Central bank digital currency (CBDC) represents a government-backed digital form of money issued directly by a central bank, offering a secure, interoperable, and widely accessible payment method. Tokenized deposits, issued by commercial banks, are digital tokens representing deposit balances held on bank ledgers, enabling faster and more efficient transaction settlement within the banking ecosystem. Explore the key distinctions and implications of CBDCs versus tokenized deposits to understand their potential impact on the future of banking.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC) and tokenized deposits is crucial for grasping their distinct roles in the banking system: CBDC represents a digital form of central bank money, providing risk-free, sovereign-backed currency, while tokenized deposits are digital representations of commercial bank money, which carry credit risk. This distinction influences monetary policy implementation, financial stability, and how payment systems operate. Knowing these differences helps regulators, banks, and users navigate legal, operational, and security implications. Clear knowledge supports better decision-making in digital finance adoption and regulatory compliance.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC) | Tokenized Deposits |
|---|---|---|
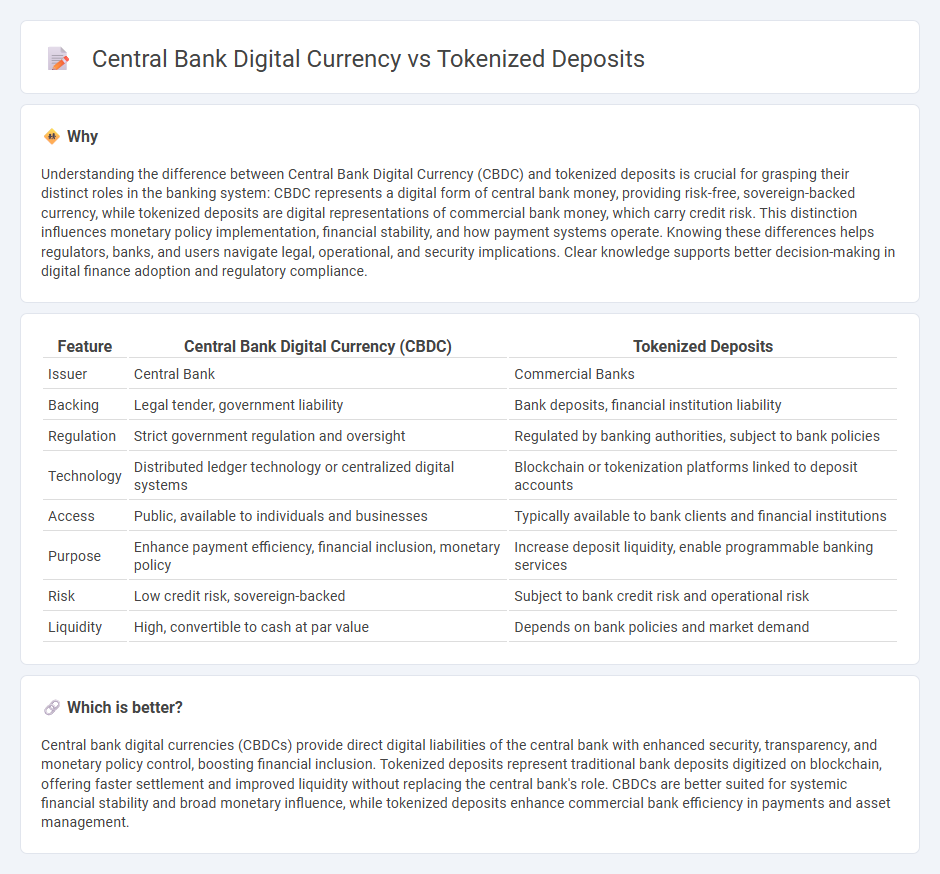
| Issuer | Central Bank | Commercial Banks |
| Backing | Legal tender, government liability | Bank deposits, financial institution liability |
| Regulation | Strict government regulation and oversight | Regulated by banking authorities, subject to bank policies |
| Technology | Distributed ledger technology or centralized digital systems | Blockchain or tokenization platforms linked to deposit accounts |
| Access | Public, available to individuals and businesses | Typically available to bank clients and financial institutions |
| Purpose | Enhance payment efficiency, financial inclusion, monetary policy | Increase deposit liquidity, enable programmable banking services |
| Risk | Low credit risk, sovereign-backed | Subject to bank credit risk and operational risk |
| Liquidity | High, convertible to cash at par value | Depends on bank policies and market demand |
Which is better?
Central bank digital currencies (CBDCs) provide direct digital liabilities of the central bank with enhanced security, transparency, and monetary policy control, boosting financial inclusion. Tokenized deposits represent traditional bank deposits digitized on blockchain, offering faster settlement and improved liquidity without replacing the central bank's role. CBDCs are better suited for systemic financial stability and broad monetary influence, while tokenized deposits enhance commercial bank efficiency in payments and asset management.
Connection
Central bank digital currency (CBDC) and tokenized deposits are interconnected as both utilize blockchain technology to enhance the efficiency and security of banking transactions. CBDCs represent a digital form of a nation's fiat currency issued directly by the central bank, while tokenized deposits convert traditional bank deposits into blockchain-based digital tokens. This integration facilitates faster settlements, improved transparency, and reduced counterparty risks in the financial system.
Key Terms
Programmability
Tokenized deposits leverage blockchain technology to offer programmable features such as automated payments and smart contract integration, enhancing flexibility in financial transactions. Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC) programmability enables policy enforcement and conditional transactions directly at the currency level, supporting monetary policy goals and compliance. Explore the detailed distinctions and use cases of programmable tokenized deposits versus CBDCs to understand their impact on the future of digital finance.
Settlement Mechanism
Tokenized deposits operate on blockchain networks, enabling near-instantaneous, peer-to-peer settlement by recording transactions on distributed ledgers. Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) are digital forms of fiat currency issued and regulated by central banks, often integrating with existing payment infrastructures to ensure settlement finality and mitigate counterparty risk. Explore further to understand how each settlement mechanism impacts financial stability and transaction efficiency.
Source and External Links
Tokenized Deposit: A Game-Changer in the Financial Industry - Tokenized deposits are traditional bank deposits converted into digital tokens on a blockchain, allowing increased liquidity, cost effectiveness, and improved accessibility for users with 24/7 trading on decentralized ledgers.
Deposit Tokens: Bridging traditional banking and the digital economy - Tokenized deposits are digital representations of commercial bank money fully backed by fiat deposits, issued by banks, transacted on blockchain platforms, programmable through smart contracts, and regulated under current banking laws.
Tokenized deposits: unlocking the future of banking - R3 - Tokenized deposits enable banks to optimize liquidity and treasury management by providing faster, more secure, and programmable settlement through permissioned distributed ledger technology, reducing counterparty risks while enhancing transparency and regulatory compliance.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com