Flash loan attacks exploit uncollateralized loans to manipulate DeFi protocols, causing rapid and substantial financial losses. Double-spending involves the fraudulent reuse of digital currency in blockchain networks, undermining transaction integrity. Explore detailed mechanisms and prevention strategies to safeguard your investments.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between flash loan attacks and double-spending is crucial in finance to effectively safeguard digital assets and maintain transactional integrity. Flash loan attacks exploit decentralized finance (DeFi) protocols by borrowing large sums without collateral to manipulate market prices or governance votes within a single transaction block. Double-spending involves the fraudulent use of the same digital currency units in multiple transactions, undermining trust in blockchain systems. Identifying these distinct threats enables the development of targeted security measures and risk management strategies.
Comparison Table
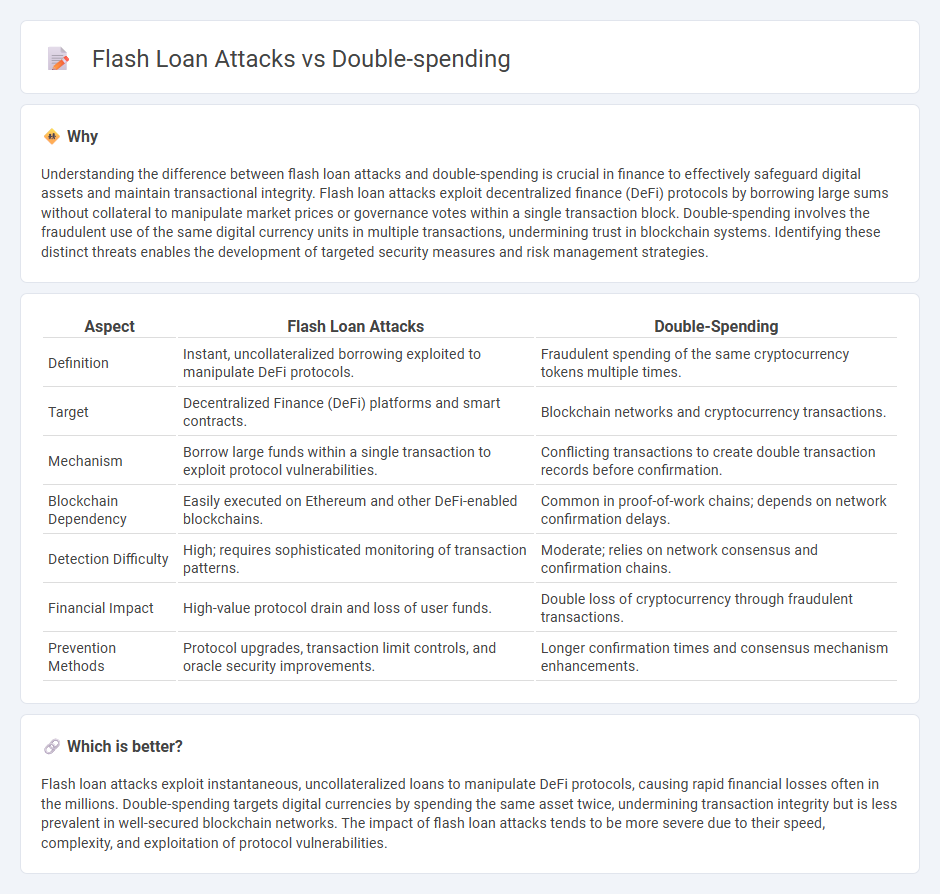
| Aspect | Flash Loan Attacks | Double-Spending |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Instant, uncollateralized borrowing exploited to manipulate DeFi protocols. | Fraudulent spending of the same cryptocurrency tokens multiple times. |
| Target | Decentralized Finance (DeFi) platforms and smart contracts. | Blockchain networks and cryptocurrency transactions. |
| Mechanism | Borrow large funds within a single transaction to exploit protocol vulnerabilities. | Conflicting transactions to create double transaction records before confirmation. |
| Blockchain Dependency | Easily executed on Ethereum and other DeFi-enabled blockchains. | Common in proof-of-work chains; depends on network confirmation delays. |
| Detection Difficulty | High; requires sophisticated monitoring of transaction patterns. | Moderate; relies on network consensus and confirmation chains. |
| Financial Impact | High-value protocol drain and loss of user funds. | Double loss of cryptocurrency through fraudulent transactions. |
| Prevention Methods | Protocol upgrades, transaction limit controls, and oracle security improvements. | Longer confirmation times and consensus mechanism enhancements. |
Which is better?
Flash loan attacks exploit instantaneous, uncollateralized loans to manipulate DeFi protocols, causing rapid financial losses often in the millions. Double-spending targets digital currencies by spending the same asset twice, undermining transaction integrity but is less prevalent in well-secured blockchain networks. The impact of flash loan attacks tends to be more severe due to their speed, complexity, and exploitation of protocol vulnerabilities.
Connection
Flash loan attacks exploit the ability to borrow large amounts of cryptocurrency instantly without collateral, enabling attackers to manipulate smart contract vulnerabilities and execute double-spending by rapidly borrowing, using, and repaying funds within a single transaction. Double-spending occurs when the same digital asset is spent more than once, often facilitated by these attack methods in decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms lacking proper transaction finality. This connection highlights security risks in blockchain protocols where flash loans amplify the potential for repeated, fraudulent transactions affecting liquidity and trust.
Key Terms
Transaction Validity
Double-spending attacks exploit transaction validity by attempting to spend the same digital asset multiple times, undermining blockchain consensus and trust. Flash loan attacks manipulate transaction validity through rapid borrowing and complex operations within a single block, enabling attackers to exploit price oracle vulnerabilities and execute arbitrage or liquidation exploits. Explore detailed mechanisms and defense strategies to safeguard transaction validity in these attacks.
Smart Contract Vulnerability
Double-spending attacks exploit blockchain consensus delays, allowing malicious actors to spend the same cryptocurrency multiple times by reversing transactions before finalization. Flash loan attacks leverage unsecured, instantaneous borrowing to manipulate smart contract states or exploit logic flaws, often draining DeFi protocols of assets in a single transaction. Explore our in-depth analysis to understand how these vulnerabilities threaten decentralized finance and learn best practices to safeguard smart contracts.
Consensus Mechanism
Double-spending exploits vulnerabilities in consensus mechanisms by allowing attackers to spend the same cryptocurrency tokens more than once, often targeting slower finality in Proof of Work (PoW) blockchains. Flash loan attacks leverage instant, uncollateralized loans to manipulate on-chain prices and governance, exploiting contract logic rather than consensus protocols themselves. Explore further to understand how different consensus designs impact vulnerability to these attack vectors.
Source and External Links
Double-spending - Wikipedia - Double-spending is the unauthorized spending of the same money more than once, which challenges the scarce nature of money; digital currencies typically prevent this by using a trusted authority or cryptographic techniques to verify transactions and prevent duplication.
What is Double Spending in Blockchain? - GeeksforGeeks - Double spending in blockchain occurs when someone tries to spend the same digital currency multiple times and is prevented by consensus mechanisms like Proof of Work or Proof of Stake that validate transactions and secure the network.
Double Spending Meaning - Ledger - Double spending is the risk in digital currencies where the same units can be used for several transactions simultaneously, but blockchain validation by miners or validators makes successful double-spends very difficult, requiring massive computing resources typically associated with 51% attacks.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com