Altcoins staking involves locking up digital assets to support blockchain operations and earn rewards, while yield farming focuses on providing liquidity to decentralized finance (DeFi) protocols in exchange for interest or tokens. Staking offers more predictable income with lower risk compared to the high-risk, high-reward nature of yield farming. Explore these strategies further to understand how they maximize crypto asset growth.
Why it is important
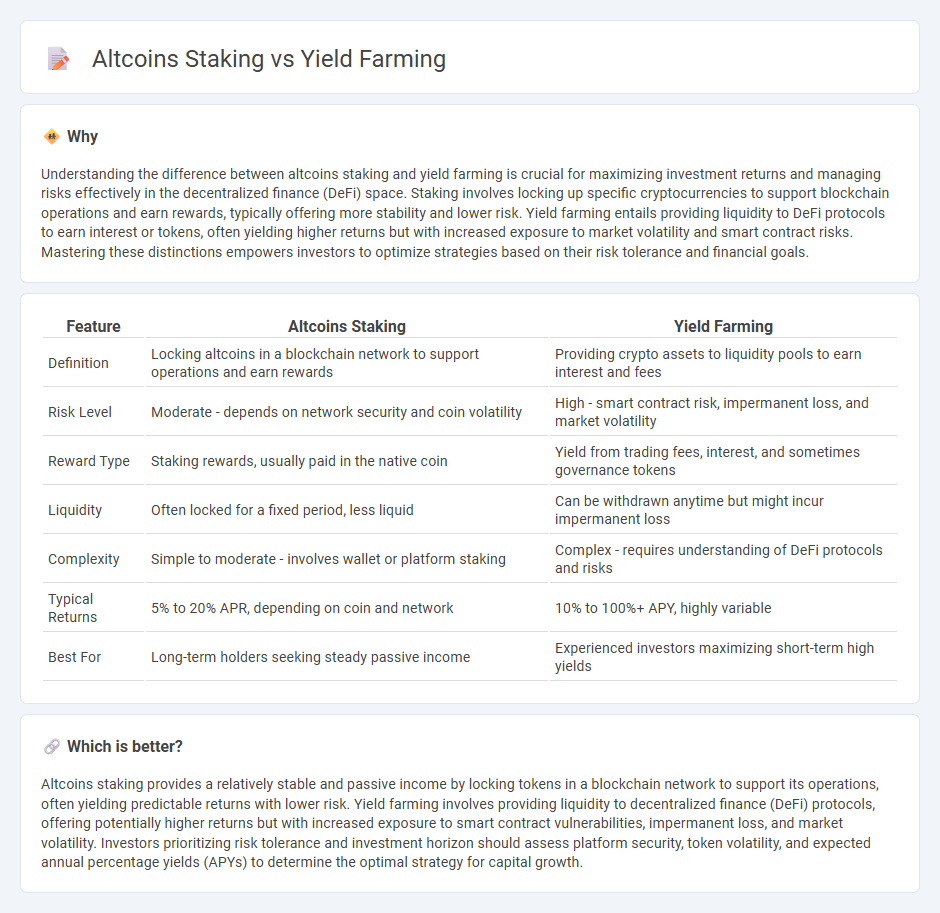
Understanding the difference between altcoins staking and yield farming is crucial for maximizing investment returns and managing risks effectively in the decentralized finance (DeFi) space. Staking involves locking up specific cryptocurrencies to support blockchain operations and earn rewards, typically offering more stability and lower risk. Yield farming entails providing liquidity to DeFi protocols to earn interest or tokens, often yielding higher returns but with increased exposure to market volatility and smart contract risks. Mastering these distinctions empowers investors to optimize strategies based on their risk tolerance and financial goals.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Altcoins Staking | Yield Farming |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Locking altcoins in a blockchain network to support operations and earn rewards | Providing crypto assets to liquidity pools to earn interest and fees |
| Risk Level | Moderate - depends on network security and coin volatility | High - smart contract risk, impermanent loss, and market volatility |
| Reward Type | Staking rewards, usually paid in the native coin | Yield from trading fees, interest, and sometimes governance tokens |
| Liquidity | Often locked for a fixed period, less liquid | Can be withdrawn anytime but might incur impermanent loss |
| Complexity | Simple to moderate - involves wallet or platform staking | Complex - requires understanding of DeFi protocols and risks |
| Typical Returns | 5% to 20% APR, depending on coin and network | 10% to 100%+ APY, highly variable |
| Best For | Long-term holders seeking steady passive income | Experienced investors maximizing short-term high yields |
Which is better?
Altcoins staking provides a relatively stable and passive income by locking tokens in a blockchain network to support its operations, often yielding predictable returns with lower risk. Yield farming involves providing liquidity to decentralized finance (DeFi) protocols, offering potentially higher returns but with increased exposure to smart contract vulnerabilities, impermanent loss, and market volatility. Investors prioritizing risk tolerance and investment horizon should assess platform security, token volatility, and expected annual percentage yields (APYs) to determine the optimal strategy for capital growth.
Connection
Altcoins staking and yield farming both involve locking up cryptocurrency assets to generate passive income, leveraging decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms. Staking altcoins secures blockchain networks through proof-of-stake mechanisms while earning rewards, whereas yield farming provides liquidity to DeFi protocols in exchange for interest or tokens. These strategies utilize smart contracts to optimize asset utilization and maximize returns within the altcoin ecosystem.
Key Terms
Liquidity Pools
Yield farming and altcoin staking both leverage liquidity pools but differ fundamentally in mechanics and risk profile. Yield farming involves providing assets to decentralized finance (DeFi) protocols' liquidity pools, earning returns from trading fees and token incentives, while altcoin staking typically means locking coins in a blockchain's proof-of-stake mechanism to support network operations and receive staking rewards. Explore deeper insights on how liquidity pools impact yield strategies and investor decisions.
Annual Percentage Yield (APY)
Yield farming often delivers higher Annual Percentage Yields (APYs) compared to altcoins staking due to its complex mechanisms involving liquidity provision and reward tokens, sometimes exceeding 100% APY. Altcoins staking typically offers lower, more stable APYs ranging from 5% to 20%, reflecting the process of securing networks and validating transactions. Explore detailed comparisons and risk factors to optimize your investment strategies in decentralized finance (DeFi).
Lock-up Period
Yield farming often requires flexible lock-up periods that can range from a few days to several weeks, impacting liquidity and potential returns. Altcoins staking usually features fixed lock-up durations, which vary by blockchain protocol and can affect reward rates and asset accessibility. Explore detailed comparisons to optimize your crypto investment strategy.
Source and External Links
What is yield farming and how does it work? - Coinbase - Yield farming, or liquidity mining, is a DeFi practice where users provide liquidity to protocols and earn rewards in the platform's tokens, but it involves risks like impermanent loss and smart contract vulnerabilities.
What Is Yield Farming? Meaning and Definition - Chainlink - Yield farming incentivizes users to deposit digital assets into DeFi protocols to bootstrap liquidity and distribute governance tokens fairly, generating returns often expressed as annual percentage returns.
Yield Farming in DeFi Explained: Possibilities, Risks & Strategies - Yield farming has evolved from inflationary token rewards to sustainable real yields based on platform revenue, increasingly incorporating AI and cross-chain functionality amid growing regulatory oversight.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com