ESG integration involves systematically incorporating environmental, social, and governance criteria into traditional financial analysis to enhance risk management and long-term returns. Impact investing focuses on generating measurable social and environmental benefits alongside financial gains by directing capital to projects or companies with explicit positive outcomes. Explore how these strategies differ in driving sustainable finance and shaping investment portfolios.
Why it is important
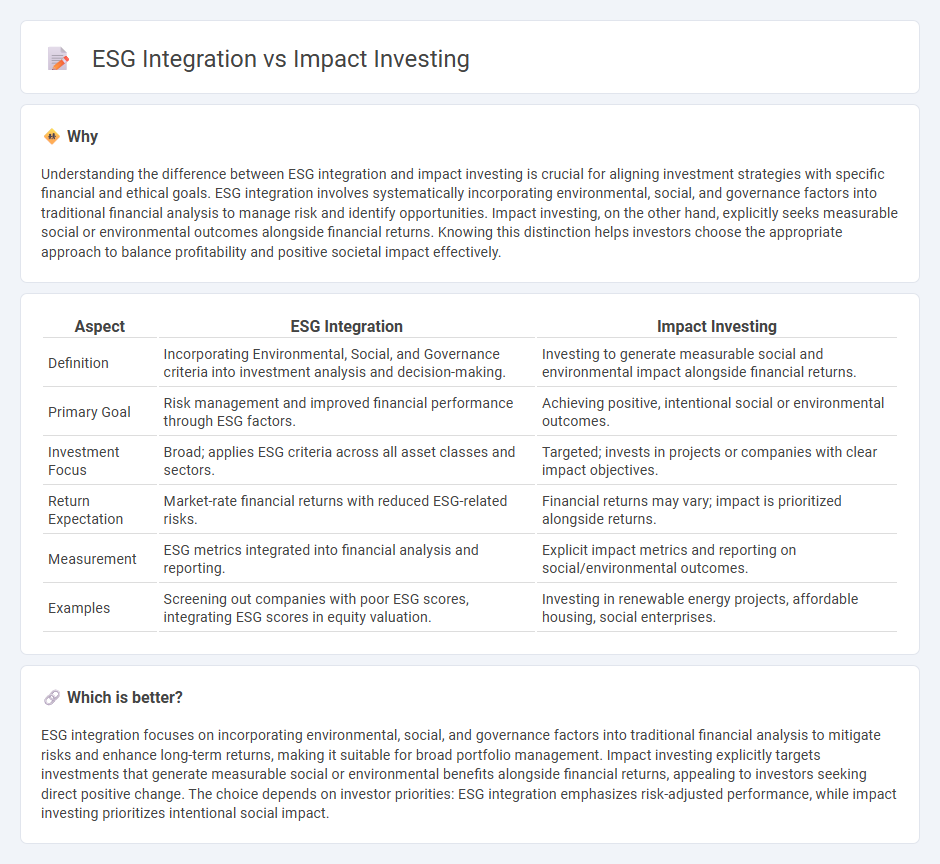
Understanding the difference between ESG integration and impact investing is crucial for aligning investment strategies with specific financial and ethical goals. ESG integration involves systematically incorporating environmental, social, and governance factors into traditional financial analysis to manage risk and identify opportunities. Impact investing, on the other hand, explicitly seeks measurable social or environmental outcomes alongside financial returns. Knowing this distinction helps investors choose the appropriate approach to balance profitability and positive societal impact effectively.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | ESG Integration | Impact Investing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Incorporating Environmental, Social, and Governance criteria into investment analysis and decision-making. | Investing to generate measurable social and environmental impact alongside financial returns. |
| Primary Goal | Risk management and improved financial performance through ESG factors. | Achieving positive, intentional social or environmental outcomes. |
| Investment Focus | Broad; applies ESG criteria across all asset classes and sectors. | Targeted; invests in projects or companies with clear impact objectives. |
| Return Expectation | Market-rate financial returns with reduced ESG-related risks. | Financial returns may vary; impact is prioritized alongside returns. |
| Measurement | ESG metrics integrated into financial analysis and reporting. | Explicit impact metrics and reporting on social/environmental outcomes. |
| Examples | Screening out companies with poor ESG scores, integrating ESG scores in equity valuation. | Investing in renewable energy projects, affordable housing, social enterprises. |
Which is better?
ESG integration focuses on incorporating environmental, social, and governance factors into traditional financial analysis to mitigate risks and enhance long-term returns, making it suitable for broad portfolio management. Impact investing explicitly targets investments that generate measurable social or environmental benefits alongside financial returns, appealing to investors seeking direct positive change. The choice depends on investor priorities: ESG integration emphasizes risk-adjusted performance, while impact investing prioritizes intentional social impact.
Connection
ESG integration involves incorporating environmental, social, and governance factors into financial analysis to identify sustainable investment opportunities, while Impact Investing focuses on generating measurable social or environmental benefits alongside financial returns. Both approaches prioritize long-term value creation by addressing non-financial risks and opportunities that traditional financial metrics may overlook. By combining ESG integration with Impact Investing, investors can enhance portfolio resilience and drive positive societal change through targeted capital allocation.
Key Terms
Social Impact
Impact investing prioritizes measurable social outcomes alongside financial returns by directing capital to projects with explicit social goals such as affordable housing or education. ESG integration evaluates environmental, social, and governance factors within traditional investment analysis to mitigate risks and enhance long-term value but may not target specific social change. Explore the distinctions and advantages of these approaches to better understand their roles in driving social impact.
Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) factors
Impact investing targets measurable environmental, social, and governance (ESG) outcomes by deliberately allocating capital to projects generating positive social or environmental effects. ESG integration evaluates these criteria to enhance risk management and long-term financial performance within investment portfolios without necessarily seeking direct impact. Explore deeper insights into how these strategies shape sustainable finance and investment decision-making.
Financial Returns
Impact investing targets measurable social and environmental outcomes alongside financial returns, typically embracing a longer-term horizon and a more active investment role. ESG integration involves incorporating environmental, social, and governance factors into traditional financial analysis to enhance risk management and identify return opportunities without sacrificing performance. Explore how these strategies compare in balancing financial goals with sustainability by learning more about their distinct approaches.
Source and External Links
What is Impact Investing? | Fidelity - Impact investing involves making purposeful investments that achieve social and environmental benefits while generating financial returns, aligning investment choices with personal values, including investing in renewable energy or avoiding certain industries, with growing popularity among Millennials and institutional investors.
What you need to know about impact investing | GIIN - Impact investing is defined by intentional commitment to measurable social or environmental impact along with financial return, covering sectors like energy, healthcare, and microfinance, and involves best practices of using data evidence, managing investments towards impact goals, and sharing learnings.
What Is Impact Investing? | NPTrust - Impact investing leverages capital to generate positive social or environmental change while also creating financial returns, challenging traditional philanthropy vs market return roles, with a growing global market valued at $1.2 trillion in 2022 and projected to reach $6 trillion by 2031, driven by increasing Millennial participation.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com