Neobanks operate entirely online without physical branches, offering streamlined digital services through mobile apps and websites that focus on user-friendly interfaces. Digital banks combine traditional banking with online platforms, often maintaining physical branches alongside comprehensive digital services, catering to both tech-savvy users and those preferring in-person support. Explore the distinct advantages and features of neobanks and digital banks to understand which suits your financial needs best.
Why it is important
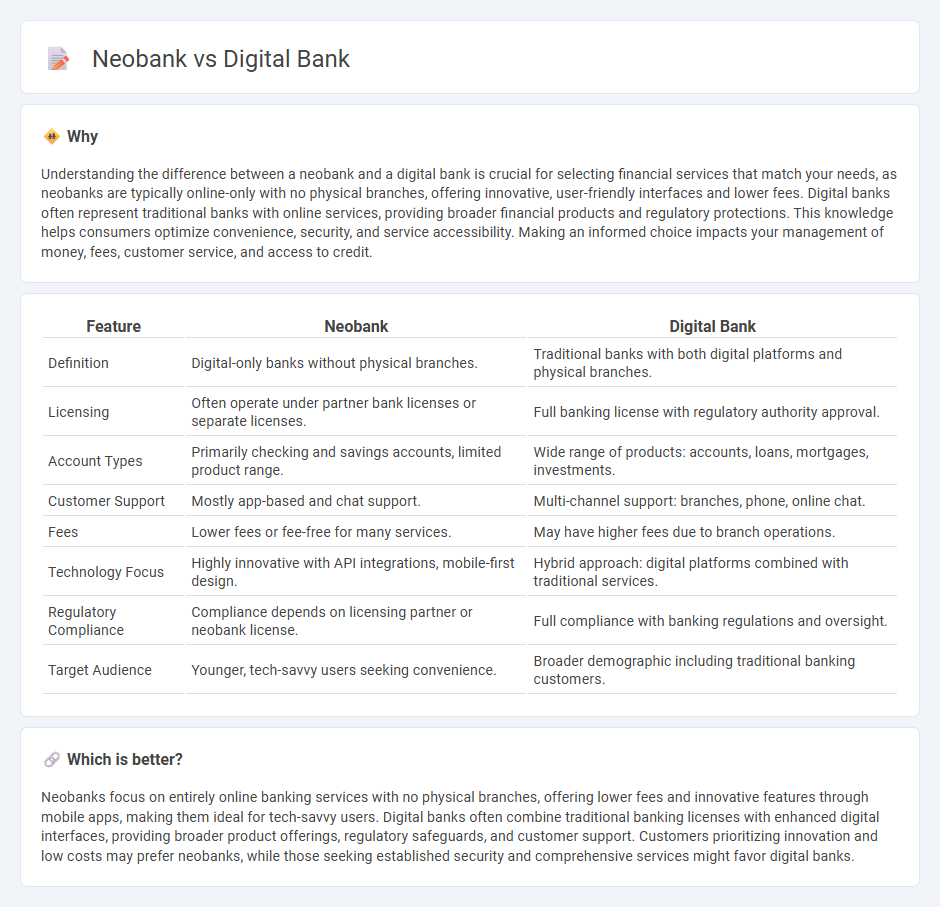
Understanding the difference between a neobank and a digital bank is crucial for selecting financial services that match your needs, as neobanks are typically online-only with no physical branches, offering innovative, user-friendly interfaces and lower fees. Digital banks often represent traditional banks with online services, providing broader financial products and regulatory protections. This knowledge helps consumers optimize convenience, security, and service accessibility. Making an informed choice impacts your management of money, fees, customer service, and access to credit.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Neobank | Digital Bank |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Digital-only banks without physical branches. | Traditional banks with both digital platforms and physical branches. |
| Licensing | Often operate under partner bank licenses or separate licenses. | Full banking license with regulatory authority approval. |
| Account Types | Primarily checking and savings accounts, limited product range. | Wide range of products: accounts, loans, mortgages, investments. |
| Customer Support | Mostly app-based and chat support. | Multi-channel support: branches, phone, online chat. |
| Fees | Lower fees or fee-free for many services. | May have higher fees due to branch operations. |
| Technology Focus | Highly innovative with API integrations, mobile-first design. | Hybrid approach: digital platforms combined with traditional services. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Compliance depends on licensing partner or neobank license. | Full compliance with banking regulations and oversight. |
| Target Audience | Younger, tech-savvy users seeking convenience. | Broader demographic including traditional banking customers. |
Which is better?
Neobanks focus on entirely online banking services with no physical branches, offering lower fees and innovative features through mobile apps, making them ideal for tech-savvy users. Digital banks often combine traditional banking licenses with enhanced digital interfaces, providing broader product offerings, regulatory safeguards, and customer support. Customers prioritizing innovation and low costs may prefer neobanks, while those seeking established security and comprehensive services might favor digital banks.
Connection
Neobanks and digital banks both operate entirely online, offering banking services through mobile apps and websites without physical branches. Neobanks are often a subset of digital banks, focusing on providing simplified, customer-centric experiences with lower fees and faster onboarding processes. Both leverage advanced financial technology and data analytics to deliver personalized banking solutions and enhance user convenience.
Key Terms
Core Banking System
Core Banking Systems (CBS) are the backbone of both digital banks and neobanks, enabling real-time processing and centralized management of banking operations. Digital banks typically integrate CBS with legacy systems, offering a blend of traditional and digital services, while neobanks rely entirely on cloud-based CBS for agile, customer-centric solutions. Explore the distinct CBS architectures powering digital banks and neobanks to understand their operational efficiencies and innovation capabilities.
Regulatory Compliance
Digital banks operate under full banking licenses and adhere strictly to regulatory compliance, including capital requirements and customer protection laws. Neobanks often function via partnerships with traditional banks or hold limited licenses, which affects their regulatory scope and compliance obligations. Explore regulatory differences between digital banks and neobanks to understand their impact on security and customer trust.
Customer Onboarding
Digital banks and neobanks both leverage technology to streamline customer onboarding, with digital banks often integrating traditional banking services and regulatory frameworks for enhanced security and compliance. Neobanks prioritize fully digital, user-friendly onboarding processes that minimize paperwork through mobile-first platforms and real-time identity verification. Explore the key differences in customer onboarding to determine which banking model best suits your needs.
Source and External Links
The World's Biggest List of Digital Banks - Digital banks offer digital banking, payments, lending, investment, and financial management services; the list includes over 350 providers globally, updated quarterly as of December 2024.
Digital Banking | Personal Online Banking - Digital banking enables managing accounts, transferring money, budgeting, and monitoring spending conveniently from any device, with access to accounts from multiple banks in one place.
Digital Banking - Truist Bank offers mobile apps and digital tools to send money, find ATMs, or deposit checks, designed around customers' lifestyles for easy access and management.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com