, provide affordable space for small businesses, and increase local economic development while facing challenges such as state regulatory limits and limited funding.
Impact in Place: Emerging Sources of Community Investment - Innovative community investing includes funds like Chicago's Small Business Resiliency Loan Fund and the democratically managed Boston Ujima Fund that empower residents and businesses to support wealth building and racial equity within their communities.
High Impact Community Investing | Green America - Community investing involves channeling investments to support disadvantaged groups underserved by traditional finance, often via community development banks, credit unions, or mutual funds that focus on underserved areas to promote home ownership, small businesses, and community well-being.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com