Tokenization transforms traditional assets into digital tokens, enabling fractional ownership and increased liquidity in financial markets. Direct investment involves purchasing assets outright, offering full control but often requiring significant capital and less flexibility. Explore the differences in risk, accessibility, and potential returns to understand which approach suits your investment strategy best.
Why it is important
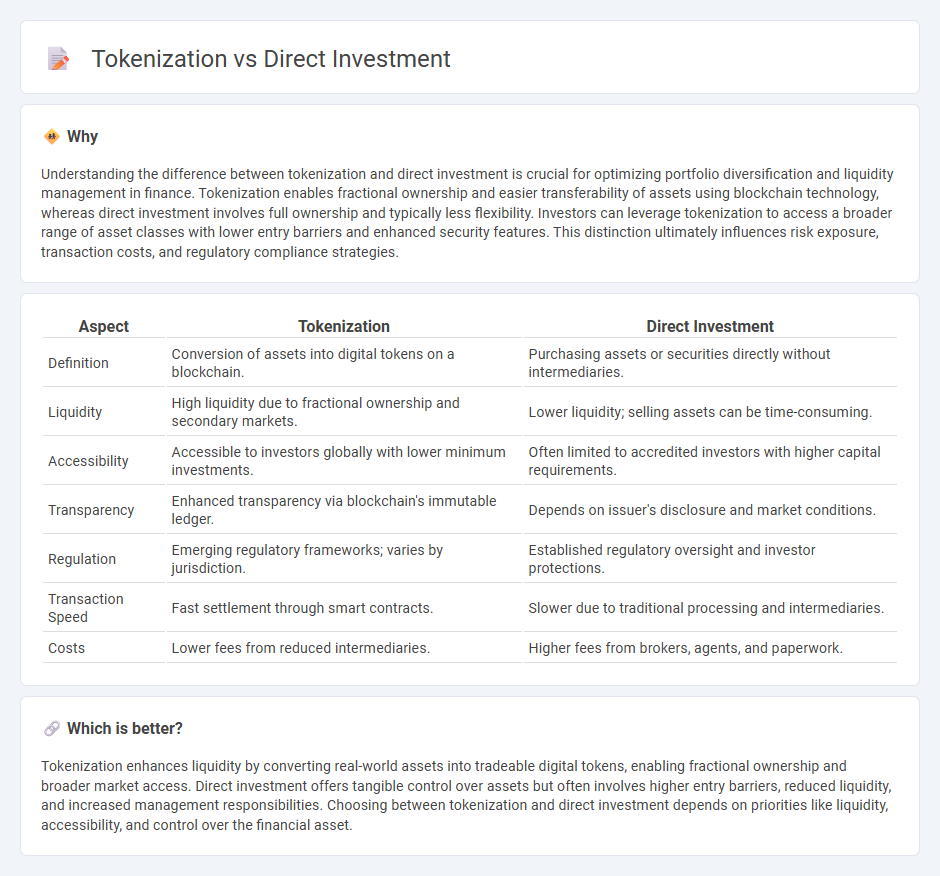
Understanding the difference between tokenization and direct investment is crucial for optimizing portfolio diversification and liquidity management in finance. Tokenization enables fractional ownership and easier transferability of assets using blockchain technology, whereas direct investment involves full ownership and typically less flexibility. Investors can leverage tokenization to access a broader range of asset classes with lower entry barriers and enhanced security features. This distinction ultimately influences risk exposure, transaction costs, and regulatory compliance strategies.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Tokenization | Direct Investment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Conversion of assets into digital tokens on a blockchain. | Purchasing assets or securities directly without intermediaries. |
| Liquidity | High liquidity due to fractional ownership and secondary markets. | Lower liquidity; selling assets can be time-consuming. |
| Accessibility | Accessible to investors globally with lower minimum investments. | Often limited to accredited investors with higher capital requirements. |
| Transparency | Enhanced transparency via blockchain's immutable ledger. | Depends on issuer's disclosure and market conditions. |
| Regulation | Emerging regulatory frameworks; varies by jurisdiction. | Established regulatory oversight and investor protections. |
| Transaction Speed | Fast settlement through smart contracts. | Slower due to traditional processing and intermediaries. |
| Costs | Lower fees from reduced intermediaries. | Higher fees from brokers, agents, and paperwork. |
Which is better?
Tokenization enhances liquidity by converting real-world assets into tradeable digital tokens, enabling fractional ownership and broader market access. Direct investment offers tangible control over assets but often involves higher entry barriers, reduced liquidity, and increased management responsibilities. Choosing between tokenization and direct investment depends on priorities like liquidity, accessibility, and control over the financial asset.
Connection
Tokenization transforms traditional assets into digital tokens on a blockchain, enabling fractional ownership and increased liquidity. Direct investment leverages tokenization by allowing investors to buy specific asset tokens without intermediaries, lowering entry barriers and transaction costs. This synergy fosters greater accessibility and transparency in financial markets.
Key Terms
Ownership
Direct investment provides clear legal ownership of physical or financial assets, ensuring traditional rights such as voting and profit entitlement. Tokenization transforms ownership into digital tokens on a blockchain, enabling fractional ownership and enhanced liquidity without transferring actual asset possession. Explore the advantages and implications of both ownership models to make informed investment decisions.
Liquidity
Direct investment typically involves longer holding periods with limited liquidity due to the challenges of finding buyers and completing transactions. Tokenization enhances liquidity by converting assets into digital tokens that can be traded on secondary markets, providing faster and more flexible access to capital. Explore how tokenization is revolutionizing asset liquidity and investment strategies.
Fractionalization
Direct investment involves acquiring full ownership or significant stakes in assets, while tokenization enables fractional ownership by dividing assets into digital tokens on a blockchain. Fractionalization through tokenization enhances liquidity, lowers entry barriers, and allows investors to diversify portfolios with smaller capital commitments. Discover how fractionalization is transforming investment opportunities and democratizing access to high-value assets.
Source and External Links
Direct Investments - Direct investment is an investment in a company or asset typically made directly by a family office or high-net-worth individual, avoiding intermediary fees and allowing closer alignment with investor values, and this strategy is growing increasingly popular among wealthy investors.
What Is Direct Investment? - Back to Basics Compilation Book - Direct investment involves acquiring a lasting interest in a foreign enterprise to gain control or significant influence over management, and it can take forms such as greenfield (building new facilities) or brownfield investment (acquiring existing facilities), often attracting governments seeking capital and jobs.
Direct Investing - Direct investing allows individuals to buy shares directly from companies through plans like direct stock plans (DSP) or dividend reinvestment plans (DRIP), often saving on commissions but requiring understanding of specific plan rules and schedules.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com