Sustainable investing focuses on integrating environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria into investment decisions to promote long-term positive impact and ethical responsibility. Thematic investing targets specific trends or sectors such as clean energy, technology, or healthcare to capitalize on emerging growth opportunities. Explore how these strategies differ and align to enhance portfolio value and societal benefits.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between sustainable investing and thematic investing is crucial for optimizing portfolio alignment with ethical values and financial goals. Sustainable investing focuses on environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria to generate long-term positive impact alongside financial returns. Thematic investing targets specific sectors or trends such as technology, healthcare, or clean energy for capital growth. Clear knowledge helps investors make informed decisions that align risk tolerance with social impact and market opportunities.
Comparison Table
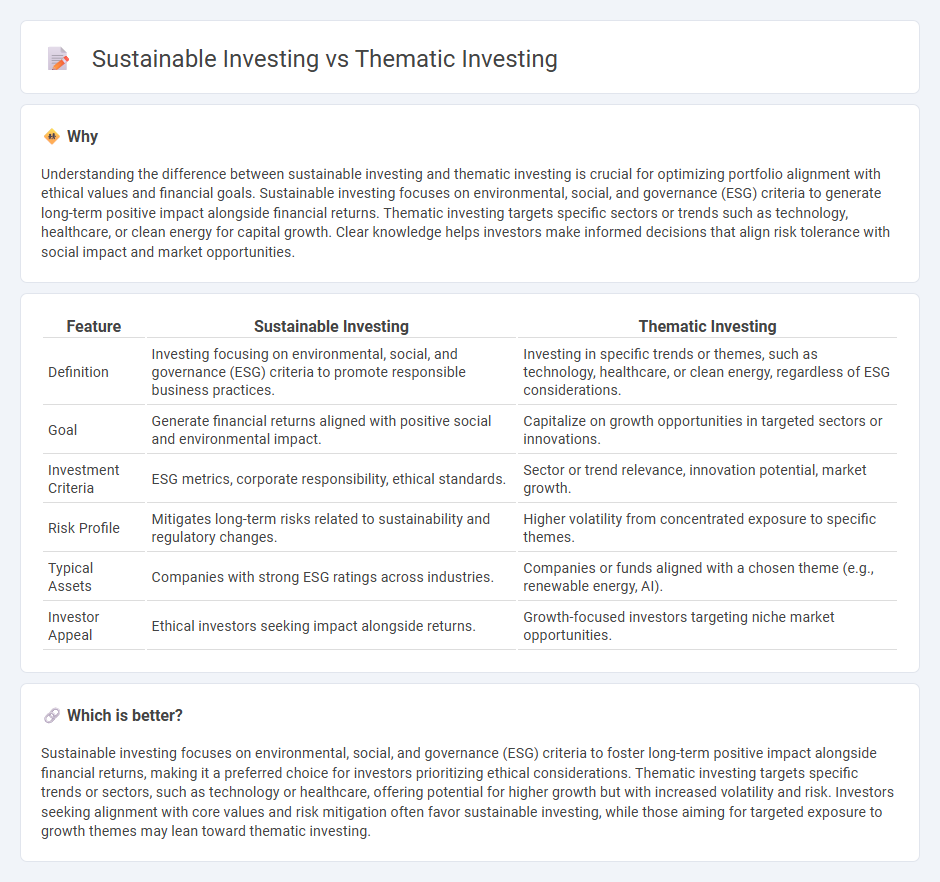
| Feature | Sustainable Investing | Thematic Investing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Investing focusing on environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria to promote responsible business practices. | Investing in specific trends or themes, such as technology, healthcare, or clean energy, regardless of ESG considerations. |
| Goal | Generate financial returns aligned with positive social and environmental impact. | Capitalize on growth opportunities in targeted sectors or innovations. |
| Investment Criteria | ESG metrics, corporate responsibility, ethical standards. | Sector or trend relevance, innovation potential, market growth. |
| Risk Profile | Mitigates long-term risks related to sustainability and regulatory changes. | Higher volatility from concentrated exposure to specific themes. |
| Typical Assets | Companies with strong ESG ratings across industries. | Companies or funds aligned with a chosen theme (e.g., renewable energy, AI). |
| Investor Appeal | Ethical investors seeking impact alongside returns. | Growth-focused investors targeting niche market opportunities. |
Which is better?
Sustainable investing focuses on environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria to foster long-term positive impact alongside financial returns, making it a preferred choice for investors prioritizing ethical considerations. Thematic investing targets specific trends or sectors, such as technology or healthcare, offering potential for higher growth but with increased volatility and risk. Investors seeking alignment with core values and risk mitigation often favor sustainable investing, while those aiming for targeted exposure to growth themes may lean toward thematic investing.
Connection
Sustainable investing focuses on companies with strong environmental, social, and governance (ESG) practices, aligning portfolios with ethical and long-term value creation goals. Thematic investing targets specific sectors or trends, such as renewable energy or clean technology, which often overlap with sustainability objectives. Both strategies drive capital toward enterprises committed to positive environmental and social impact, fostering innovation and responsible growth in the banking sector.
Key Terms
ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance)
Thematic investing targets specific trends or sectors, such as clean energy or technology, while sustainable investing integrates ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance) criteria to evaluate companies' long-term impact on society and the environment. ESG-focused sustainable investments assess factors like carbon footprint, labor practices, and corporate governance to drive ethical and responsible decision-making. Discover how aligning thematic strategies with ESG principles can enhance both financial performance and positive societal outcomes.
Megatrends
Thematic investing targets long-term Megatrends such as technological innovation, demographic shifts, and urbanization to capture growth opportunities across sectors. Sustainable investing integrates environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria to support responsible business practices while addressing global challenges like climate change and social equity. Explore the distinctions and strategic benefits of thematic versus sustainable investing to align portfolios with future-focused objectives.
Impact Investing
Impact investing targets measurable social and environmental outcomes alongside financial returns, differentiating itself from broader thematic and sustainable investing approaches. Thematic investing involves focusing on specific sectors or trends, while sustainable investing integrates ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance) criteria to manage risk and opportunity. Discover how impact investing drives change by aligning capital with purpose.
Source and External Links
Thematic Investing: Tomorrow's themes, today - Thematic investing involves aligning portfolios with evolving trends, allowing investors to capitalize on dynamic themes that drive market returns.
Thematic investing - Thematic investing focuses on investing in companies across various sectors that benefit from macro-level trends such as digital revolution and sustainable development.
Is Thematic Investing Right for You? - Thematic investing enables investors to invest in broader trends or concepts, such as AI or green energy, by identifying a diverse set of companies involved in these areas.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com