Tokenized treasuries represent digital versions of government bonds secured on blockchain platforms, enabling fractional ownership and enhanced liquidity. Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) are state-backed digital currencies designed for secure, efficient retail and wholesale transactions within a national banking system. Explore the detailed differences and potential impacts of tokenized treasuries versus CBDCs to understand their role in modern finance.
Why it is important
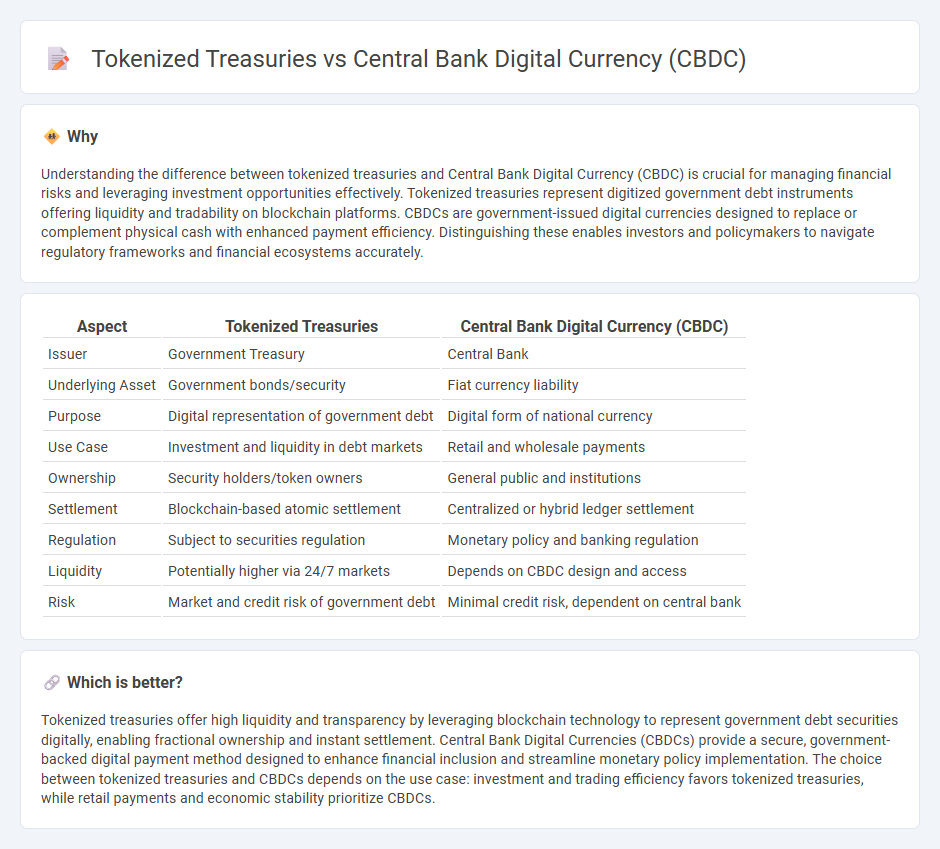
Understanding the difference between tokenized treasuries and Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC) is crucial for managing financial risks and leveraging investment opportunities effectively. Tokenized treasuries represent digitized government debt instruments offering liquidity and tradability on blockchain platforms. CBDCs are government-issued digital currencies designed to replace or complement physical cash with enhanced payment efficiency. Distinguishing these enables investors and policymakers to navigate regulatory frameworks and financial ecosystems accurately.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Tokenized Treasuries | Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC) |
|---|---|---|
| Issuer | Government Treasury | Central Bank |
| Underlying Asset | Government bonds/security | Fiat currency liability |
| Purpose | Digital representation of government debt | Digital form of national currency |
| Use Case | Investment and liquidity in debt markets | Retail and wholesale payments |
| Ownership | Security holders/token owners | General public and institutions |
| Settlement | Blockchain-based atomic settlement | Centralized or hybrid ledger settlement |
| Regulation | Subject to securities regulation | Monetary policy and banking regulation |
| Liquidity | Potentially higher via 24/7 markets | Depends on CBDC design and access |
| Risk | Market and credit risk of government debt | Minimal credit risk, dependent on central bank |
Which is better?
Tokenized treasuries offer high liquidity and transparency by leveraging blockchain technology to represent government debt securities digitally, enabling fractional ownership and instant settlement. Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) provide a secure, government-backed digital payment method designed to enhance financial inclusion and streamline monetary policy implementation. The choice between tokenized treasuries and CBDCs depends on the use case: investment and trading efficiency favors tokenized treasuries, while retail payments and economic stability prioritize CBDCs.
Connection
Tokenized treasuries enable the digital representation of government debt securities on blockchain platforms, facilitating faster settlement and increased liquidity. Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC) acts as a digital legal tender issued by the central bank, providing a stable and secure medium of exchange compatible with tokenized assets. The integration of tokenized treasuries with CBDC can revolutionize financial markets by enhancing transparency, reducing transaction costs, and improving monetary policy implementation.
Key Terms
Digital Currency
Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC) offers a state-backed digital payment solution designed to enhance monetary policy efficiency and financial inclusion, while tokenized treasuries represent digital assets backed by government securities, primarily aiming to optimize liquidity and secondary market trading. CBDCs operate as legal tender issued by central banks, incorporating privacy and security protocols to ensure trust in digital transactions. Explore the nuances, benefits, and implementation strategies of digital currencies to understand their evolving role in the financial ecosystem.
Tokenization
Tokenization transforms traditional assets like treasuries into digital tokens, enabling enhanced liquidity, fractional ownership, and streamlined trading on blockchain networks. Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC) serves as a digital form of fiat money issued by central banks, focusing primarily on payment efficiency and financial inclusion rather than asset representation. Explore the distinctions and benefits of tokenization versus CBDCs to understand their impact on modern financial ecosystems.
Sovereign Debt
Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC) represents a digital form of a nation's fiat currency issued directly by the central bank, ensuring sovereign control and financial stability. Tokenized treasuries convert government debt instruments into blockchain-based tokens, enhancing transparency, liquidity, and fractional ownership of sovereign debt. Explore the distinctions and implications of CBDCs versus tokenized treasuries to understand their impact on modern sovereign debt management.
Source and External Links
Central Bank Digital Currency | European Data Protection Supervisor - CBDC is a new form of digital money issued by central banks to simplify transactions, with adoption growing worldwide due to shifts toward digital payments and competition from cryptocurrencies.
Central bank digital currency - Wikipedia - A CBDC is a digital counterpart to fiat money issued by central banks, serving as a means of payment, unit of account, and store of value, and is considered a liability of the central bank similar to physical currency.
Central Bank Digital Currency Tracker - Atlantic Council - CBDCs are digital forms of national currencies that aim to increase financial inclusion, improve payment efficiency, lower transaction costs, and provide programmable money controlled by governments.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com