Green bond laddering involves strategically purchasing green bonds with staggered maturities to manage liquidity and reduce reinvestment risk while supporting sustainable projects. Bond immunization is a risk management technique that aligns a bond portfolio's duration with the investor's investment horizon to protect against interest rate fluctuations. Explore the differences and benefits of these strategies to optimize your fixed-income investment approach.
Why it is important
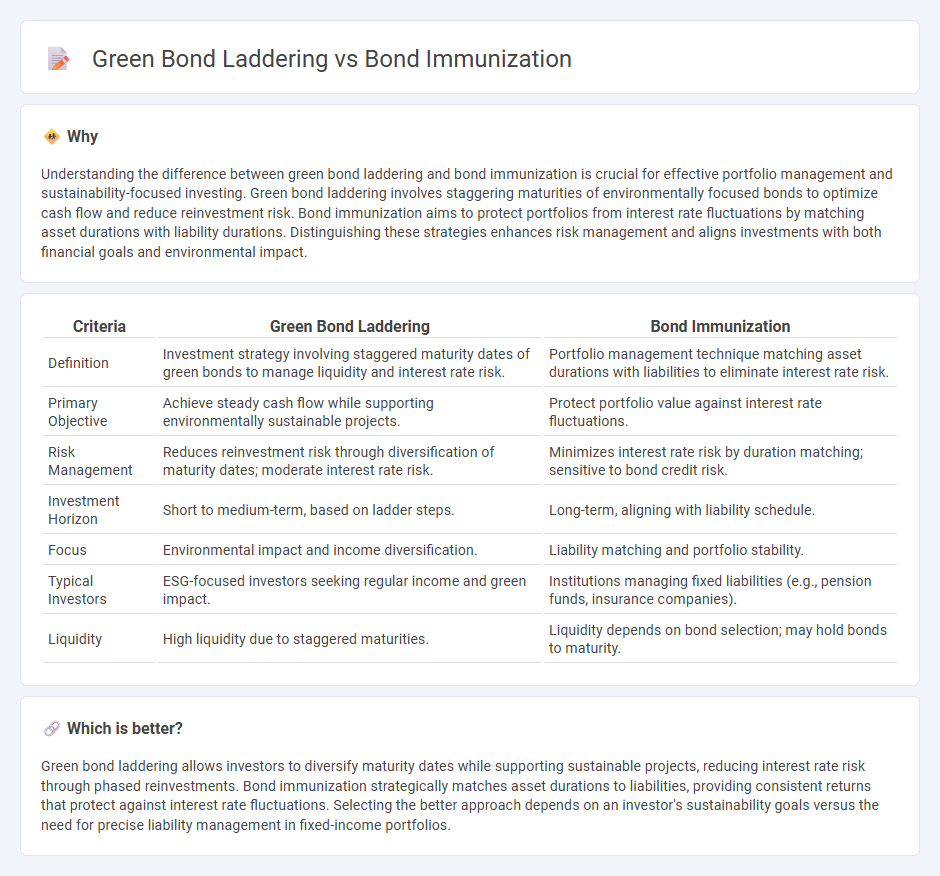
Understanding the difference between green bond laddering and bond immunization is crucial for effective portfolio management and sustainability-focused investing. Green bond laddering involves staggering maturities of environmentally focused bonds to optimize cash flow and reduce reinvestment risk. Bond immunization aims to protect portfolios from interest rate fluctuations by matching asset durations with liability durations. Distinguishing these strategies enhances risk management and aligns investments with both financial goals and environmental impact.
Comparison Table
| Criteria | Green Bond Laddering | Bond Immunization |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Investment strategy involving staggered maturity dates of green bonds to manage liquidity and interest rate risk. | Portfolio management technique matching asset durations with liabilities to eliminate interest rate risk. |
| Primary Objective | Achieve steady cash flow while supporting environmentally sustainable projects. | Protect portfolio value against interest rate fluctuations. |
| Risk Management | Reduces reinvestment risk through diversification of maturity dates; moderate interest rate risk. | Minimizes interest rate risk by duration matching; sensitive to bond credit risk. |
| Investment Horizon | Short to medium-term, based on ladder steps. | Long-term, aligning with liability schedule. |
| Focus | Environmental impact and income diversification. | Liability matching and portfolio stability. |
| Typical Investors | ESG-focused investors seeking regular income and green impact. | Institutions managing fixed liabilities (e.g., pension funds, insurance companies). |
| Liquidity | High liquidity due to staggered maturities. | Liquidity depends on bond selection; may hold bonds to maturity. |
Which is better?
Green bond laddering allows investors to diversify maturity dates while supporting sustainable projects, reducing interest rate risk through phased reinvestments. Bond immunization strategically matches asset durations to liabilities, providing consistent returns that protect against interest rate fluctuations. Selecting the better approach depends on an investor's sustainability goals versus the need for precise liability management in fixed-income portfolios.
Connection
Green bond laddering and bond immunization both aim to manage interest rate risk and cash flow timing within investment portfolios, enhancing financial stability. Green bond laddering involves purchasing green bonds with staggered maturities to ensure steady cash flows while supporting environmentally sustainable projects. Bond immunization strategically matches asset durations with liabilities, protecting portfolios from interest rate fluctuations and reinforcing long-term financial commitments.
Key Terms
Interest Rate Risk
Bond immunization is a strategy that matches the duration of assets and liabilities to minimize interest rate risk by locking in a specific yield, ensuring portfolio value stability regardless of rate fluctuations. Green bond laddering involves spreading investments across green bonds with staggered maturities, reducing reinvestment risk but exposing the portfolio to varying interest rate impacts over time. Explore how these distinct methods optimize interest rate risk management in sustainable fixed-income investing.
Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG)
Bond immunization strategically manages interest rate risk by matching bond durations to ensure portfolio value stability, while green bond laddering involves investing in staggered-maturity green bonds to optimize cash flow and reinvestment opportunities. Both approaches support ESG objectives, with green bond laddering directly targeting environmental and social projects through sustainable investments, whereas bond immunization emphasizes financial risk management with ESG-compliant bonds. Explore deeper insights into balancing risk and impact within ESG-focused fixed income strategies.
Duration Matching
Bond immunization strategically manages interest rate risk by matching the duration of assets and liabilities to protect portfolio value against rate fluctuations. Green bond laddering structures investments across staggered maturities, enhancing cash flow predictability while supporting environmental projects. Explore how duration matching techniques differ to optimize sustainable fixed-income strategies effectively.
Source and External Links
Immunization: Explained - Bond immunization is a strategy that protects an investor's portfolio from interest rate fluctuations by matching the portfolio's duration with the investment horizon, offsetting the impact of rate changes on bond value with interest income.
Duration & Portfolio Immunization - Immunization is achieved by calculating the duration of future liabilities and investing in bonds with identical duration, making the portfolio less sensitive to adverse interest rate changes.
Bond Portfolio Management - Target date immunization ensures fixed outflows can be met by setting the portfolio duration equal to the investment horizon and the portfolio value equal to the present value of liabilities, thereby minimizing portfolio value volatility due to interest rate changes.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com