Liquidity staking allows investors to earn rewards by locking their assets in a blockchain protocol while retaining the ability to trade tokenized staking derivatives. Lending involves providing assets to borrowers in exchange for interest payments, offering passive income with varying risk levels depending on the platform and collateral. Explore these methods to determine which strategy maximizes your portfolio's yield and flexibility.
Why it is important
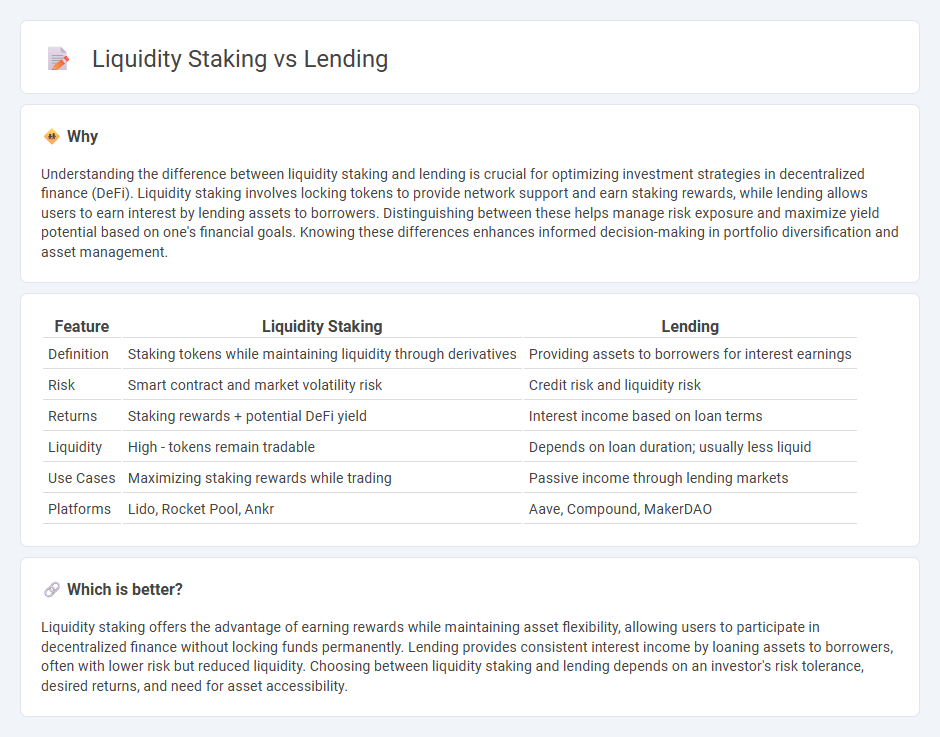
Understanding the difference between liquidity staking and lending is crucial for optimizing investment strategies in decentralized finance (DeFi). Liquidity staking involves locking tokens to provide network support and earn staking rewards, while lending allows users to earn interest by lending assets to borrowers. Distinguishing between these helps manage risk exposure and maximize yield potential based on one's financial goals. Knowing these differences enhances informed decision-making in portfolio diversification and asset management.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Liquidity Staking | Lending |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Staking tokens while maintaining liquidity through derivatives | Providing assets to borrowers for interest earnings |
| Risk | Smart contract and market volatility risk | Credit risk and liquidity risk |
| Returns | Staking rewards + potential DeFi yield | Interest income based on loan terms |
| Liquidity | High - tokens remain tradable | Depends on loan duration; usually less liquid |
| Use Cases | Maximizing staking rewards while trading | Passive income through lending markets |
| Platforms | Lido, Rocket Pool, Ankr | Aave, Compound, MakerDAO |
Which is better?
Liquidity staking offers the advantage of earning rewards while maintaining asset flexibility, allowing users to participate in decentralized finance without locking funds permanently. Lending provides consistent interest income by loaning assets to borrowers, often with lower risk but reduced liquidity. Choosing between liquidity staking and lending depends on an investor's risk tolerance, desired returns, and need for asset accessibility.
Connection
Liquidity staking and lending are interconnected through the utilization of staked assets as collateral or liquidity sources in decentralized finance (DeFi) protocols. Stakers lock tokens to earn rewards, which can then be lent out to borrowers, creating a dynamic flow of capital that enhances market liquidity and asset utility. This synergy boosts yield opportunities while maintaining asset security within blockchain ecosystems.
Key Terms
Collateral
Lending platforms allow users to borrow assets by providing collateral, often in the form of cryptocurrencies, which secures the loan and reduces risk for lenders. Liquidity staking involves locking tokens in a staking protocol to provide liquidity, earning rewards without the need for direct collateral backing each transaction. Explore the differences in collateral use between lending and liquidity staking to optimize your DeFi strategy.
Yield
Lending platforms typically offer fixed or variable interest rates by allowing users to loan their assets to borrowers, generating yield from interest payments. Liquidity staking involves locking tokens in a protocol to support network operations and earn staking rewards, often combining yield from transaction fees and protocol incentives. Explore detailed comparisons to understand which strategy maximizes your crypto portfolio's yield potential.
Lock-up Period
Lending in DeFi involves users locking their assets for a fixed lock-up period, typically ranging from days to months, which impacts access to funds but often yields higher interest rates. Liquidity staking offers more flexible lock-up durations, sometimes with instant or short-term withdrawal options, balancing staking rewards with asset accessibility. Explore detailed comparisons to optimize your investment strategy based on lock-up requirements.
Source and External Links
Marketplace Lending - FDIC - Marketplace lending is an alternative financial model where borrowers and lenders are connected through online platforms without traditional bank intermediaries, often using proprietary credit scoring and allowing both retail and institutional investors to fund loans.
Apply for a Personal Loan - Lending Club - Personal loans provide fixed-term, fixed-rate borrowing for a variety of purposes with no collateral required, and approval depends on credit score, income, and debt-to-income ratio, commonly used for debt consolidation and unexpected expenses.
Investment Lending - Inter-American Development Bank - Offers short-, medium-, and long-term loans targeting economic and social development projects, including loans to support micro, small, and medium enterprises through intermediaries and loans linked directly to sustainable development results.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com