Degen box and option contract are distinct financial instruments used for trading and risk management; degen box strategies involve complex, high-risk option spreads aiming to capitalize on volatility, whereas option contracts allow the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an asset at a predetermined price. Degen boxes often appeal to experienced traders seeking speculative gains, while option contracts are fundamental tools for hedging and income generation in portfolios. Explore the mechanics and strategic uses of each to optimize your financial decisions.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between a degen box and an option contract is crucial in finance because it directly impacts risk management and investment strategy. A degen box typically involves highly speculative, high-risk trades with uncertain outcomes, whereas an option contract is a regulated financial derivative offering the right but not the obligation to buy or sell an asset at a predetermined price. Knowing these distinctions helps investors make informed decisions, optimize portfolio performance, and avoid substantial losses. Mastery of these concepts enhances strategic planning in derivatives trading and risk assessment.
Comparison Table
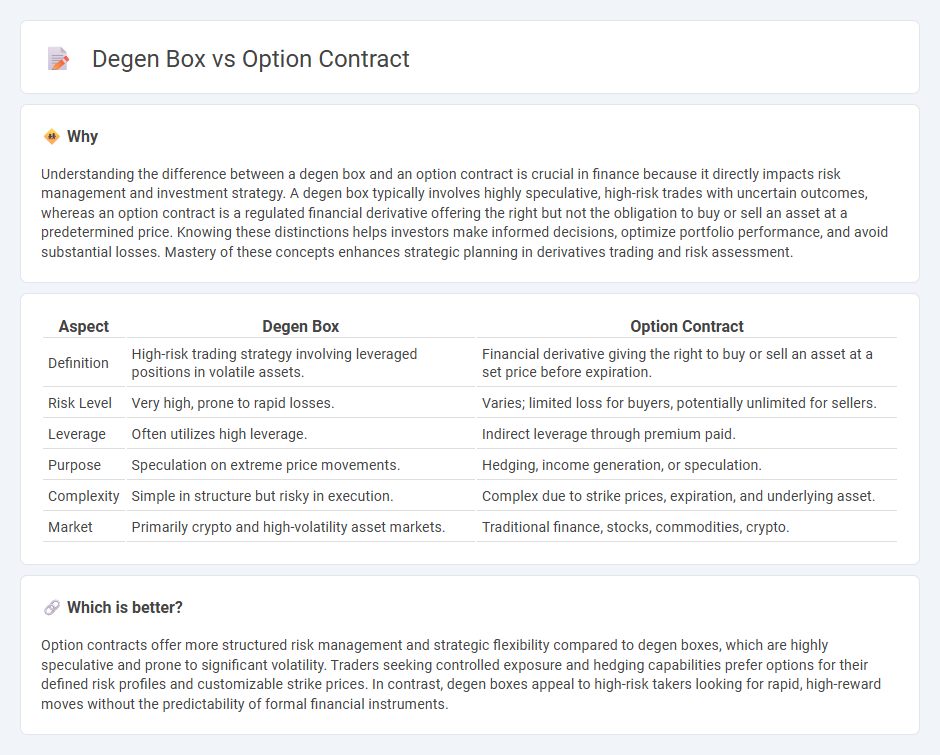
| Aspect | Degen Box | Option Contract |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | High-risk trading strategy involving leveraged positions in volatile assets. | Financial derivative giving the right to buy or sell an asset at a set price before expiration. |
| Risk Level | Very high, prone to rapid losses. | Varies; limited loss for buyers, potentially unlimited for sellers. |
| Leverage | Often utilizes high leverage. | Indirect leverage through premium paid. |
| Purpose | Speculation on extreme price movements. | Hedging, income generation, or speculation. |
| Complexity | Simple in structure but risky in execution. | Complex due to strike prices, expiration, and underlying asset. |
| Market | Primarily crypto and high-volatility asset markets. | Traditional finance, stocks, commodities, crypto. |
Which is better?
Option contracts offer more structured risk management and strategic flexibility compared to degen boxes, which are highly speculative and prone to significant volatility. Traders seeking controlled exposure and hedging capabilities prefer options for their defined risk profiles and customizable strike prices. In contrast, degen boxes appeal to high-risk takers looking for rapid, high-reward moves without the predictability of formal financial instruments.
Connection
Degen boxes in finance represent high-risk, speculative trading environments often associated with decentralized finance (DeFi), where traders engage in leveraged positions using options contracts. Option contracts provide the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an asset at a specified price before expiration, enabling strategic hedging or speculative plays within degen boxes. The interplay between degen boxes and options contracts amplifies potential gains and losses, attracting risk-tolerant investors aiming for significant returns in volatile markets.
Key Terms
Strike Price
The strike price in an option contract determines the fixed price at which the underlying asset can be bought or sold, crucial for defining potential profit and loss scenarios. In contrast, the degen box strategy uses multiple strike prices to create a range-bound position, optimizing returns within a specific price corridor. Explore further to understand how strike prices shape these distinct trading mechanisms.
Leverage
Option contracts provide leverage by allowing traders to control large positions with a relatively small capital outlay, amplifying potential returns while limiting risk to the premium paid. Degen boxes offer higher leverage through margin trading on decentralized platforms, often exposing users to increased liquidation risk but enabling significant exposure to volatile assets. Explore the comparative mechanics of leverage in option contracts and degen boxes to optimize your trading strategy.
Risk Management
Option contracts offer structured risk management by allowing investors to hedge positions through defined strike prices and expiration dates, limiting potential losses to the premium paid. In contrast, degen boxes involve higher risk exposure due to their decentralized, often leveraged nature and lack of standardized protections, resulting in potentially significant gains or losses. Explore more to understand how these instruments can fit different risk management strategies.
Source and External Links
Options: Calls and Puts - Overview, Examples, Trading Long & Short - An option contract is a derivative giving the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an asset at a specified strike price by the expiration date, with calls allowing buying and puts allowing selling of the asset.
What is an options contract? (Definition and examples) - Indeed - An options contract is an agreement between two parties facilitating a transaction on an asset, including terms like strike price, intrinsic value, maturity date, and premium that affect the contract's value and execution.
option contract | Wex | US Law | LII / Legal Information Institute - In law, an option contract is a promise to keep an offer open for acceptance within a specified period, preventing the offeror from revoking it during that time, often requiring consideration to be enforceable.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com