Sustainable investing focuses on long-term environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria to generate financial returns while positively impacting the planet and society. Socially responsible investing (SRI) emphasizes ethical considerations by excluding companies or sectors that conflict with specific moral or social values. Explore the key differences and benefits of sustainable investing versus socially responsible investing to make informed banking decisions.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between sustainable investing and socially responsible investing is crucial for aligning investment portfolios with specific ethical and financial goals. Sustainable investing focuses on companies' environmental, social, and governance (ESG) performance to generate long-term financial returns and positive societal impact. Socially responsible investing involves actively excluding industries or companies that do not meet certain ethical criteria, such as tobacco or firearms. Clear knowledge ensures investors make informed decisions that reflect their values and risk tolerance effectively.
Comparison Table
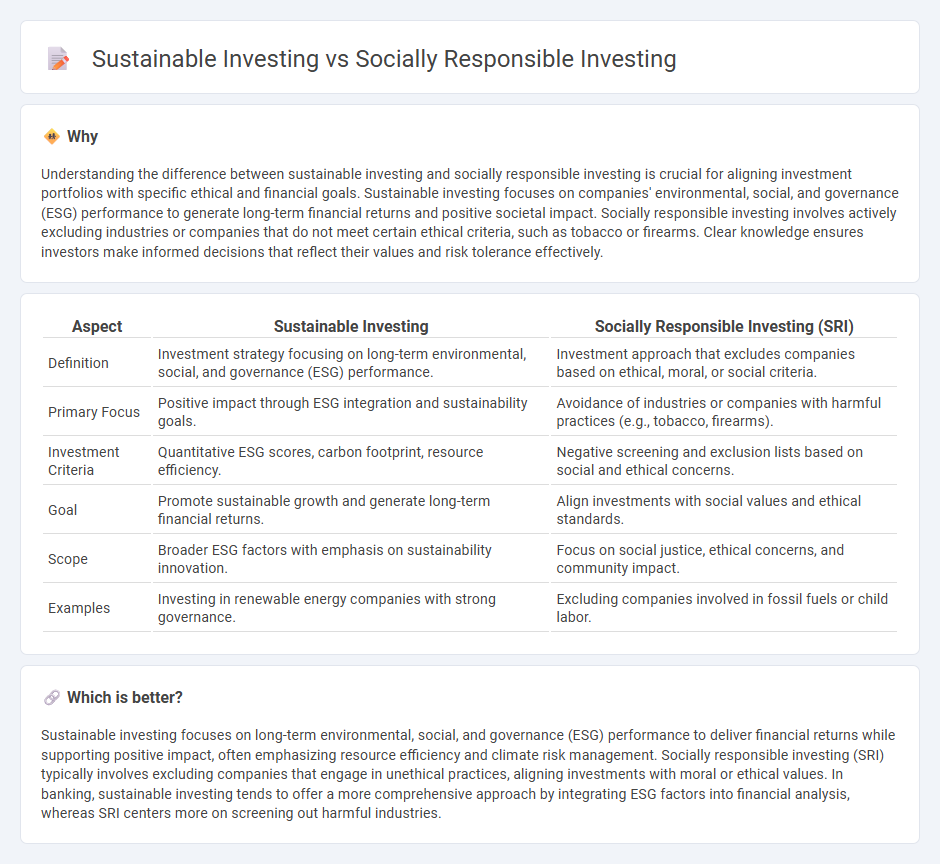
| Aspect | Sustainable Investing | Socially Responsible Investing (SRI) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Investment strategy focusing on long-term environmental, social, and governance (ESG) performance. | Investment approach that excludes companies based on ethical, moral, or social criteria. |
| Primary Focus | Positive impact through ESG integration and sustainability goals. | Avoidance of industries or companies with harmful practices (e.g., tobacco, firearms). |
| Investment Criteria | Quantitative ESG scores, carbon footprint, resource efficiency. | Negative screening and exclusion lists based on social and ethical concerns. |
| Goal | Promote sustainable growth and generate long-term financial returns. | Align investments with social values and ethical standards. |
| Scope | Broader ESG factors with emphasis on sustainability innovation. | Focus on social justice, ethical concerns, and community impact. |
| Examples | Investing in renewable energy companies with strong governance. | Excluding companies involved in fossil fuels or child labor. |
Which is better?
Sustainable investing focuses on long-term environmental, social, and governance (ESG) performance to deliver financial returns while supporting positive impact, often emphasizing resource efficiency and climate risk management. Socially responsible investing (SRI) typically involves excluding companies that engage in unethical practices, aligning investments with moral or ethical values. In banking, sustainable investing tends to offer a more comprehensive approach by integrating ESG factors into financial analysis, whereas SRI centers more on screening out harmful industries.
Connection
Sustainable investing and socially responsible investing (SRI) both prioritize ethical considerations by integrating environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria into banking and financial decision-making. They drive capital towards companies demonstrating strong ESG performance, promoting long-term resilience and positive societal impact. This alignment enhances risk management and supports the transition to a low-carbon, equitable economy.
Key Terms
ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance)
Socially responsible investing (SRI) emphasizes avoiding investments in companies with harmful practices, while sustainable investing prioritizes long-term environmental, social, and governance (ESG) performance to generate positive impact and financial returns. ESG criteria evaluate factors such as carbon emissions, labor practices, diversity, and corporate governance to guide investment decisions. Explore deeper insights into how ESG integration shapes investment strategies and outcomes.
Impact Investing
Socially responsible investing (SRI) prioritizes avoiding companies engaged in harmful practices by screening for ESG compliance, while sustainable investing targets companies with strong environmental and social performance to drive long-term value. Impact investing goes beyond by actively seeking measurable social and environmental outcomes alongside financial returns, often funding sectors like renewable energy, education, and affordable housing. Explore how impact investing combines profit with purpose to create transformative change in global markets.
Negative Screening
Negative screening in socially responsible investing (SRI) involves excluding companies or industries that do not meet specific ethical criteria, such as tobacco, firearms, or fossil fuels. Sustainable investing, while also incorporating negative screening, emphasizes investing in companies that actively contribute to environmental, social, and governance (ESG) improvements alongside avoiding harmful sectors. Explore further to understand how negative screening shapes impactful investment strategies.
Source and External Links
Socially responsible investing - Wikipedia - Socially responsible investing (SRI) is any investment strategy that seeks to achieve financial returns alongside ethical, social, or environmental goals, often linked to environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria and can include practices like impact investing, shareholder advocacy, and community investing.
Socially Responsible Investing - Green America - Socially responsible investing integrates personal values with investment decisions by selecting companies with transparent operations, positive environmental impact, respect for human rights, and community involvement, while avoiding investments in companies that fall short in these areas.
What Is Socially Responsible Investing (SRI) and How to Get Started - NerdWallet - SRI aims to create both positive social change and financial returns, has become more popular and accessible, and involves investing in companies that align with sustainability and ethical values.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com