Cloud core banking leverages fully cloud-hosted infrastructure to deliver scalable, flexible, and cost-efficient banking services with real-time data access and seamless updates. Hybrid cloud core banking integrates on-premises systems with cloud environments to balance security, compliance, and operational flexibility while modernizing legacy platforms. Explore the differences and advantages of each model to optimize your banking technology strategy.
Why it is important
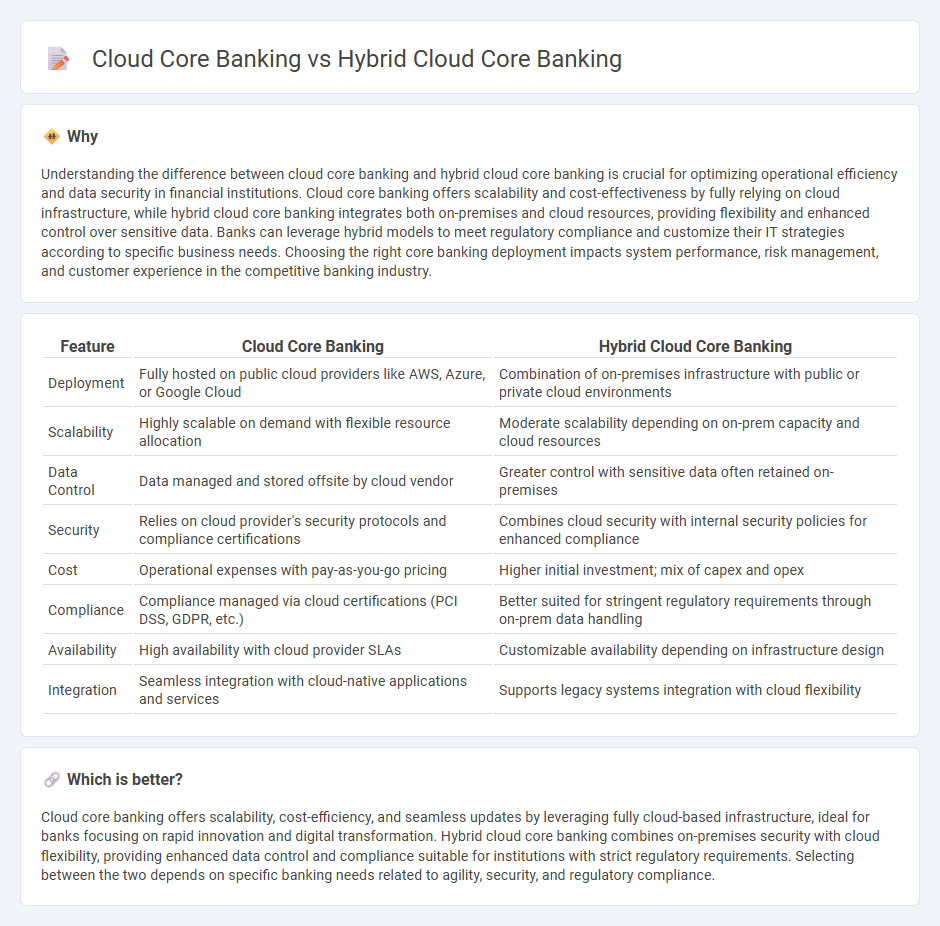
Understanding the difference between cloud core banking and hybrid cloud core banking is crucial for optimizing operational efficiency and data security in financial institutions. Cloud core banking offers scalability and cost-effectiveness by fully relying on cloud infrastructure, while hybrid cloud core banking integrates both on-premises and cloud resources, providing flexibility and enhanced control over sensitive data. Banks can leverage hybrid models to meet regulatory compliance and customize their IT strategies according to specific business needs. Choosing the right core banking deployment impacts system performance, risk management, and customer experience in the competitive banking industry.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Cloud Core Banking | Hybrid Cloud Core Banking |
|---|---|---|
| Deployment | Fully hosted on public cloud providers like AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud | Combination of on-premises infrastructure with public or private cloud environments |
| Scalability | Highly scalable on demand with flexible resource allocation | Moderate scalability depending on on-prem capacity and cloud resources |
| Data Control | Data managed and stored offsite by cloud vendor | Greater control with sensitive data often retained on-premises |
| Security | Relies on cloud provider's security protocols and compliance certifications | Combines cloud security with internal security policies for enhanced compliance |
| Cost | Operational expenses with pay-as-you-go pricing | Higher initial investment; mix of capex and opex |
| Compliance | Compliance managed via cloud certifications (PCI DSS, GDPR, etc.) | Better suited for stringent regulatory requirements through on-prem data handling |
| Availability | High availability with cloud provider SLAs | Customizable availability depending on infrastructure design |
| Integration | Seamless integration with cloud-native applications and services | Supports legacy systems integration with cloud flexibility |
Which is better?
Cloud core banking offers scalability, cost-efficiency, and seamless updates by leveraging fully cloud-based infrastructure, ideal for banks focusing on rapid innovation and digital transformation. Hybrid cloud core banking combines on-premises security with cloud flexibility, providing enhanced data control and compliance suitable for institutions with strict regulatory requirements. Selecting between the two depends on specific banking needs related to agility, security, and regulatory compliance.
Connection
Cloud core banking leverages fully cloud-native platforms to deliver scalable, real-time financial services, while hybrid cloud core banking integrates on-premises infrastructure with cloud solutions for enhanced flexibility and security. Both models utilize cloud technologies to optimize transaction processing, data management, and regulatory compliance in banking systems. The hybrid approach connects traditional banking architecture with cloud innovation, enabling seamless data flow and operational continuity across multiple environments.
Key Terms
Deployment Model
Hybrid cloud core banking combines private and public cloud infrastructures, enabling banks to deploy critical workloads securely on private clouds while leveraging public clouds for scalability and cost-efficiency. Cloud core banking systems are fully deployed on public cloud platforms, offering rapid provisioning, elasticity, and innovation but may raise concerns about data sovereignty and regulatory compliance. Explore the deployment advantages and compliance considerations to choose the optimal core banking solution for your financial institution.
Data Residency
Hybrid cloud core banking systems offer greater control over data residency by allowing sensitive financial data to remain on-premises while leveraging public cloud resources for scalability. Cloud core banking typically involves storing and processing data entirely in public cloud environments, which can raise compliance challenges related to jurisdiction-specific data residency laws. Explore how different core banking models address regulatory requirements and data sovereignty to optimize your financial technology infrastructure.
Scalability
Hybrid cloud core banking offers enhanced scalability by combining on-premises infrastructure with public cloud resources, allowing banks to dynamically adjust capacity based on demand and regulatory requirements. Cloud core banking, hosted entirely on the public cloud, provides rapid scalability with minimal upfront investment but may face constraints in data sovereignty and compliance. Explore deeper insights into how hybrid and cloud core banking solutions scale to meet evolving financial industry needs.
Source and External Links
Banks Leverage Investments with Hybrid Cloud - This article discusses how hybrid cloud environments provide banks with the flexibility to manage workloads effectively between private and public clouds, enhancing agility and scalability.
The Benefits of a Core Banking System in Cloud - This webpage explores the advantages of core banking systems in cloud environments, including greater flexibility, scalability, and resilience compared to traditional on-premises systems.
Temenos and IBM Help Banks Accelerate Core Banking Modernization with Hybrid Cloud - This blog post highlights how Temenos and IBM collaborate to help banks accelerate their core banking modernization using hybrid cloud for greater flexibility and innovation.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com