Yield farming and market making are pivotal strategies in decentralized finance (DeFi) that optimize asset returns through liquidity provision and trading activities. Yield farming involves locking cryptocurrencies in smart contracts to earn interest or rewards, while market making focuses on providing buy and sell orders to facilitate trading and capture spreads. Explore these finance methods to understand how they drive liquidity and profitability in crypto markets.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between yield farming and market making is crucial for optimizing crypto investment strategies and risk management. Yield farming focuses on earning passive income through liquidity provision in decentralized finance (DeFi) protocols, while market making involves actively providing buy and sell orders to facilitate trades and capture bid-ask spreads. Distinguishing these roles helps investors tailor their approach based on liquidity needs, risk tolerance, and potential returns. Mastery of these concepts enhances decision-making in volatile financial markets and maximizes profit opportunities.
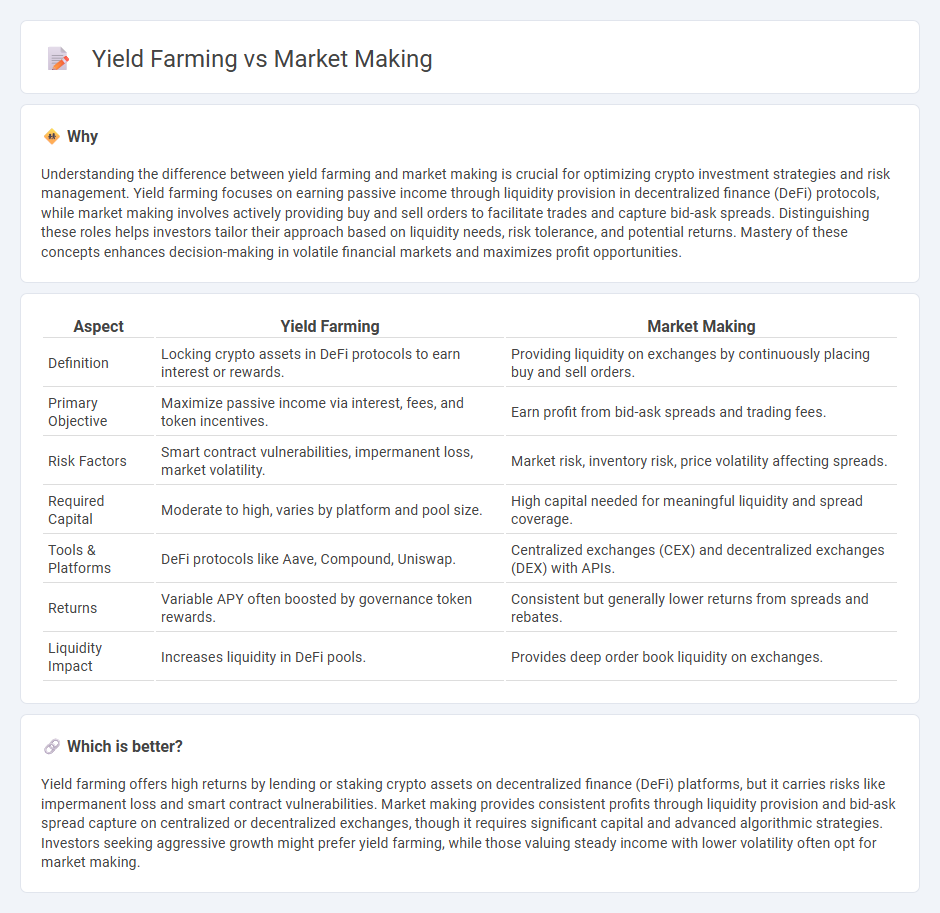
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Yield Farming | Market Making |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Locking crypto assets in DeFi protocols to earn interest or rewards. | Providing liquidity on exchanges by continuously placing buy and sell orders. |
| Primary Objective | Maximize passive income via interest, fees, and token incentives. | Earn profit from bid-ask spreads and trading fees. |
| Risk Factors | Smart contract vulnerabilities, impermanent loss, market volatility. | Market risk, inventory risk, price volatility affecting spreads. |
| Required Capital | Moderate to high, varies by platform and pool size. | High capital needed for meaningful liquidity and spread coverage. |
| Tools & Platforms | DeFi protocols like Aave, Compound, Uniswap. | Centralized exchanges (CEX) and decentralized exchanges (DEX) with APIs. |
| Returns | Variable APY often boosted by governance token rewards. | Consistent but generally lower returns from spreads and rebates. |
| Liquidity Impact | Increases liquidity in DeFi pools. | Provides deep order book liquidity on exchanges. |
Which is better?
Yield farming offers high returns by lending or staking crypto assets on decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms, but it carries risks like impermanent loss and smart contract vulnerabilities. Market making provides consistent profits through liquidity provision and bid-ask spread capture on centralized or decentralized exchanges, though it requires significant capital and advanced algorithmic strategies. Investors seeking aggressive growth might prefer yield farming, while those valuing steady income with lower volatility often opt for market making.
Connection
Yield farming leverages liquidity provision in decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms, where market making plays a crucial role by supplying assets to automated market makers (AMMs). This connection allows yield farmers to earn rewards from trading fees and incentives while market makers maintain asset liquidity and price stability. The synergy between yield farming and market making drives capital efficiency and enhances decentralized exchange ecosystems.
Key Terms
Liquidity
Market making involves providing continuous buy and sell orders to facilitate trading and maintain liquidity on exchanges, often earning profits through bid-ask spreads. Yield farming consists of locking or staking crypto assets in decentralized finance (DeFi) protocols to earn rewards, with liquidity provision typically rewarded via interest or tokens. Explore more about how each strategy impacts liquidity utilization and risk management in crypto markets.
Spread
Market making involves capturing the spread, the difference between buy and sell prices, as a primary source of profit, ensuring liquidity on trading platforms. Yield farming, however, typically generates returns through staking or lending cryptocurrencies rather than exploiting spreads between bid and ask prices. Explore our detailed analysis to understand how spread dynamics influence profitability in both strategies.
APR (Annual Percentage Rate)
Market making typically offers stable APRs ranging from 5% to 20%, driven by transaction fees and liquidity provision incentives on decentralized exchanges. Yield farming APRs can be significantly higher, often exceeding 50%, but they come with increased risks such as impermanent loss and smart contract vulnerabilities. Explore detailed comparisons of APR fluctuations and risk profiles to make informed decisions in decentralized finance.
Source and External Links
Mastering the Market Maker Trading Strategy - Market makers earn profits primarily by exploiting the bid-ask spread, managing inventory risk, and analyzing order flow, providing liquidity while adhering to regulations to avoid price manipulation.
Market Making and Mean Reversion - CIS UPenn - Market making involves continuously quoting buy and sell prices to provide liquidity and profit from the spread, typically avoiding large net positions by balancing buy and sell volumes.
What is a market maker? - Market makers use algorithms and quantitative strategies to quickly provide liquidity by quoting buy and sell prices, profiting from the spread while managing inventory risk.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com