Sustainable investing focuses on allocating capital to companies and projects that prioritize environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria to generate long-term positive impact alongside financial returns. Responsible lending involves evaluating borrowers' creditworthiness while considering ethical standards and social consequences to minimize harm and promote economic inclusion. Discover how these strategies are transforming the banking sector toward a more sustainable future.
Why it is important
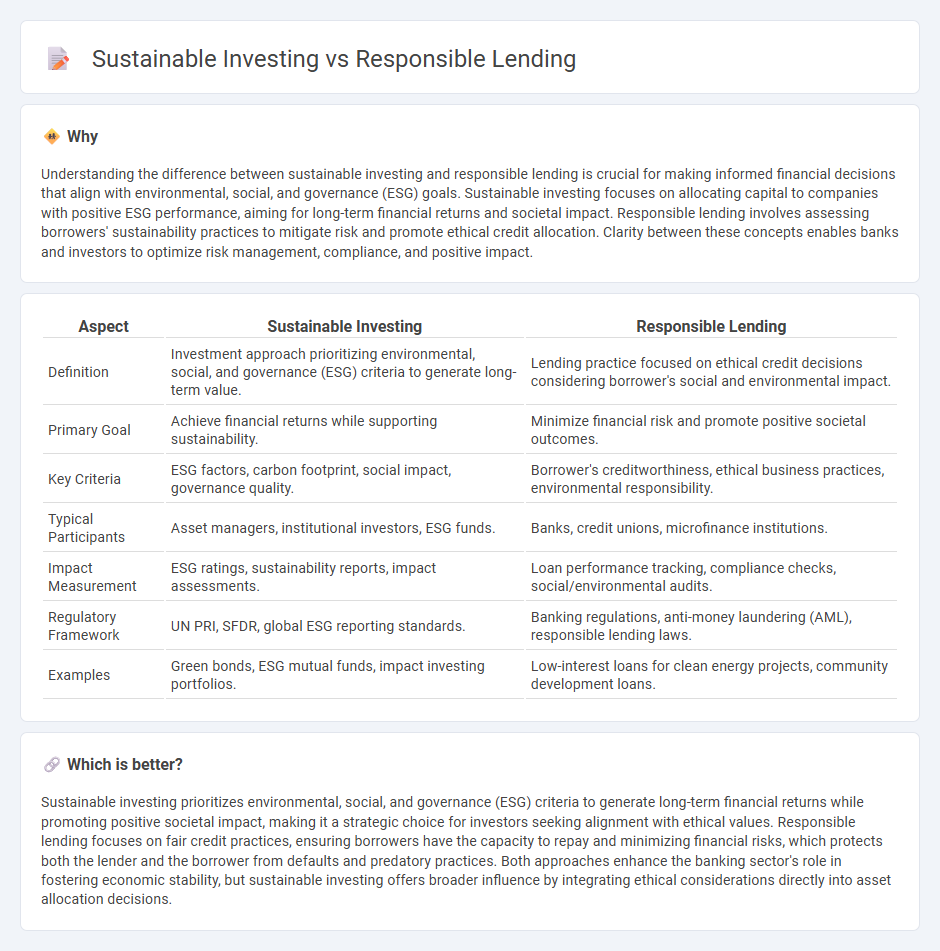
Understanding the difference between sustainable investing and responsible lending is crucial for making informed financial decisions that align with environmental, social, and governance (ESG) goals. Sustainable investing focuses on allocating capital to companies with positive ESG performance, aiming for long-term financial returns and societal impact. Responsible lending involves assessing borrowers' sustainability practices to mitigate risk and promote ethical credit allocation. Clarity between these concepts enables banks and investors to optimize risk management, compliance, and positive impact.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Sustainable Investing | Responsible Lending |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Investment approach prioritizing environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria to generate long-term value. | Lending practice focused on ethical credit decisions considering borrower's social and environmental impact. |
| Primary Goal | Achieve financial returns while supporting sustainability. | Minimize financial risk and promote positive societal outcomes. |
| Key Criteria | ESG factors, carbon footprint, social impact, governance quality. | Borrower's creditworthiness, ethical business practices, environmental responsibility. |
| Typical Participants | Asset managers, institutional investors, ESG funds. | Banks, credit unions, microfinance institutions. |
| Impact Measurement | ESG ratings, sustainability reports, impact assessments. | Loan performance tracking, compliance checks, social/environmental audits. |
| Regulatory Framework | UN PRI, SFDR, global ESG reporting standards. | Banking regulations, anti-money laundering (AML), responsible lending laws. |
| Examples | Green bonds, ESG mutual funds, impact investing portfolios. | Low-interest loans for clean energy projects, community development loans. |
Which is better?
Sustainable investing prioritizes environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria to generate long-term financial returns while promoting positive societal impact, making it a strategic choice for investors seeking alignment with ethical values. Responsible lending focuses on fair credit practices, ensuring borrowers have the capacity to repay and minimizing financial risks, which protects both the lender and the borrower from defaults and predatory practices. Both approaches enhance the banking sector's role in fostering economic stability, but sustainable investing offers broader influence by integrating ethical considerations directly into asset allocation decisions.
Connection
Sustainable investing and responsible lending are interconnected through their shared focus on environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria to promote long-term financial stability and positive societal impact. Banks integrate ESG risk assessments into lending decisions to support businesses committed to sustainable practices, thereby reducing exposure to harmful environmental and social risks. This alignment fosters a financial ecosystem that encourages capital flow towards projects and companies prioritizing sustainability and ethical governance.
Key Terms
Creditworthiness
Responsible lending prioritizes thorough assessment of a borrower's creditworthiness to minimize default risk and ensure fair loan terms. Sustainable investing, while considering financial returns, integrates environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria that may influence credit risk but extends beyond individual credit profiles to broader impact goals. Explore how creditworthiness evaluation shapes both responsible lending practices and sustainable investment strategies.
ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance)
Responsible lending integrates ESG criteria by assessing borrowers' environmental impact, social responsibility, and governance practices to minimize financial risks and promote ethical credit allocation. Sustainable investing prioritizes ESG factors to support companies committed to long-term environmental stewardship, social equity, and transparent governance, aiming to generate positive societal impact alongside financial returns. Explore the nuances and benefits of responsible lending and sustainable investing within the ESG framework to enhance your financial strategy.
Risk assessment
Responsible lending prioritizes comprehensive risk assessment by evaluating borrowers' creditworthiness and repayment capacity to prevent defaults and ensure financial stability. Sustainable investing incorporates environmental, social, and governance (ESG) risks alongside traditional financial risks, aiming to protect investments while fostering positive societal impact. Explore in-depth analysis of risk frameworks in responsible lending versus sustainable investing for enhanced financial decision-making.
Source and External Links
Guide to Responsible Lending, Affordability & Vulnerability - Experian - Responsible lending means acting in the consumer's best interest by ensuring they can afford and understand credit agreements, with ongoing support if they face financial difficulties.
A3-2-02, Responsible Lending Practices - Fannie Mae Selling Guide - Lenders must use prudent, sound business practices in marketing and origination, with policies to ensure compliance and avoid predatory lending.
Responsible lending - ASIC - Credit providers must make reasonable inquiries and verify a consumer's financial situation to ensure credit is suitable, and provide assessments if requested.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com