Tokenization of real-world assets leverages blockchain technology to convert ownership rights into digital tokens, enhancing liquidity and transparency compared to traditional securitization processes that bundle financial assets into securities. While securitization relies on intermediaries and often faces regulatory complexities, tokenization offers fractional ownership, faster settlements, and accessibility to a broader investor base. Explore how tokenization is reshaping asset management and disrupting conventional finance models.
Why it is important
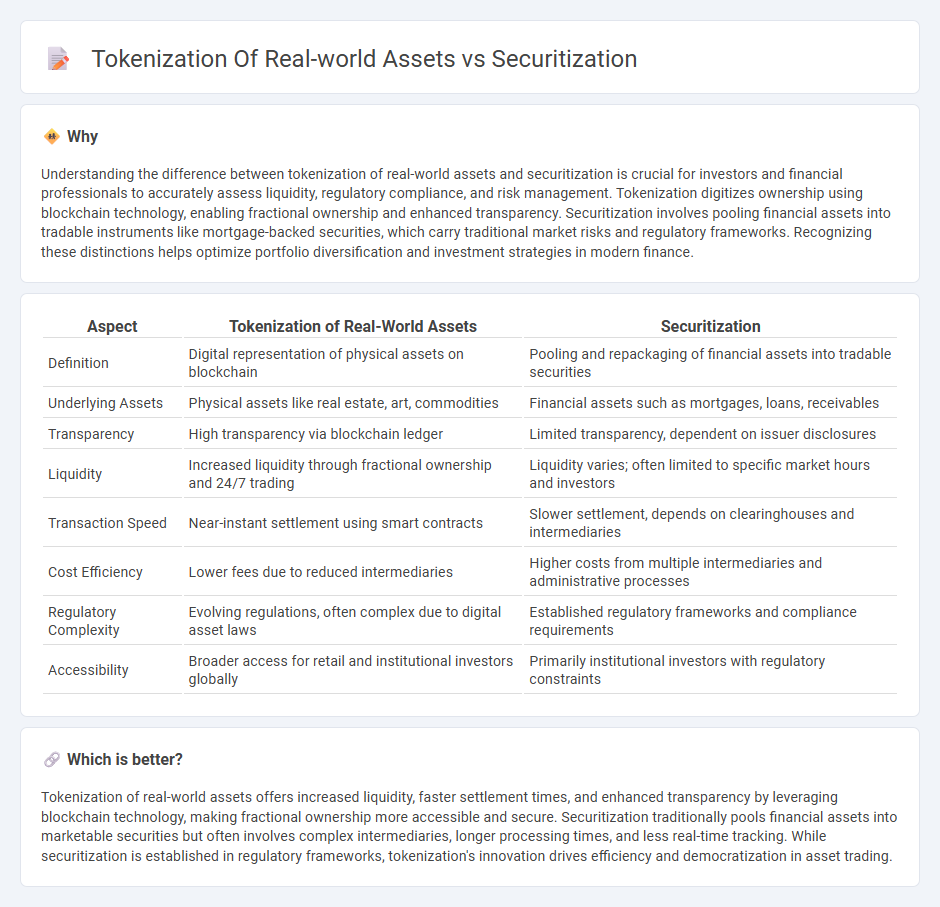
Understanding the difference between tokenization of real-world assets and securitization is crucial for investors and financial professionals to accurately assess liquidity, regulatory compliance, and risk management. Tokenization digitizes ownership using blockchain technology, enabling fractional ownership and enhanced transparency. Securitization involves pooling financial assets into tradable instruments like mortgage-backed securities, which carry traditional market risks and regulatory frameworks. Recognizing these distinctions helps optimize portfolio diversification and investment strategies in modern finance.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Tokenization of Real-World Assets | Securitization |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Digital representation of physical assets on blockchain | Pooling and repackaging of financial assets into tradable securities |
| Underlying Assets | Physical assets like real estate, art, commodities | Financial assets such as mortgages, loans, receivables |
| Transparency | High transparency via blockchain ledger | Limited transparency, dependent on issuer disclosures |
| Liquidity | Increased liquidity through fractional ownership and 24/7 trading | Liquidity varies; often limited to specific market hours and investors |
| Transaction Speed | Near-instant settlement using smart contracts | Slower settlement, depends on clearinghouses and intermediaries |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower fees due to reduced intermediaries | Higher costs from multiple intermediaries and administrative processes |
| Regulatory Complexity | Evolving regulations, often complex due to digital asset laws | Established regulatory frameworks and compliance requirements |
| Accessibility | Broader access for retail and institutional investors globally | Primarily institutional investors with regulatory constraints |
Which is better?
Tokenization of real-world assets offers increased liquidity, faster settlement times, and enhanced transparency by leveraging blockchain technology, making fractional ownership more accessible and secure. Securitization traditionally pools financial assets into marketable securities but often involves complex intermediaries, longer processing times, and less real-time tracking. While securitization is established in regulatory frameworks, tokenization's innovation drives efficiency and democratization in asset trading.
Connection
Tokenization of real-world assets and securitization are connected through their shared goal of enhancing liquidity and accessibility in financial markets by converting physical assets into tradable digital or financial instruments. Tokenization leverages blockchain technology to divide assets into fractional digital tokens, enabling broader participation, while securitization pools various debt instruments into tradable securities to diversify risk and attract investment. Both methods facilitate increased market efficiency, risk distribution, and capital formation by transforming illiquid assets into standardized, marketable units.
Key Terms
Asset Pooling
Securitization involves pooling various financial assets like loans or receivables into a single asset-backed security sold to investors, while tokenization converts individual real-world assets into digital tokens on a blockchain, enabling fractional ownership and liquidity. Asset pooling in securitization creates diversified risk exposure by combining multiple assets, whereas tokenization facilitates direct digital representation of each asset, enhancing transparency and transferability. Explore how these methods transform real estate, commodities, and other asset classes by unlocking new investment opportunities.
Digital Tokens
Digital tokens enable fractional ownership and increased liquidity of real-world assets through tokenization, representing specific rights or assets on a blockchain. Securitization bundles assets into tradable financial instruments, offering structured investment opportunities but often involves complex regulatory frameworks. Explore how digital tokens are transforming asset management and investment accessibility in modern finance.
Liquidity
Securitization of real-world assets pools financial instruments to create marketable securities, enhancing liquidity through traditional financial channels. Tokenization converts assets into blockchain-based digital tokens, enabling fractional ownership and faster, borderless trading, significantly boosting liquidity. Discover how these methods transform market access and liquidity dynamics in asset management.
Source and External Links
Securitization - Wikipedia - Securitization is the financial practice of pooling various types of contractual debt such as mortgages, auto loans, or credit card debt and selling their related cash flows as securities to investors, who are repaid from the principal and interest cash flows collected from the underlying debt.
Back to basics: What Is Securitization? - IMF - The securitization process involves a company pooling income-producing assets, selling them to a special purpose vehicle (SPV), which then issues tradable securities backed by the pool's cash flows to investors, effectively removing the assets from the originator's balance sheet.
Introduction to Securitizations - American Bar Association - Securitizations provide isolated assets from the originator's bankruptcy risk, use credit enhancement methods like tranching and overcollateralization, and involve key legal and regulatory considerations including securities laws.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com