Neo banking offers digital-first financial services with seamless mobile app interfaces and lower fees, targeting tech-savvy customers seeking convenience and speed. Traditional banking provides comprehensive in-branch services, extensive product portfolios, and established trust through decades of regulatory compliance and physical presence. Explore the evolving landscape of banking to understand which model best suits your financial needs.
Why it is important
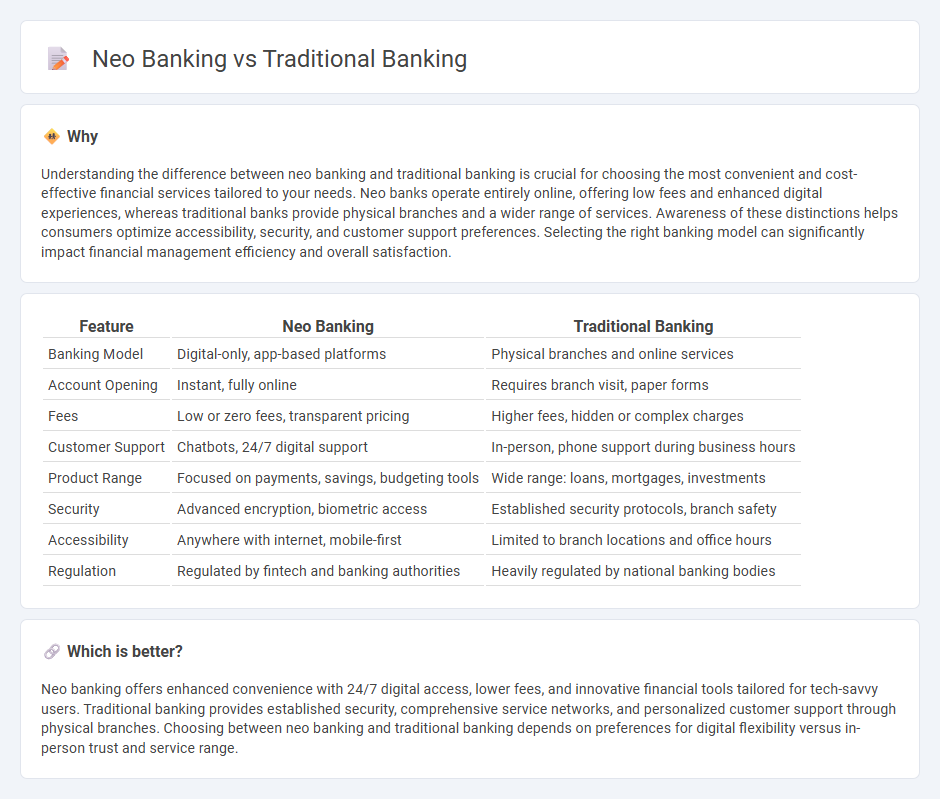
Understanding the difference between neo banking and traditional banking is crucial for choosing the most convenient and cost-effective financial services tailored to your needs. Neo banks operate entirely online, offering low fees and enhanced digital experiences, whereas traditional banks provide physical branches and a wider range of services. Awareness of these distinctions helps consumers optimize accessibility, security, and customer support preferences. Selecting the right banking model can significantly impact financial management efficiency and overall satisfaction.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Neo Banking | Traditional Banking |
|---|---|---|
| Banking Model | Digital-only, app-based platforms | Physical branches and online services |
| Account Opening | Instant, fully online | Requires branch visit, paper forms |
| Fees | Low or zero fees, transparent pricing | Higher fees, hidden or complex charges |
| Customer Support | Chatbots, 24/7 digital support | In-person, phone support during business hours |
| Product Range | Focused on payments, savings, budgeting tools | Wide range: loans, mortgages, investments |
| Security | Advanced encryption, biometric access | Established security protocols, branch safety |
| Accessibility | Anywhere with internet, mobile-first | Limited to branch locations and office hours |
| Regulation | Regulated by fintech and banking authorities | Heavily regulated by national banking bodies |
Which is better?
Neo banking offers enhanced convenience with 24/7 digital access, lower fees, and innovative financial tools tailored for tech-savvy users. Traditional banking provides established security, comprehensive service networks, and personalized customer support through physical branches. Choosing between neo banking and traditional banking depends on preferences for digital flexibility versus in-person trust and service range.
Connection
Neo banking leverages digital platforms to enhance customer experience by offering real-time banking services, while traditional banking provides established financial infrastructure and regulatory compliance. Both systems coexist through APIs and partnerships that enable seamless integration of digital solutions with conventional banking processes. This synergy allows customers to benefit from advanced technology alongside trusted financial services.
Key Terms
Branch Network
Traditional banking relies heavily on extensive physical branch networks, offering face-to-face customer service and in-person transactions for increased trust and convenience. Neo banking operates primarily online, eliminating the need for branches by providing digital-only platforms that facilitate 24/7 access to banking services via mobile apps and websites. Explore the evolving landscape of banking by learning more about how branch networks impact customer experience and operational efficiency.
Digital-Only Platform
Traditional banking relies on physical branches and in-person services, whereas neo banking operates exclusively through digital platforms without brick-and-mortar locations. Neo banks offer streamlined user experiences, real-time transaction updates, and lower fees enabled by advanced technology integrations like AI and cloud computing. Explore how digital-only banking platforms are transforming financial services and customer engagement.
Regulation
Traditional banking operates under strict regulatory frameworks including Basel III and Dodd-Frank, ensuring comprehensive compliance with capital adequacy, risk management, and consumer protection standards. Neo banks, while also regulated, often face evolving and less rigid oversight due to their digital-only model and partnerships with traditional banks, enabling faster innovation but posing unique regulatory challenges. Explore the detailed regulatory distinctions and their impact on customer security and innovation in banking services.
Source and External Links
Online Banking vs. Traditional Banking - Traditional banking involves physical local branches offering a wider range of services, including cash deposits, in-person customer support, and developed ATM networks, emphasizing personal relationship banking but requiring visits to branches for some services.
Traditional vs. Online Banking - Traditional banks have physical locations and often combine in-person services with online platforms, providing benefits such as face-to-face customer service, ATM networks, easy cash deposits, and a broader scope of financial products compared to online-only banks.
Online vs Traditional Banks: Pros, Cons, and More Explained - Traditional banks provide physical branches where customers can get personal guidance and deposit cash, benefit from a developed ATM network, but face drawbacks like limited hours, potentially higher fees, and variable service quality depending on location and staff.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com