Digital identity verification in banking ensures secure customer onboarding by confirming user identity through biometric data, government ID checks, and multi-factor authentication, reducing fraud risks significantly. Social login authentication simplifies access by allowing users to sign in with credentials from platforms like Google or Facebook but may lack stringent verification, posing potential security vulnerabilities. Discover how combining these methods enhances both security and user experience in modern banking.
Why it is important
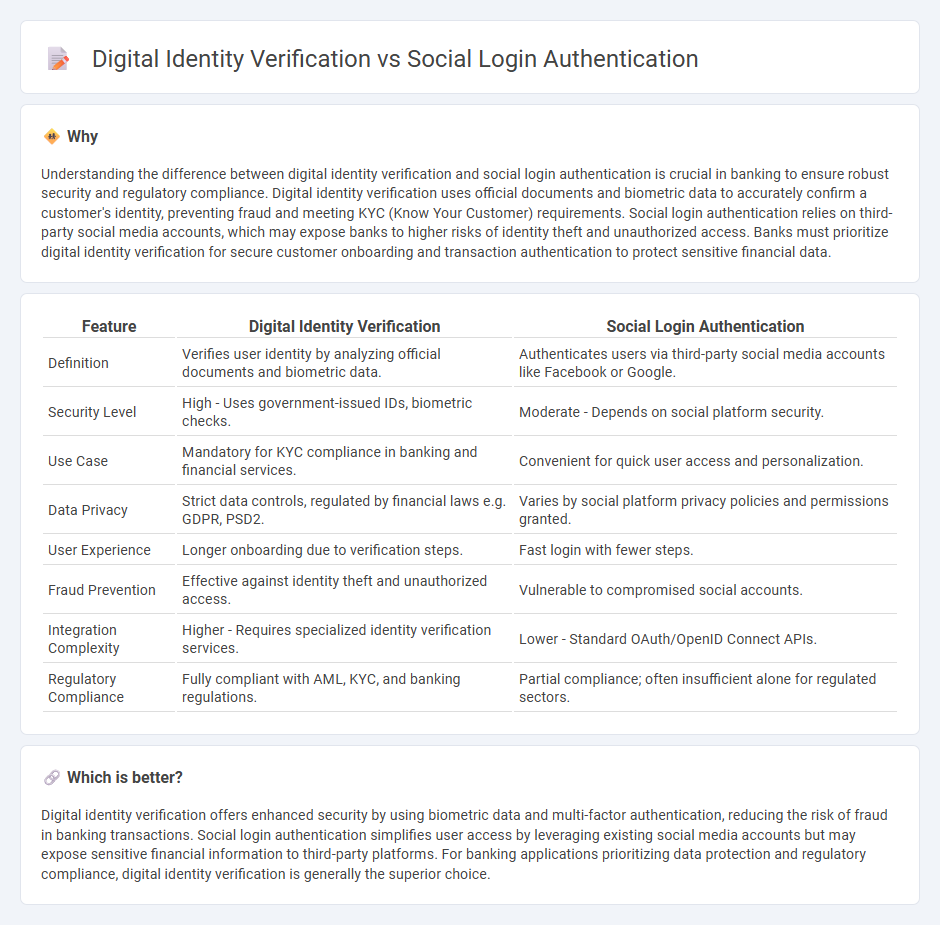
Understanding the difference between digital identity verification and social login authentication is crucial in banking to ensure robust security and regulatory compliance. Digital identity verification uses official documents and biometric data to accurately confirm a customer's identity, preventing fraud and meeting KYC (Know Your Customer) requirements. Social login authentication relies on third-party social media accounts, which may expose banks to higher risks of identity theft and unauthorized access. Banks must prioritize digital identity verification for secure customer onboarding and transaction authentication to protect sensitive financial data.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Digital Identity Verification | Social Login Authentication |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Verifies user identity by analyzing official documents and biometric data. | Authenticates users via third-party social media accounts like Facebook or Google. |
| Security Level | High - Uses government-issued IDs, biometric checks. | Moderate - Depends on social platform security. |
| Use Case | Mandatory for KYC compliance in banking and financial services. | Convenient for quick user access and personalization. |
| Data Privacy | Strict data controls, regulated by financial laws e.g. GDPR, PSD2. | Varies by social platform privacy policies and permissions granted. |
| User Experience | Longer onboarding due to verification steps. | Fast login with fewer steps. |
| Fraud Prevention | Effective against identity theft and unauthorized access. | Vulnerable to compromised social accounts. |
| Integration Complexity | Higher - Requires specialized identity verification services. | Lower - Standard OAuth/OpenID Connect APIs. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Fully compliant with AML, KYC, and banking regulations. | Partial compliance; often insufficient alone for regulated sectors. |
Which is better?
Digital identity verification offers enhanced security by using biometric data and multi-factor authentication, reducing the risk of fraud in banking transactions. Social login authentication simplifies user access by leveraging existing social media accounts but may expose sensitive financial information to third-party platforms. For banking applications prioritizing data protection and regulatory compliance, digital identity verification is generally the superior choice.
Connection
Digital identity verification enhances security by confirming user credentials during online banking access, reducing fraud risk. Social login authentication streamlines this process by allowing users to sign in through trusted platforms, linking their verified digital identities seamlessly. Integrating these methods improves user experience while maintaining robust security protocols in banking services.
Key Terms
OAuth (for social login authentication)
OAuth is a widely adopted protocol for social login authentication, enabling users to access multiple applications using credentials from platforms like Google, Facebook, or Twitter without sharing passwords. Digital identity verification, however, entails comprehensive identity confirmation methods such as biometric checks, government ID validation, or multi-factor authentication to ensure user legitimacy beyond mere credential delegation. Explore deeper insights into how OAuth streamlines user experience while balancing security requirements in modern authentication systems.
KYC (Know Your Customer)
Social login authentication simplifies user access by leveraging existing social media credentials but offers limited assurance for regulatory compliance in KYC processes due to weak identity validation. Digital identity verification employs advanced technologies like biometric checks, document verification, and AI-driven risk assessment to ensure robust, compliant customer identification aligned with anti-money laundering (AML) and KYC regulations. Explore deeper insights on integrating digital identity verification for enhanced security and compliance in your KYC framework.
Biometric verification
Social login authentication enables users to access services using credentials from platforms like Facebook or Google but offers limited assurance of identity. Digital identity verification, especially biometric verification, employs unique physical traits such as fingerprints or facial recognition to confirm a user's real-world identity with higher security and accuracy. Discover how biometric verification is revolutionizing secure access by enhancing trust and preventing fraud in digital transactions.
Source and External Links
Social login - Wikipedia - Social login is a single sign-on method using existing credentials from social networks like Facebook or Google to authenticate users on third-party websites, simplifying login and providing demographic data to developers, mostly implemented using OAuth for consumer sites.
Social Login - Time to implement it in your apps - Auth0 - Social login enables users to sign in using existing social network accounts such as Facebook, Twitter, or Google, streamlining authentication by leveraging these providers' credentials.
What is Social Login? How does Social Login works - miniOrange - Social login, also called social SSO, allows users to authenticate using their social media accounts through standards like OAuth 2.0 and OpenID Connect, offering a seamless, passwordless login experience while enabling data insights for site admins.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com