Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC) is a digital form of a country's official currency, issued and regulated by the central bank to ensure monetary stability and security. A CBDC wallet serves as a secure, user-friendly application that enables individuals and businesses to store, transfer, and manage their digital currency directly. Explore how CBDC and its wallets are reshaping the future of financial transactions and digital banking.
Why it is important
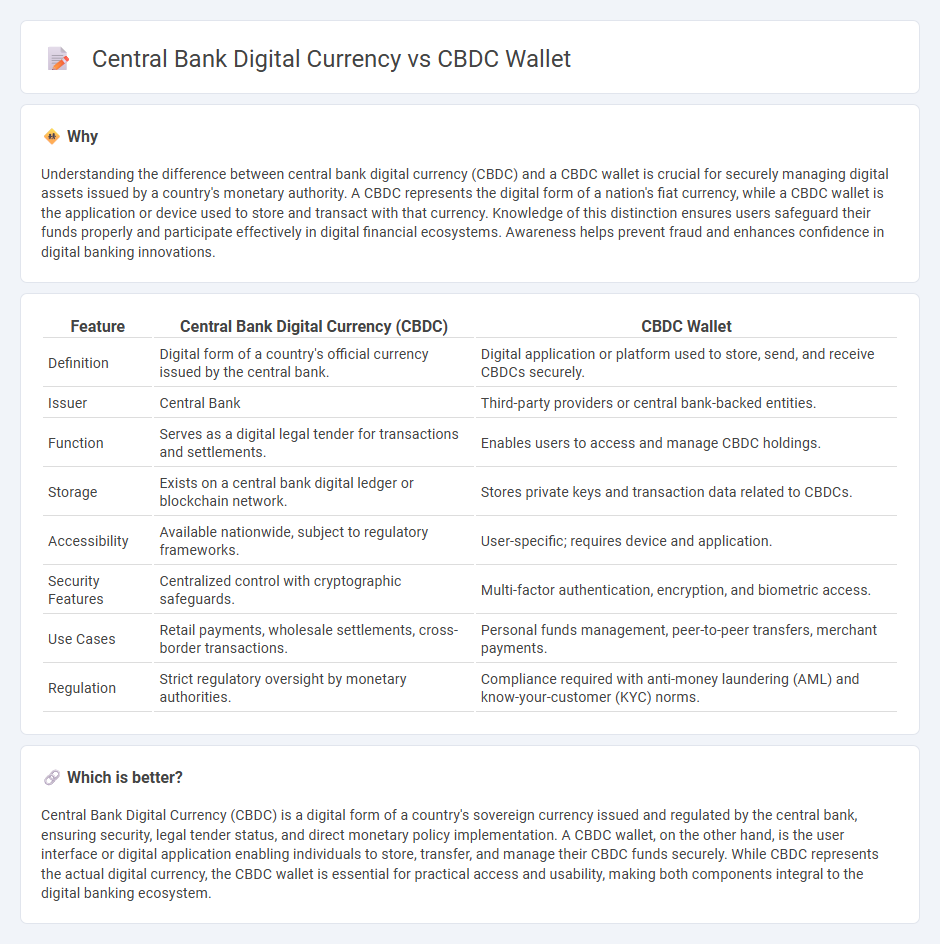
Understanding the difference between central bank digital currency (CBDC) and a CBDC wallet is crucial for securely managing digital assets issued by a country's monetary authority. A CBDC represents the digital form of a nation's fiat currency, while a CBDC wallet is the application or device used to store and transact with that currency. Knowledge of this distinction ensures users safeguard their funds properly and participate effectively in digital financial ecosystems. Awareness helps prevent fraud and enhances confidence in digital banking innovations.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC) | CBDC Wallet |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Digital form of a country's official currency issued by the central bank. | Digital application or platform used to store, send, and receive CBDCs securely. |
| Issuer | Central Bank | Third-party providers or central bank-backed entities. |
| Function | Serves as a digital legal tender for transactions and settlements. | Enables users to access and manage CBDC holdings. |
| Storage | Exists on a central bank digital ledger or blockchain network. | Stores private keys and transaction data related to CBDCs. |
| Accessibility | Available nationwide, subject to regulatory frameworks. | User-specific; requires device and application. |
| Security Features | Centralized control with cryptographic safeguards. | Multi-factor authentication, encryption, and biometric access. |
| Use Cases | Retail payments, wholesale settlements, cross-border transactions. | Personal funds management, peer-to-peer transfers, merchant payments. |
| Regulation | Strict regulatory oversight by monetary authorities. | Compliance required with anti-money laundering (AML) and know-your-customer (KYC) norms. |
Which is better?
Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC) is a digital form of a country's sovereign currency issued and regulated by the central bank, ensuring security, legal tender status, and direct monetary policy implementation. A CBDC wallet, on the other hand, is the user interface or digital application enabling individuals to store, transfer, and manage their CBDC funds securely. While CBDC represents the actual digital currency, the CBDC wallet is essential for practical access and usability, making both components integral to the digital banking ecosystem.
Connection
Central bank digital currency (CBDC) represents a digital form of a nation's official currency issued and regulated by the central bank, enabling secure and efficient transactions. A CBDC wallet functions as a digital tool that allows individuals and businesses to store, manage, and transfer CBDCs seamlessly, enhancing accessibility and financial inclusion. The connection between the two ensures direct user access to the central bank's digital currency, facilitating real-time payments and reducing reliance on traditional banking intermediaries.
Key Terms
Digital Ledger
CBDC wallets serve as secure digital interfaces enabling users to store, manage, and transact with central bank digital currency (CBDC), leveraging blockchain or other digital ledger technologies to ensure transparency and traceability. Central bank digital currencies operate on distributed ledgers that provide immutable, real-time record-keeping, reducing fraud and enhancing monetary policy implementation efficiency. Explore how digital ledger innovations are shaping the future of CBDC wallets and central bank currency infrastructures.
Issuer (Central Bank)
A CBDC wallet acts as the digital interface for users to access Central Bank Digital Currency issued directly by the central bank, ensuring secure and regulated transactions. The central bank serves as the sole issuer of CBDC, maintaining control over monetary policy and financial stability while providing a reliable medium of exchange. Explore more about how the central bank's role influences CBDC issuance and wallet functionality.
User Wallet
A CBDC wallet serves as the interface allowing users to store, send, and receive central bank digital currency, ensuring secure and seamless transactions with direct access to the digital fiat. Unlike the broader concept of central bank digital currency, which encompasses the digital form of a nation's currency issued and regulated by the central bank, the wallet emphasizes usability, security, and user experience in managing these assets. Explore how innovative CBDC wallet designs are shaping the future of digital payments and financial inclusion.
Source and External Links
CBDC FAQs - Bank of Jamaica - A CBDC wallet is a digital wallet issued by banks or authorized payment service providers to hold the digital version of central bank money; it is not held in a traditional bank account, incurs no fees, and allows 1-for-1 exchange with physical cash.
CBDC Wallet - Peersyst - The CBDC wallet provides an intuitive, user-friendly interface similar to banking apps, supports offline transactions, and simplifies digital currency use to facilitate seamless adoption by everyday users.
Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC) - Federal Reserve Board - A CBDC is a digital form of central bank money accessible to the public, distinct from money in commercial bank accounts, though the U.S. Federal Reserve has not decided to issue a CBDC yet.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com