Composable banking enables financial institutions to build customized services by assembling modular components, while API banking focuses on exposing application programming interfaces for seamless integration with third-party services. Both approaches enhance flexibility and innovation in digital banking ecosystems by allowing banks to quickly adapt to market demands and customer needs. Explore how composable banking and API banking can transform your financial services strategy.
Why it is important
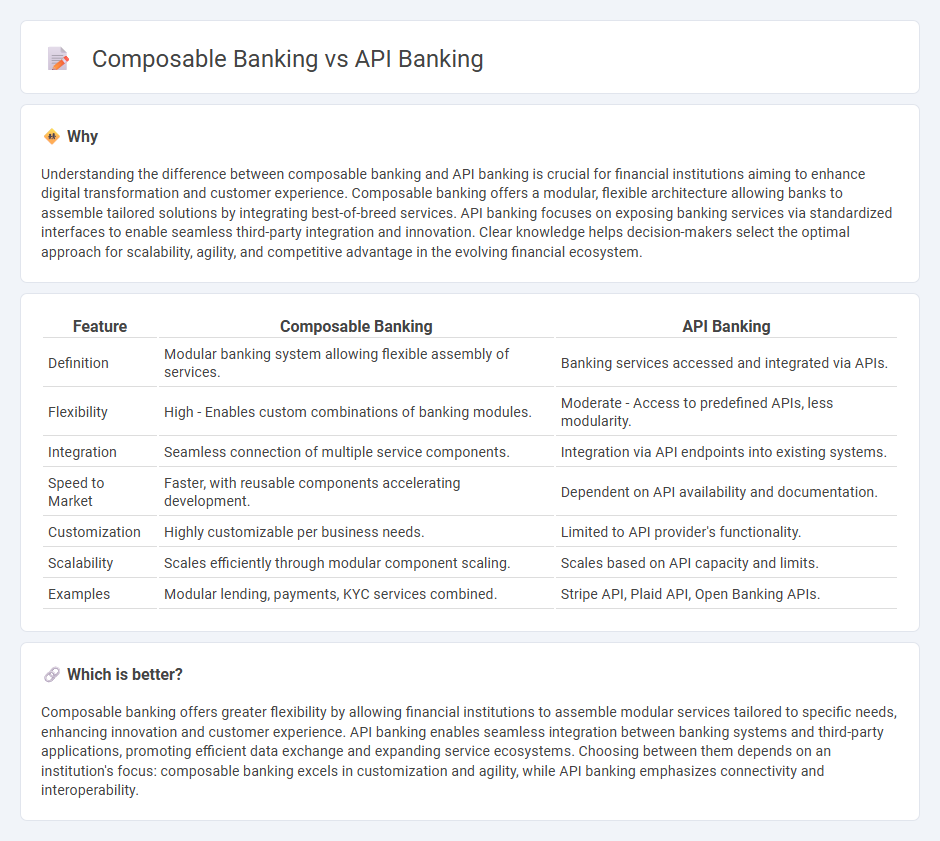
Understanding the difference between composable banking and API banking is crucial for financial institutions aiming to enhance digital transformation and customer experience. Composable banking offers a modular, flexible architecture allowing banks to assemble tailored solutions by integrating best-of-breed services. API banking focuses on exposing banking services via standardized interfaces to enable seamless third-party integration and innovation. Clear knowledge helps decision-makers select the optimal approach for scalability, agility, and competitive advantage in the evolving financial ecosystem.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Composable Banking | API Banking |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Modular banking system allowing flexible assembly of services. | Banking services accessed and integrated via APIs. |
| Flexibility | High - Enables custom combinations of banking modules. | Moderate - Access to predefined APIs, less modularity. |
| Integration | Seamless connection of multiple service components. | Integration via API endpoints into existing systems. |
| Speed to Market | Faster, with reusable components accelerating development. | Dependent on API availability and documentation. |
| Customization | Highly customizable per business needs. | Limited to API provider's functionality. |
| Scalability | Scales efficiently through modular component scaling. | Scales based on API capacity and limits. |
| Examples | Modular lending, payments, KYC services combined. | Stripe API, Plaid API, Open Banking APIs. |
Which is better?
Composable banking offers greater flexibility by allowing financial institutions to assemble modular services tailored to specific needs, enhancing innovation and customer experience. API banking enables seamless integration between banking systems and third-party applications, promoting efficient data exchange and expanding service ecosystems. Choosing between them depends on an institution's focus: composable banking excels in customization and agility, while API banking emphasizes connectivity and interoperability.
Connection
Composable banking relies on modular, API-driven components that enable financial institutions to rapidly build and customize banking services. API banking provides the essential interfaces allowing seamless integration of various banking functions into composable architectures. Together, they empower banks to enhance flexibility, accelerate innovation, and deliver personalized customer experiences.
Key Terms
Integration
API banking enables seamless integration by providing standardized endpoints for secure data exchange between financial institutions and third-party developers. Composable banking extends this approach by allowing modular assembly of banking services through APIs, facilitating highly customizable and scalable financial solutions. Discover more about how these integration strategies revolutionize banking technology.
Modularity
API banking enables financial institutions to connect and integrate services through predefined interfaces, offering flexibility but often limited by rigid system architectures. Composable banking emphasizes modularity, allowing banks to build and customize their tech stack through interchangeable, independent components for faster innovation and tailored customer experiences. Explore how modular composable banking reshapes financial services by unlocking agility and reducing time-to-market.
Interoperability
API banking enables seamless integration of financial services by exposing banking functionalities through standardized APIs, promoting interoperability across diverse platforms and third-party applications. Composable banking advances this concept by offering modular, reusable banking components that can be dynamically assembled and reconfigured to tailor financial products and services, enhancing flexibility and scalability. Discover how these approaches revolutionize interoperability in modern banking ecosystems by exploring their strategic differences and practical applications.
Source and External Links
Banking application programming interfaces (APIs) - Stripe - API banking enables financial institutions to open their core banking functions through APIs, allowing seamless interaction with third parties, rapid development of specialized financial services, and a shift in how businesses and customers access financial services.
API Banking and Banking as a Service | Deloitte US - API banking allows banks to expose their services to external users and vendors via APIs, facilitating instant payments, real-time data, and reducing costs, while Banking as a Service enables nonbanks to offer banking features through partnerships with regulated banks.
Banking APIs: Definition, Examples and Benefits | Priority Commerce - Banking APIs connect companies directly to banks to integrate financial services such as transaction processing, payment gateways, customer data management, and risk assessment without the complexity of traditional banking integration.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com