Impact investing targets measurable social and environmental outcomes alongside financial returns, often funding projects with quantifiable benefits like renewable energy or affordable housing. Sustainable investing integrates environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria into investment decisions to promote long-term value and risk management without compromising financial performance. Discover how these strategies shape the future of ethical finance and drive meaningful change.
Why it is important
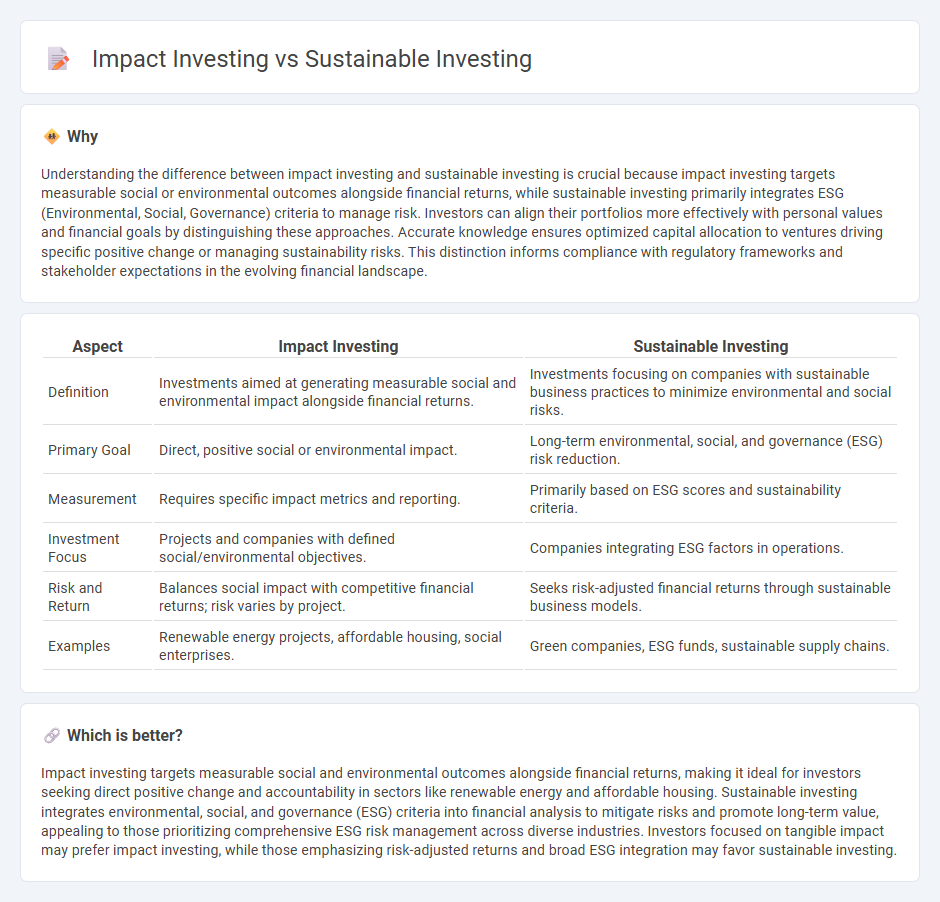
Understanding the difference between impact investing and sustainable investing is crucial because impact investing targets measurable social or environmental outcomes alongside financial returns, while sustainable investing primarily integrates ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance) criteria to manage risk. Investors can align their portfolios more effectively with personal values and financial goals by distinguishing these approaches. Accurate knowledge ensures optimized capital allocation to ventures driving specific positive change or managing sustainability risks. This distinction informs compliance with regulatory frameworks and stakeholder expectations in the evolving financial landscape.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Impact Investing | Sustainable Investing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Investments aimed at generating measurable social and environmental impact alongside financial returns. | Investments focusing on companies with sustainable business practices to minimize environmental and social risks. |
| Primary Goal | Direct, positive social or environmental impact. | Long-term environmental, social, and governance (ESG) risk reduction. |
| Measurement | Requires specific impact metrics and reporting. | Primarily based on ESG scores and sustainability criteria. |
| Investment Focus | Projects and companies with defined social/environmental objectives. | Companies integrating ESG factors in operations. |
| Risk and Return | Balances social impact with competitive financial returns; risk varies by project. | Seeks risk-adjusted financial returns through sustainable business models. |
| Examples | Renewable energy projects, affordable housing, social enterprises. | Green companies, ESG funds, sustainable supply chains. |
Which is better?
Impact investing targets measurable social and environmental outcomes alongside financial returns, making it ideal for investors seeking direct positive change and accountability in sectors like renewable energy and affordable housing. Sustainable investing integrates environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria into financial analysis to mitigate risks and promote long-term value, appealing to those prioritizing comprehensive ESG risk management across diverse industries. Investors focused on tangible impact may prefer impact investing, while those emphasizing risk-adjusted returns and broad ESG integration may favor sustainable investing.
Connection
Impact investing and sustainable investing both prioritize generating positive environmental and social outcomes alongside financial returns, integrating Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) criteria to guide investment decisions. Impact investing specifically targets measurable social and environmental impact, often funding projects in renewable energy, affordable housing, or clean water, which aligns with sustainable investing's broader goal of supporting long-term economic resilience and responsible resource management. Their connection lies in fostering capital allocation that promotes ethical growth and addresses global challenges such as climate change, social inequality, and corporate responsibility.
Key Terms
ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance)
Sustainable investing emphasizes integrating Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) criteria to minimize risk and promote long-term value by selecting companies with responsible practices. Impact investing directly targets measurable positive social and environmental outcomes alongside financial returns, often supporting projects or businesses with clear, intentional effects. Explore the differences and benefits of these strategies to enhance your investment approach with ESG insights.
Intentionality
Sustainable investing integrates environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria to minimize risks and promote long-term value, while impact investing intentionally targets measurable positive social or environmental outcomes alongside financial returns. The core distinction lies in intentionality; impact investing explicitly seeks to generate social impact as a primary goal, whereas sustainable investing incorporates ethical considerations to enhance financial performance. Explore these investment strategies further to understand how intentionality shapes their objectives and outcomes.
Measurable Outcomes
Sustainable investing prioritizes environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors to manage risks and generate long-term returns, whereas impact investing targets specific, measurable social or environmental outcomes alongside financial gains. Key metrics such as carbon footprint reduction, community development indices, and social return on investment (SROI) are essential to evaluating impact investments. Explore detailed frameworks and case studies to understand how measurable outcomes drive investment decisions.
Source and External Links
What Is Sustainable Investing? - Sustainable investing integrates environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors into investment decisions to achieve financial returns while promoting long-term social and environmental value.
SUSTAINABLE INVESTING - Major Sustainability - Penn State - Sustainable investing uses various strategies like ESG integration, positive and negative screening, and impact investing to balance financial returns with social and environmental goals.
Sustainability Solutions - MSCI provides data-driven tools and ratings that help investors measure, report, and manage ESG risks and opportunities, enhancing sustainability integration across asset classes for long-term investment resilience.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com